Ch 3 PowerPoint - Gilbert Public Schools

Family Traditions
Showcase
Child Development
Chapter 3
Family Traditions Showcase
We will be having a Traditions Gallery Walk!
DATE: Friday Sep 13 th WRITE THIS DOWN!
Bring in a family tradition to share with the class.
item to display
food to share (must bring enough for 36)
picture to show one of your family’s traditions.
Type or write very neatly a brief description of your family’s tradition in paragraph format.
During the Family Traditions Showcase, you will view all your classmates’ displays and write down their family traditions on the paper provided.
Families
Within every culture…
There are families
Each culture is different
Some include parents and children
Others include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins
Families are…
The foundation on which human culture is built
Families
What are some of the physical needs that families meet?
Clothing
Shelter
Health
Safety
Families
Besides physical needs, what other needs do families meet for us?
Social and emotional needs
to love and be loved
To give and receive help
Learning social skills
Sharing
taking turns, working together to achieve common goals
Families
What social skills do we learn from our families?
Manners
Sharing and taking turns
Working together to achieve common goals
Families
Do families meet intellectual goals too?
Strong families do
Family is a child’s first teacher
Language, numbers, colors
Does the strength and support of the family impact how a child does in school?
Absolutely
can have a direct relationship to the success of a child
Families
Families teach children how to live in society
Basics
“Share everything”
“Don’t hit people”
“Play fair”
Families
How do families go about teaching these values?
Through example
Through communication
Explaining rules and why we have them
Through religious training
Families
Families teach about their society’s unique way of life…
Art
Music
Cooking
Foods
Views about work and play
Holidays
Language
Families
What are the different family structures?
Nuclear Family
Single-Parent Family
Blended Family
Extended Family
Families
What is a nuclear family?
Includes mother, father and at least one child
Two parents to help raise the child
Families
What is a blended family?
Formed when a single parent marries another person, who may or may not have children
“step-parents”
Families
What is a single-parent family?
Either a mother or father and at least one child
Absent parent may have died, left after divorce, parents never married
Extended Family
What is an extended family?
Includes parent or parents, at least one child, and relatives other than the parents who live with them
For example…
Mom, dad, child and grandma or grandpa
Mom, dad, child, aunt or uncle
Families
How does a child “join” a family?
Usually born into a family
Sometimes through “legal guardian”
Adoption
An adopted child has the same rights as any biological child
Families
How do they match foster children with adoptive parents?
In the past…
race
Ethnic or religious background
physical characteristics
Nowadays…
Emphasis is on finding a good home, not physical characteristics
Families
Some children join a family as a “foster child.”
Can be anyone
May have come from troubled family
Sometimes becomes part of adopted family or rejoins original family
Bree is a typical 9 year old girl. She lives with Mr. and Mrs.
Mason, her foster parents. When Bree was 7,her biological parents weren’t able to care for her, so they allowed her to be adopted.
Bree lived with several families before she came to stay with the
Mason’s. Many families who want to adopt are looking for a baby, and sometimes it is more difficult for an older child to be adopted.
Moving from family to family and home to home has been hard for
Bree. Sometimes she has to change schools and make new friends.
Bree has lived with the Mason’s for a year now, and they are seeking to formally adopt her. Nothing would make her happier.
Do you know anyone who has foster parents? What were his or her experiences like? How are they similar and different from your own?
Let’s play…
What type of family is this?
The Brady’s
Blended Family
The Kardashian’s
Blended Family
The Cullen’s
Nuclear (Adopted) Family
Fresh Prince of Bel Air
Extended Family
Full House
Extended Family
The Simmon’s
Blended Family
Brad and Angelina
Nuclear (Adopted) Family
Rosie O’Donnell & Kelly Carpenter
Nuclear* Family
Sheryl Crow
Single Parent Family
Jay-Z and Beyonce (and Baby)
Nuclear Family
Ben Affleck and Jennifer Garner
Nuclear Family
Denise Richards
Single-Parent Family
Heidi Klum and Seal
Blended Family
Elton John and David Furnish
Nuclear* Family
Tim McGraw and Faith Hill
Nuclear Family
Sandra Bullock
Single Parent Family
Tom Cruise and Katie Holmes
Nuclear Family
Families…
Some that didn’t live happily ever after…
Jenny McCarthy and Jim Carrey
Blended Family
The Hogan’s
Nuclear Family (originally…)
Families
All families go through a life cycle with six stages
Beginning Stage
Couple works to establish a home and their marriage
Parental Stage 1
Expanding stage
Couple prepares for and adjusts to parenthood
Families
Parental Stage 2
Developing stage
As children grow, parents work to meet their changing needs and help them develop independence
Parental Stage 3
Launching stage
Children leave home and support themselves
Parents adapt to life on their own
Families
Middle age
Couple renews their relationship
Prepares for retirement
If children have left home, they are “empty nesters”
Retirement
Couple stops full-time work
Adjusts to having more free time
Trends Affecting Families
All families…
are affected by the trends in society around them
Some trends support families
Some add pressure to families
Mobility
What is mobility?
