1st SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015 Lab Safety & Equip

1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
Lab Safety & Equip, Scientific Method, Characteristics Of Life, BioChem, Conversion
1-8. Define the following words: Biology: the study of life
Evolution: gradual genetic change in a species over time
Homeostasis: a constant, stable internal environment
Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Stimulus: anything in the environment that will cause a reaction
Response: a reaction to a stimulus
Organism: anything possessing all 8 characteristics of life
Metabolism: all of the chemical reactions in the body
9. Be able to identify the following lab equipment: Identify lab equipment and know functions:
Test tube: small glass container used to view chemical reactions
Erlenmeyer flask: narrow mouthed container used to transport materials; can be corked
Beaker: wide mouthed container used to transport materials
Petri dish: used for growing bacteria
Graduated cylinder: used for measuring volumes precisely
Triple beam balance: used for measuring mass
10. Explain what these major fields of biology study: A&P: structure and function of living things
Botany: study of plants
Microbiology: study of microorganisms
Zoology: study of animals
11. What are cells and what do they enable us to be? Basic units of life—complex
12. What are the six steps of the scientific method in order?
indentify a problem
-form a hypothesis
-design an experiment
-collect and analyze data
-form a conclusion
-make a prediction
13. Be able to identify the following in given a scenario: hypothesis, control group, experimental group, independent variable, dependent variable, and conclusion.
Ms. Aycock believes that students will perform better on exams if she promises a cookie to any student who gets an A or B on an exam. She tests this by promising 1 st Period the cookies but not telling 2 nd period anything about the new idea. After the first exam, 1 st Period’s test scores were 15% higher than 2 nd Period.
Hypothesis: If Ms. Aycock promises cookies then the students will get higher grades.
Control: 2 nd Period
Experimental: 1 st Period
IV: cookies DV: higher grades
Conclusion: In her experiment, Ms. Aycock discovered that offering cookies can improve test scores.
14. What are the eight characteristics of life? How many must you have to be considered alive?
Organized into cells
-Able to reproduce
-React to stimuli
-Maintain homeostasis
-Use of energy
-Evolution
-Growth & development
-Adaptation
15. T or F: Always put unused chemicals back into its original container FALSE
16. Know LAB Safety: You should always smell chemicals before using them??? NO!
17. T or F You should read all directions before beginning the lab. YES
15. Goggles and gloves are not mandatory for lab involving chemicals. False
16. Horseplay such as running or hitting is never allowed in the lab. True
17. Long hair should always be tied back. True
18. You should always smell chemicals before using them. False
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
19. You should always read the directions before beginning a lab. True
18. Know how to label and use the STEP method for conversions with base units and prefixes King Henry Died
Unexpectedly Drinking Chocolate Milk.
Kilo
Hecta
Deca
UNITS
Deci
Centi
Mili
19. Know functions and where we get organic compounds.
Organic
Compound
Class
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acid
Function
Energy & structural support
Provides waxy coating on plants & energy storage in animals
Used to build cells
& do much of the work inside organisms
Carry genetic information within cells
Monomer &
Example
Monosaccharide- ex. glucose
Triglyceride-ex. glycerol
Amino acid-ex. leucine
Nucleotide-ex. ATP,
DNA or RNA bases
Polymer & Example
Carbs/Polysaccharide- ex. Chitin, cellulose, starch
Lipids-ex. Steroid (cholesterol), waxes (plant cuticle), phospholipids
Proteins-ex. enzymes
Nucleic Acid-ex. DNA or RNA
Picture of where we get it from in our diet
Breads, pasta, soda
Meats, nuts, oils
Meats, proteinenriched foods
Meats, vegetables
20. Types of bonds between atoms: Covalent and Ionic
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonding
occurs when electrons are transferred between atoms.
NaCl (sodium chloride or table salt) is an example of this.
Usually occurs between an metal and a nonmetal
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding
occurs when atoms share electrons.
Atoms held together by covalent bonds form molecules
21. How to determine number of protons and neutrons using the periodic table (Atomic number and mass)
Atomic mass minus atomic number = neutrons
22-24 Define proton, neutron, electron, solid, liquid and gas
Atoms are the smallest unit of matter
Atoms of are made of 3 subatomic particles: protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-
).
Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom
Electrons are found around the nucleus
The number of protons in an atom is the atomic number
The sum of protons and neutrons is the atomic mass
Isotopes have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.
3 states of matter: solids (definite shape, definite volume), liquids (takes of the shape of the container, definite volume), and gases (no definite shape, no definite volume)
Ch 7: Cells-Theory, Microscopes, and Organelles Study Guide
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
1. What did Hooke, Schwann, and Schleiden each contribute to the cell theory?
Leeuwenhoek-first to use a microscope; Hooke-came up with the name cells; Schwann-said that all animals are made of cells; Schleiden-said that plants are made of cells; Virchow-nucleus is responsible for cell division
2. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? 1) all organisms are made of one or more cells, 2) the cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of an organism, 3) all cells come from pre-existing cells
3. Describe the 2 types of electron microscopes: magnification power, what they can see, the type of pictures they can produce, and how they magnify:
Magnification power
SEM
500,000
TEM
500,000
What they can see
Type of picture produced
How they magnify
Cell surface
3D
Beam of electrons
Within the cell
2D
Beam of electrons
4. Compare and contrast the 2 basic cell types prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes on: See Ch 7 PP slides 13-16
5. Know these vocabulary words : phospholipid, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, organelle, selective permeability, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, and transport proteins.
