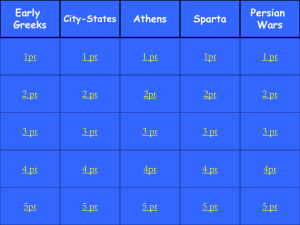
Sparta and Athens: Totalitarianism vs. Democracy
advertisement

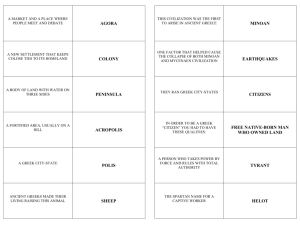
Sparta and Athens: Oligarchy vs. Democracy World History I The Greek City -State • Greece was made up of city-states, or polis – Polis: made up of a city and its countryside which included numerous villages • Citizenship of the polis – Citizens (free adult males) had political rights and the responsibility of civic participation in government – Women and foreigners had no political rights – Slaves had no political rights Sparta – Totalitarian Oligarchy • Definition of Totalitarianism – a form of government that uses force and power to rule a people • Oligarchy – Sparta’s form of totalitarianism government – Few ruled over many Spartan Society • 3 groups of people in Sparta – Helots: Spartan slaves (80% of population) • Provided food and labor to Spartans • Treated horribly by the Spartans • Under constant threat of death from Spartans – Noncitizens • Free people who paid taxes and served in the military, but had no political power • Included farmers, and others who lived and worked in the city as artisans or traders Spartan Society –Equals: controlled Sparta • Spartan Males: all became warriors • Goal was to make every male citizen a part of the military –Newborn males judged to be weak left to die • Spartan Females: taught to be physically fit, brave, and patriotic –Main role: birth strong Spartans Spartan Government • Executive – 2 kings elected by the Assembly • 1 king – ran military • 1 king – ran domestic affairs – 5 ephors (magistrates) with unlimited power • Legislative – Assembly: all (male) citizens over 30 • Voted on major policies – Council of Elders: 28 members all over age 60 • Proposed laws to the Assembly • Judicial: Kings acted as judges Spartan Military Training • Age 7: Left home to live in barracks to start military training • Went bare foot and wore little clothing (even in the winter!) • Received intense military training • Did learn to read and write, but more focused on training • Practiced all forms of athletics – Wrestling, boxing, etc. • Married at age 20, but lived in barracks until 30 • Stayed in military until age 60 or death Athens • Went through stages of evolution in government –Monarchy –Aristocracy –Tyranny –Democracy Early Athenian Government • After the monarchy ended, an aristocracy took its place – Ruled by wealthy landowners who told everyone else what to do • Draco (born c. 650 BCE) - lawgiver and reformer – Created first written code around 621 • Made it so all laws had to be written • Known for harsh penalties – “draconian” • Tyrants began seizing power – Gained power through the support of the people – Usually made promises to earn support but did not follow through on promises • Solon (archon in 594 BCE) – tyrant and reformer – Outlawed selling people into slavery to pay their debt – Divided citizens into 4 groups based on wealth: wealthiest 2 could hold office Athens - Democracy • Definition of Democracy – a form of government where the people rule • Direct Democracy – Direct participation of citizens in government activities and decisions – Origins of democratic principles • Public debate • Duties of the citizen Athenian Government • Executive: 9 archons (rulers) – Power limited by the Assembly • Legislative – Council of 500: (male) citizens over 30 and chosen by the Assembly • Proposed laws to the Assembly – Assembly: all male citizens over 20 • Voted on policies and laws • Full and final power • Majority ruled • Judicial – Court chosen by the Assembly – Juries were very large – Used secret ballots to reach verdict Athenian Society • All (male) citizens participated in governmental activities • All (male) citizens equal before the law • Women, foreigners, and slaves were not allowed citizenship – Had no say in government Athenian Youth • Encouraged to develop artistic and intellectual talents • Experienced great development in arts, philosophy, and politics – Golden Age of Greece • Girls were taught to run the house, raise children, and be seen and not heard Group Discussion • Split into groups of 2-3. • You will be given two quotes to read. • Discuss amongst your group and determine which civilization – Athens or Sparta – that influenced the quote and why. • Take a guess where or who stated this quote. Quotation #1 • “The fundamental motif through all the centuries has been the principle that force and power are the determining factors. All development is struggle. Only force rules. Force is the first law…Only through struggle have states and the world become great. If one should ask whether this struggle is gruesome, then the only answer could be – for the weak, yes, for humanity as a whole, no. Instead of everlasting struggle, the world preaches cowardly pacifism, and everlasting peace. These three things, considered in the light of their ultimate consequences, are the causes of the downfall of all humanity.” Which city-state influenced this quotation? Sparta! Who or what do you think stated this quotation? Quotation #1 • This quote is taken from a speech from Adolf Hitler in 1926 • Hitler would have loved Sparta! • Hitler modeled aspects of the Nazis after the Spartans. Quotation #2 • “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these rights Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.” What city-state influenced this quotation? Athens! Who or what stated this quotation? Quotation #2 • This quote came from the Declaration of Independence • Written by Thomas Jefferson in 1776 • Founding fathers were greatly influenced by Athens and its philosophers Conclusion • Who benefited most in each society – the rich or poor, males or females? • Who benefited the least? • What are the pros and cons of each civilization? • Where do we see the seeds of their governments today? Homework Assignment • Use what you learned about Sparta and Athens, and imagine what it would have been like to have lived in one of those city-states • Write a one-page fictional diary entry that describes your life as an Athenian or Spartan youth • Your diary entry should include 3 aspects of Spartan or Athenian life • Be sure to consider your age and gender. • Be creative!!