Many adults move from where they were raised
No family around
Must rely on themselves, neighbors, close friends
Aging Population
How has the “aging population” affected families?
People live longer
People care for their children and their parents
Grandparents sometimes help raise the children
Economic Changes
What “economic struggles” are affecting families?
Many families struggle to make ends meet
Money is often the reason that both parents work
Many families are smaller
Have first child later in marriage
Demand for child care
All day, before and after school care
Workplace Changes
How has the workplace changed over the years?
Many companies employ fewer people
Types of jobs available are shifting
Manufacturing has declined
Health and technology have grown
Layoffs are common
Often affects both income and insurance
Need to always learn new skills
Many people work outside their home
Technology
How has technology changed families?
Makes life easier and more complicated
Need to make sure kids are safe online
Technology can isolate people from one another
“Silent Generation”
Families
Which trends do you think affect families the most?
Mobility
Aging population
Economic changes
Workplace changes
technology
Which family type and trend?
The Michelsons family includes a father, a mother, and one child from the mother’s previous marriage. Both parents work from offices in the family home.
Family Type?
Blended Family
Trend?
Workplace Changes
Which family type and trend?
Pete Washburn won custody of his two children when he and his wife divorced. He works two jobs to earn extra money.
Family Type?
Single Parent Family
Trend?
Economic Changes
Which family type and trend?
Alberto and Anamarie Nunez have two children. They have moved three times over a 20 year period.
Family Type?
Nuclear Family
Trend?
Mobility
Which family type and trend?
The Iversons married when they were 20 and have three children. Recently, they brought Erik Iverson’s mother to live with them because she is no longer able to care for herself.
Family Type?
Extended Family
Trend?
Aging population
Which family type and trend?
Sue Watsom is raising her daughter on her own. She and her daughter had to move to another town so she could keep her job.
Family Type?
Single Parent Family
Trend?
Mobility
Families
Family life can be stressful! Who can you lean on for support?
Friends
Relatives
Coworkers
What if you need professional help?
Counselor
Doctor
Religious leader
Families
What does a “strong” family feel like?
Accepted
Loved/cared for
Sense of belonging
Support
Nurturing
Protection
Security
Families
What things do strong families do to keep close?
Spend time together
Share responsibilities
Work together to resolve differences
Listen to each other with an open mind
Allow everyone to express opinions and share feelings
Families
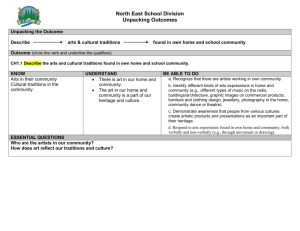
What are traditions?
Things that a family may do together more than once
Examples:
Family movie or game night
Making Christmas cookies or tamales
Summer vacation
Eating dinner together each night
Families
Three types of traditions
Celebration Traditions
Activities formed around special occasions
Birthdays
Holidays
Families
Family Traditions
Special activities created to fit a family’s lifestyle
Vacations
Family meetings
Patterned Family Interactions
Centered on daily life
Dinner time
Bed time routines
Families
Why are traditions so important? They create a sense of…
Togetherness
Appreciation
Continuity
“little things” that make a big difference
Create lasting memories
Families
How do we build strong families?
Forming Traditions
Sharing Values
Handling Family Conflict appropriately
Meeting Children’s Needs
It is important to meet the needs of children
What happens to children whose needs are not met?
Lag behind other children in their overall development
Suffer from deprivation
Is deprivation the same as poverty?