PL: made of a polar head and two fatty acid tails
HPL: water loving
HPB: water fearing
O: a collection of molecules put together to serve a specific purpose within the cell
SP: only allowing certain things in and out
PK: a cell without a true nucleus
EK: a cell with a true nucleus
TP: gatekeeper; moves needed substances into the cell
6. What are the functions of the: cell membrane, cell wall, ER, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, mitochondria, nucleus, ribosomes, and vacuole?
CM: Flexible boundary that maintains cell homeostasis;
CW: protection & support;
ER: transports proteins, site of chemical reactions;
CH: produces food from light energy and turns it into chemical energy;
GB: modifies, sorts, and packs proteins;
LY: get rid of cell wastes;
M: make energy for the cell;
N: directs all cell activities;
R: makes proteins;
NO: makes ribosomes
WV: temporary storage for food, wastes, or water
7. What are 3 organelles found only in plant cells? 2 organelles found only in animal cells?
Plants: chloroplast, cell wall, water vacuole
Animal: cilia and flagella, centriole
Label the following structures :
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
Study Guide for Cell Transport: Answer on your own paper and attach this to the front.
SEE POWERPOINT ON WEBSITE!!!!!! CH 8.1 SG Answers
1.When does diffusion of molecules stop?
2. Vocab to know : Page 21 of notebook (Vocab Sheet)
3. What cell structure is responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis?
4. What will happen to an animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution? A plant cell? Draw a picture of each.
5. What will happen to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution? A plant cell? Draw a picture of each.
6. What will happen to an animal cell placed in an isotonic solution? A plant cell? Draw a picture of each.
****Use a Venn diagram or a T-chart to answer 7-12****
7. Compare and contrast active and passive transport on the following: energy requirement, use of transport proteins, and movement of molecules .
8. What are the two types of transport proteins? How are they alike? Different?
9. How are the two types of diffusion (simple and facilitated) alike?(2 reasons) Different?(1 reason)
10. What is similar between diffusion and osmosis? What is the one difference?
11. Describe the processes of endocytosis/exocytosis. Include in your explanation how they are alike and different.
12. How are phagocytosis and pinocytosis alike? Different?
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
13. Why must cells be small? Explain.
14. Know how to calculate Surface area and Volume of a cube
Mitosis Study Guide
1. What are the three causes of cancer in our bodies? UV radiation/radiation, viruses, & environmental influences
2. What are three ways to possibly prevent cancer? Diet, exercise, and not using tobacco
3. Describe the 3 major steps of the cell cycle. Interphase-cell growth, mitosis-cell division, cytokinesis-2 new cells produced
4. What is mitosis? Cell division
5. Explain the steps of mitosis (what happens in each) and draw a picture to represent each. I. P. M. A. T. C. know what this means and what happens in each stage.
6. What is the longest phase of the cell cycle? How does the cell get ready to divide? Interphase; chromosomes are copied
7. What is a chromosome? A chromatid? A centromere? Carrier of genetic material; the halves of a chromosome; structure that pulls apart the chromatids during cell division
8. Which cellular transport process limits cell size? Diffusion
9. What are 3 reasons why a cell divides? Repair, replacement, and growth
10. Definitions from page 33. These will help you a lot.
11. Why is cell size limited? Because a cells size can slow down the rate of diffusion, cells have to have a way to limit their growth. Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over a short distance.
12. What is the cell cycle? The stages and steps a cell takes during its lifetime (Interphase, Mitosis and
Cytokinesis). The process of cells growing and dividing before they die.
13. What are the 2 leading causes of death in the U.S.? Heart disease followed by Cancer
14. What are 3 treatment options for cancer? Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy.
CH 9 Study Guide
1. Define the following words: ADP, ATP, cellular respiration, electron transport chain, photosynthesis, pigment
ADP: Adenosine Diphosphate (two phosphate groups)—an energy molecule
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate (three phosphate groups)—an energy molecule
Cellular Respiration: process by which cells break down food molecules into energy (ATP)
Electron Transport Chain: in chloroplast and mitochondria—transforms energy from electrons into ATP
Photosynthesis: process that uses the sun’s energy to make glucose
Pigment: a light absorbing compound (chlorophyll)
