Our Laws and Legal System
advertisement

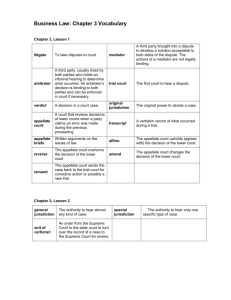
THE COURT SYSTEM DISPUTE RESOLUTION AND THE COURTS FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM STATE COURT SYSTEMS CAN DISPUTES BE RESOLVED PRIVATELY? • Mediation • Arbitration MEDIATION • Mediator tries to develop a solution acceptable to both sides of the dispute. • The actions of a mediator are advisory—not binding. ARBITRATION • An arbitrator usually holds an informal hearing to determine what happened. • The arbitrator’s decision is binding on both parties. • The decision can be enforced by court order if necessary. DIFFERENT LEVELS OF COURTS • Trial courts • Appellate courts TRIAL COURTS • A trial court is the first court to hear a dispute. • A trial court has original jurisdiction over a case. APPELLATE COURTS • An appellate court reviews decisions of lower courts when a party claims an error was made during the previous proceeding. • Appellate courts are concerned with errors of law rather than questions of fact • Do not hear witnesses • Examine transcripts of trial • Review appellate briefs POSSIBLE APPELLATE COURT DECISIONS • Affirm (uphold) the decision of the lower court • Reverse (overturn) the decision of the lower court • Amend (change) the decision of the lower court • Remand the case—send it back to the trial court for corrective action or possibly a new trial. FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM IDENTIFY THE SOURCE OF POWER OF THE FEDERAL COURTS NAME THE VARIOUS LEVELS OF FEDERAL COURTS AND DESCRIBE THEIR JURISDICTIONS ORIGINS OF OUR FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM • Federal courts received their power from the Constitution. • The Constitution granted Congress the power to establish courts inferior to the U.S. Supreme Court. JURISDICTION OF THE FEDERAL COURTS • 3 Levels of Federal Courts • Federal District Courts • Federal Courts of Appeals • United States Supreme Court FEDERAL DISTRICT COURTS • Lowest level of federal court with general jurisdiction (1st court to hear a dispute) • Trial court of the federal system • Jurisdiction over: • Federal questions or cases that arise under the Constitution, US laws or treaties • Lawsuits b/w citizens of different states or US citizen and a foreign nation • >$75,000 in dispute FEDERAL COURT OF APPEALS • Appellate court for Federal District Courts • No new evidence or witnesses • Review transcripts & oral arguments • 13 Federal Courts of Appeal • 12 assigned to a geographic area • 1 Federal Circuit • Patent cases • Special jurisdiction (Int’l Trade Commission) US SUPREME COURT (USSC) • Some original jurisdiction • Cases affecting ambassadors • Mostly appellate jurisdiction • Decisions of USSC re: Constitution are final FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM United States Supreme Court 13 United States Courts of Appeals (12 Circuit Courts) (1 Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit) State Supreme Courts United States District Courts Specialized Federal Courts Many Federal Agencies STATE COURT SYSTEMS COMPARE THE STRUCTURE OF A TY OF THE F I DENTIFY STATE COURTS DISCUSS THE JURI SDICTION OF PICAL STATE COURT WI TH THE STRUCTUR E EDERAL COURTS OF SPECI ALI ZED JURI SDICTION THE VARI OUS TYPICAL STATE COURTS STRUCTURE OF STATE COURT SYSTEMS • Courts of Limited Jurisdiction • State Trial Courts • State Courts of Appeals • State Supreme Courts COURTS OF LIMITED JURISDICTION • Lessens burden on Trial Court • Specialized or relatively minor jurisdiction • Can be appealed to the circuit court JUVENILE COURT • Emphasis on rehabilitation, not punishment • Records do not become public knowledge • Rehabilitation fails, can be tried as an adult MUNICIPAL COURTS • Courts that administer ordinances • Traffic division • Traffic and misdemeanor fine schedule • Criminal division PROBATE COURT • Wills and estates • Mr. Deeds SMALL CLAIMS COURT • Attorneys generally are not required • <$5,000 • Judge Judy • Judge Judy Sheindlin, a former judge from New York, tackles real-life small claims cases with her no nonsense attitude in which damages of no more than $5,000 can be awarded. Also by her side is bailiff Petri Hawkins-Byrd who keeps order in the court. Then after a case is closed, the defendant and plaintiff briefly confront each other outside the courtroom. A TYPICAL STATE COURT SYSTEM Supreme Court Intermediate Appeals Court (In Populous States) Trial Court (Of Original General Jurisdiction) Family Court Juvenile Court Municipal Court Justice’s Court (The Court of a Justice of the Peace) Probate Court Criminal Court Small Claims Court