protein synthesis
advertisement

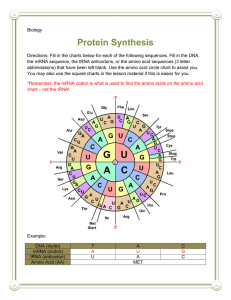
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Learning Outcomes B7 Demonstrate an understanding of the process of protein synthesis State roles of DNA, mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes Explain the processes of transcription and translation Determine the sequence of amino acids for a DNA sequences using a table of mRNA codons DNA, Chromosomes and Genes Each chromosome contains many genes Each gene contains many base pairs (3000 is average) Each gene carries the code for one specific polypeptide The Central Dogma of Genetics DNA RNA Protein The Genetic Code How many possible combinations of 3 can you make using A,T,C,G? THE GENETIC CODE sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide Triplet code - 3 bases for one amino acid (ex. AAG,GTC, etc.) code is redundant - more than one triplet can code for the same amino acid Proteins Recall that polypeptides are chains of amino acids, and a protein can contain several polypeptides A typical protein contains 100 - 200 amino acids All proteins are made up of only 20 different amino acids RNA How is RNA different from DNA? 3 types of RNA are involved in Protein synthesis Types of RNA mRNA (messenger RNA) copies the code from DNA rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is part of the ribosomes tRNA (transfer RNA)carries amino acids to the ribosomes mRNA Each group of 3 mRNA nucleotides is called a codon Each codon codes for a specific amino acid tRNA Each tRNA molecule has a 3-base anticodon which is complementary to a mRNA codon Also has a binding site for a specific amino acid rRNA A complex molecule that makes up the structure of a ribosome Binds to tRNA and mRNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • Protein synthesis consists of two stages – • • Transcription (in the nucleus) Translation (at ribosomes) TRANSCRIPTION • • • • • • Takes place in the nucleus Part of DNA strand unzips mRNA nucleotides attach to DNA strand, forming a complementary strand (enzyme – RNA polymerase) mRNA detaches from the DNA strand DNA zips back together mRNA can now carry the instructions out of the nucleus mRNA & DNA Base Pairing: • • • • U pairs with A A pairs with T G pairs with C C pairs with G RNA processing Not all of the DNA is part of a gene Introns are pieces that are not part of the gene Exons are the parts that make up the gene (expressed) Intron sections of mRNA are removed by ribozymes (RNA enzymes ) Translation Takes place outside the nucleus, at ribosomes (attached to ER or free in the cytoplasm) Takes place in 3 stages: 1. 2. 3. Initiation Elongation Termination 1. Initiation Ribosomal subunits attach to mRNA strand at the “Start” codon 2 codons of mRNA are in the ribosome at a time 2. Elongation As each mRNA codon binds to the ribosome, a tRNA with the complementary anticodon brings the correct amino acid As amino acids are delivered to the ribosome, they are joined by peptide bonds forming a growing chain Sequence of codons determines the primary structure Ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon at a time 3. Termination When the “Stop” codon is reached, the ribosome detached from the mRNA and the polypeptide is released The new polypeptide may now enter the ER for modification Mass Production of Proteins Many ribosomes may move along the same mRNA strand (polyribosome), producing many copies of the polypetide