LAN- TC-01 Edisi Ke 2 : Tatacara Kelulusan Bagi Kursus Pengajian
advertisement

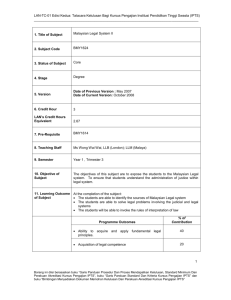
LAN- TC-01 Edisi Ke 2 : Tatacara Kelulusan Bagi Kursus Pengajian Institusi Tinggi Swasta (IPTS) Bagi Peringkat Sijil, Diploma dan Ijazah Sarjana Muda. 1. TITLE OF SUBJECT 2. SUBJECT CODE 3. STATUS OF SUBJECT 4. STAGE 5. VERSION 6. CREDIT HOUR theory of Soil Mechanics MEU Core Diploma in Civil Engineering Date of current version: January 2010 3 EAC’s CREDIT HOUR EQUIVALENT 7. PRE-REQUISITE 8. TEACHING STAFF Not assigned yet 9. SEMESTER / YEAR Year 2, Semester 2 10. AIM OF SUBJECT 11. LEARNING OUTCOME OF SUBJECT Concept of stress, strain in relation to one-dimension and two-dimension element, torsion of circular section, shear forces, bending moment and deflection in beam, shear stress in beam. Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Apply the basic understanding on components and application of stresses and strains. 2. Calculate the structural properties of a cross section. 3. Analysis the shear force, bending moment and deflection of statistically determine beams. 4. Apply the concept of pure torsion in soil and hollow uniform circular sections. 12. ASSESSMENT Assignment Individual Assignment Group Assignment 10% Test 1 Written Exam 10% Test 2 Written Exam 10% Borang ini diisi berasaskan buku “ Garis Panduan Dan Proses mendapatkan Kelulusan, Standard Minimum Dan Perakuan Akreditasi Kursus Pengajian IPTS”, Garis Panduan Standard Dan Kriteria kursus Pengajian IPTS” dan buku “ Bimbingan menyediakan Dokumen Memohon Kelulusan dan perakuan akreditasi Kursus Pengajian IPTS” Page 1 LAN- TC-01 Edisi Ke 2 : Tatacara Kelulusan Bagi Kursus Pengajian Institusi Tinggi Swasta (IPTS) Bagi Peringkat Sijil, Diploma dan Ijazah Sarjana Muda. Final exam 13. DETAILS OF SUBJECT Written Exam TOPICS 70% HOURS The Structural Properties of a Cross Section Center of gravity (centroid) and moment of inertia Symmetrical Bending of beams Moment of forces equilibrium and compatibility condition, types of supports, types of statically determinate beams, plane of bending and plane of symmetry. Internal forces – overall and part free body diagram, shear force, axial force and bending moment diagram. Relationship between load, shear and bending moment. Stresses – theory of pure bending, flexural and shear stresses. Deflection and relations – double integration and Macaulay’s methods. Bending of composite beams – introduction, transformed sections and flexural strain and stress distributions. Torsion of Circular Shafts Determinate and introduction to indeterminate solid and hollow uniform cross-section circular shafts-internal torques, equilibrium and compatibility conditions, internal torque diagram, free-body diagrams. 14. TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Textbook Reference Material 15. READING MATERIALS 1. Hibbeler, R.CJ. (2008). Mechanics of materials (7th edition).USA: Prentice Hall Inc. 1. Beer, F.P, and Johnston Jr. E.R. (1992). Mechanics of materials, Sl version. McGram Hill. 2. Hearn, E. J.( 1998). Mechanics of materials (7th edition, Vols. 1 and 2). Pergamon Press. 3. Logan, D. L.(1992). Mechanics of material. Harper Collins. 4. Papov, E.P. (1983). Mechanics of materials, Sl version (2nd edition). Prentice Hall. 5. Gere, J. M. and Timoshenko, S. P. (1991). Mechanics of materials, Sl version (3rd edition). Chapman and Hall. 6. Abu Bakar, A., Mohd Ridzuan, R. A., Ibrahim, A., Mat Isa, C. M., Ahmad, H., Abdul Hamid, H., et al (2003). Basic solid mechanics. Malaysia: Cerdik Publications snd. Bhd. 7. Bemham, P. P and Crawford, R. J. (1994). Mechanics of engineering material, Sl version. Longman. Borang ini diisi berasaskan buku “ Garis Panduan Dan Proses mendapatkan Kelulusan, Standard Minimum Dan Perakuan Akreditasi Kursus Pengajian IPTS”, Garis Panduan Standard Dan Kriteria kursus Pengajian IPTS” dan buku “ Bimbingan menyediakan Dokumen Memohon Kelulusan dan perakuan akreditasi Kursus Pengajian IPTS” Page 2