No!
Meeting Children’s Needs
What physical needs do children have?
Food
Clothing
Shelter
Health
Doctor visits
Safety
Car seats
Meeting Children’s Needs
What emotional and social needs do children have?
Need for nurturing
Love (hug, kiss, smile)
Support
Concern and caring
Opportunities for enrichment
Provide a safe environment for children to explore
Meeting Children’s Needs
When do children begin learning from their caregivers?
At birth
What intellectual needs do children have?
Stimulation
Playing with children
Providing interesting sounds, smells, sights, touch
Parenting Styles
One example of a way to intellectually nurture a child…
Helping them learn to enjoy books
Infants – enjoy the sound
Preschoolers – enjoy pictures, story
School age – learning to read
Parenting Styles
What is a parenting style?
How parents and caregivers care for and discipline their child
Some tips…
Best to use a style you are comfortable with
No one style is considered “best” or “right”
No one style works with all children
Parents often need to adapt their style as each child grows
Parenting Styles
What does the Authoritarian style look like?
Believes children should obey their parents without question
Parent tells child what to do, child’s responsibility is to do what he/she is told
When rules are broken, parent responds quickly and firmly
Parenting Styles
What does the Assertive-Democratic style look like?
Children have more input intro rules and limits
Children given some independence and freedom of choice within rules
When rules are broken, children learn best from accepting the results of their actions or by problem solving to find an acceptable punishment
Parenting Styles
What does the permissive style look like?
Parents give children a wide range of freedom
Children set their own rules
Encouraged to think for themselves, not follow trends
Parents typically ignore rule breaking
Parenting Styles
Sometimes parents use one style on some things and another style on others
Authoritarian – health or safety
Assertive-democratic – clothing or hairstyles
Parenting style used may change as children age
Authoritarian – younger kids
Assertive-democratic - teenagers
Guiding Children’s Behavior
What do you think is important when giving children effective directions?
Be sure you have child’s attention
Get down to their eye level
Make eye contact
Be polite
Use positive statements
“please walk” instead of “don’t run”
Guiding Children’s Behavior
How to give children effective directions, cont.
Begin with an action verb
“Get ready for bed, please”
Give a limited number of directions at a time
Be clear
Give praise and love
Guiding Children’s Behavior
Be a good role model
Children are always watching!
This is good and bad
Set limits
Children must be told what is expected of them
Limits stated simply, briefly, calmly
Guiding Children
Parents guide children in three basic ways
Positive role models
Set limits and redirect their children’s behavior
Use positive reinforcement
Guiding Children
Three questions to help parents determine limits
Does the limit allow the child to learn, explore and grow?
Is the limit fair and appropriate for the child’ age?
Does the limit benefit the child, or is merely for the adult’s convenience?
Guiding Children
How do you use Positive Reinforcement?
Be specific
Comment on the behavior as soon as possible
Recognize small steps
Help children take pride in their actions
Tailor the encouragement to the needs of the child
Use positive reinforcement wisely
Guiding Children
When you are dealing with inappropriate behavior and considering how to respond, keep in mind:
Is the expected behavior appropriate, given the child’s age and development?
Does the child understand that the behavior is wrong?
Did the child do the behavior knowingly and deliberately, or was it beyond the child’s control?
Guiding Children
What is negative reinforcement?
A response aimed at discouraging children from repeating an inappropriate behavior
Natural Consequences
Child suffers as result of their action
If a child loses his new jacket, he has to wear the old one
Logical Consequences
Connected to behavior
Color on the table, lose the crayons
Guiding Children
Loss of Privileges
Most effective for children 5 and up
Works best when item being taken away is related to the behavior
Time Out
Gives child a chance to calm down and reflect
Gives caregiver a moment to do the same
How long should a time out last?
One minute per year of age
Guiding Children
What are some poor disciplinary measures?
Bribing
Making children promise to behave
Shouting or yelling
Shaming or belittling
Threatening to withhold love
Exaggerating the consequences
Guiding Children’s Behavior
Think about the parenting style that you have experienced.
What are some of the positives of this style?
What are some of the negatives of this style?
Has it always been this style, or has it changed over the years?
What parenting style do you think you like to have with your children? Why?
Think about a time that you misbehaved as a child.
How was it handled?
Was it effective?