Do Now - TeacherWeb
advertisement
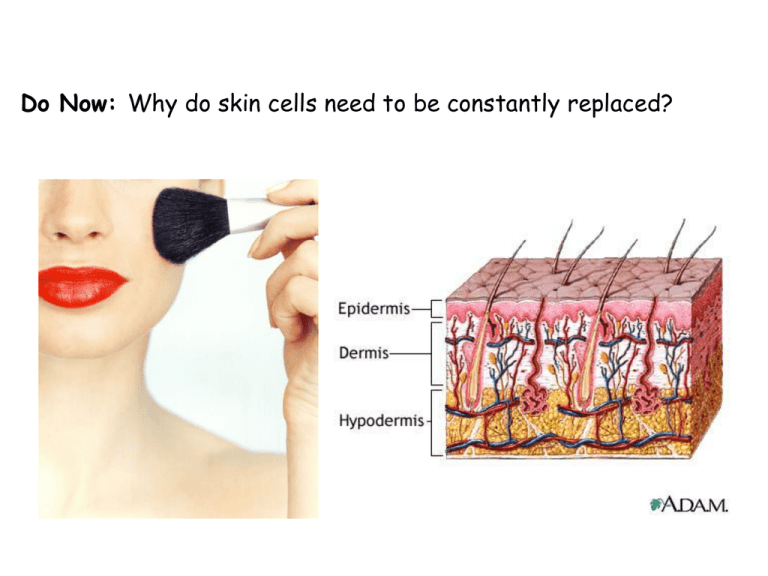
Do Now: Why do skin cells need to be constantly replaced? Explain how you think the pumpkin grew so big from a small flower. DNA Chromatin Chromosomes Chromatids Which # is DNA? 2. Which # has sister chromatids? 3. What is happening in these pictures? 1. Cell Cycle Human Life Cycle Do Now: What is happening in this cartoon? Do Now: Compare these two cycles. Human Life Cycle Cell Cycle Stages 1. Interphase 2. Mitosis • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase 3. Cytokinesis Phases Study Help…… Stages 1. Interphase 2. Mitosis • Prophase (Pieces) • Metaphase (Middle) • Anaphase (Apart) • Telophase (Two) 3. Cytokinesis The Cell Cycle Stage One: Interphase • Longest stage • Cell grows to its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA (replication), and prepares to divide. Phases of Mitosis Prophase • Chromatin condenses and becomes fully visible • Nuclear membrane disappears • Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell • Spindle fibers stretch across the cell Prophase (Hint: Pieces) Phases of Mitosis Metaphase • Chromosomes line up • Centromeres become attached to spindle fibers Metaphase (Hint: Middle) Phases of Mitosis Anaphase • Chromatids separate and move away from each other to opposite ends of the cell Anaphase (Hint: Apart) Phases of Mitosis Telophase • A nuclear membrane forms around each mass of chromosomes Telophase (Hint: Two) The Cell Cycle Stage Three: Cytokinesis • Cytoplasm divides • Each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the original parent cell Do Now: What is the longest part of the Cell Cycle and why? How are plant cells different from animal cells? How are plant cells different from animal cells? The rigid cell wall will not allow the cell to pinch like an animal cell. How are plant cells different from animal cells? • The rigid cell wall will not allow the cell to pinch like an animal cell. How are plant cells different from animal cells? • The rigid cell wall will not allow the cell to pinch like an animal cell. • Plant cells form cell plates to divide the cell. How are plant cells different from animal cells? The rigid cell wall will not allow the cell to pinch like an animal cell. • Plant cells form cell plates to divide the cell. • Plant cells do not have centrioles. • Complete the Venn Diagram How is mitosis different in plant and anima cells? Do Now: What phases can you see here? Do Now: Identify these phases of Mitosis? Do Now: Draw the following diagram. What is happening in this picture? How is this connected to the Cell Cycle. Binary Fission Binary fission produces daughter cells with DNA identical to the parent. It is a way for protozoa to increase in number when environmental conditions are stable. When environmental conditions change, the protozoa reproduce, because combining DNA from two organisms allows more genetic variation and more options for survival in a changing environment. Regeneration When an organism is able to regrow part of their organism or most of an organism from just a section. A part of the nervous system must be included for regeneration to occur. In such an organisms cells are able to differentiate (change into cells of different function). Regeneration Regeneration BUDDING A form of asexual reproduction in living organisms in which new individuals form from outgrowths (buds) on the bodies of mature organisms. These outgrowths grow by means of mitotic cell division. Many simple multicellular animals such as hydras and unicellular organisms such as yeasts reproduce by budding. BUDDING Equal division of the nucleus, unequal division of the cytoplasm BUDDING BUDDING Reproduction Sexual Reproduction: sex cells from two parents combine Egg + Sperm = Zygote (cell that forms in fertilization) Fertilization: the joining of an egg and sperm Asexual Reproduction: independent of the sexual process 1. Regeneration – a new organism grows from just a part of the parent organism (re-grow a body part) Ex. lizard and starfish Yeast Sponge Reproduction Sexual Reproduction: sex cells from two parents combine Egg + Sperm = Zygote (cell that forms in fertilization) Fertilization: the joining of an egg and sperm Asexual Reproduction: independent of the sexual process 1. Regeneration – a new organism grows from just a part of the parent organism (re-grow a body part) Ex. lizard and starfish 2. Budding – new offspring grows on the parent Ex. Yeast, sponge and hydra Reproduction Sexual Reproduction: sex cells from two parents combine Egg + Sperm = Zygote (cell that forms in fertilization) Fertilization: the joining of an egg and sperm Asexual Reproduction: independent of the sexual process 1. Regeneration – a new organism grows from just a part of the parent organism (re-grow a body part) Ex. lizard and starfish 2. Budding – new offspring grows on the parent Ex. Yeast, sponge and hydra 3. Fission – to split in two Ex. bacteria, sea anemone Do Now: Label the phases.