2. Draw and describe the three parts of a chloroplast.
Stroma: Space inside the chloroplast
Thylakoid: Green disk in the chloroplast
Granum stack: Stack of green thylakoids
3. What is the chemical equation of photosynthesis? What is it written in words ?
6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + LIGHT ENERGY C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6 O
2
OR carbon dioxide + water + sunlight glucose + oxygen
4. What is the chemical equation of cellular respiration? What is it written in words ?
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6 O
2
6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + ATP
OR glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + sunlight
5. In the first step of photosynthesis (the light reaction):
A. What powers this reaction? Sunlight
B. What is happening in the light reaction? (What was made?) Energized Electrons
C. Where does it occur? Thylakoid
D. What is the byproduct? Oxygen
E. Where do we cash in these electrons? Electron Transport Chain
And who carries the energy for them to the next step? ATP and NADPH
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
6. In the second step of photosynthesis (the calvin cycle):
A. What powers this reaction? Carbon dioxide and water
B. What is happening in the dark reaction? using energy from ATP and NADPH to create glucose
C. Where does it occur? stroma
D. What is produced? 1 glucose molecule
E. Once the energy is converted, what have our carriers turned into? ADP and NADP
How do we recharge? With sunlight
7. Make a chart of cellular respiration that contains the following: the names of the 3 steps, what happens in each (think flow-chart), is it aerobic or anaerobic, and how much ATP is produced. (3 rows, 4 columns)
Stage What happens ATP Produced Location
1. Glycolysis
Aerobic/
Anaerobic
Anaerobic Glucose
Pyruvate 2 Cytoplasm
2. Krebs Cycle Aerobic Pyruvate broken down 2
Mitochondria’s Matrix
3. Electron Transport
Chain (ETC)
Aerobic All leftovers plus donated electrons broken down
32
8. What is fermentation? Begins with Glycolysis and will continue if no oxygen is present
What are the two types and what causes each?
Alcoholic: yeast or bacteria must be present—creates alcohol and carbon dioxide as products
Lactic Acid: occurs in muscles with a high need for ATP and a low supply of oxygen
9. How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related? They are opposites
10. Draw a flow chart of cellular respiration.
Mitochondria’s inner membrane
11. How much ATP is produced from each stage in CR?
Glycolysis- 2 ATP
Krebs Cycle- 2 ATP
ETC- 32 ATP
1 st
SEMESTER EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
Total is up to 36 ATP
12. Know how to label a picture for cellular respiration and/or photosynthesis (coloring activity we did)
13. LOOK UP POWERPOINT (UNIT 5) TO STUDY!
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
1.
What are the complementary base pairs in DNA? Write the 1 letter symbol & spell them out.
Adenine (A)-Thymine (T) and Guanine (G)-Cytosine (C)
2.
What are the complementary base pairs in RNA? Write the 1 letter symbol & spell them out.
Adenine (A)-Uracil (U) and Guanine (G)-Cytosine (C)
3.
Use a chart to compare and contrast RNA and DNA in terms of structure, sugars, and bases.
DNA RNA
Structure
Sugar
2 strands
Deoxyribose
1 strand
Ribose
4.
List the three types of RNA and explain the function of each. mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
rRNA: combines with proteins to form the ribosome
tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made
5.
Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick
6.
IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is the corresponding sequence in a strand of mRNA? What tRNA sequence would pair up to this mRNA?
mRNA: UUG AUC CCA tRNA: AAC UAG GGT
7.
What will happen to a protein after a silent mutation? A missense mutation? A nonsense mutation?
Silent: no change Missense: changes 1+ amino acid Nonsense: stop codon
8.
What does the enzyme DNA helicase, polymerase, and ligase do during DNA replication? H:It unzips/unwinds
DNA P:adds correct nucleotides L:glues pairs together
9.
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? Sugar, nitrogenous bases, & phosphate group
10.
What process forms messenger RNA? What process forms proteins? transcription; translation
11.
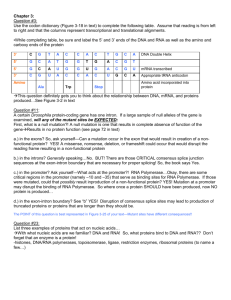
What do structures I, II, III, IV in the picture represent?
I: Anticodon II: mRNA III: Amino acid IV: tRNA
12.
What process is illustrated in the figure? translation
13.
A DNA segment is changed from- AATTAG- to-
AAATAG. What kind of mutation is this?
Point,
14.
What four things can cause a mutation? o spontaneous mistakes in base pairings o radiation o chemicals o UV rays
15.
Where does translation and transcription take place in the cell?
Translation-cytoplasm; transcription-nucleus
16.
What is the start codon? What amino acid does it code for? AUG; methionine
17.
Which type of RNA is the anticodon? Which type is the codon? tRNA; mRNA
18.
Point: Only 1 base is mismatched. FrameShift: a base is inserted or deleted causing a shift in all codons.
19.
Missense: mutation where codon changes the amino acid. Nonsense: amino acid is changed to a STOP codon.
Silent: mutation casues a change in Codon but Amino acid stays the same.
20.