MATLAB
advertisement

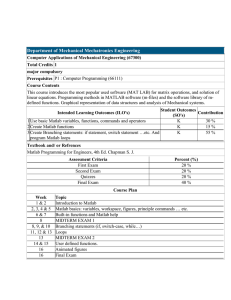
MATLAB FOR PATTERN RECOGNITION By: Özge Öztimur How Much Do We Know? Anybody who has never used MATLAB? MATLAB Environment Workspace: Variables defined so far. Command History Command Window Edit Window Plot Window … Current Directory: Start by setting the current directory to the directoy that you are working. Generally, it is where your files are. LOOKFOR & HELP LOOKFOR: Type ‘lookfor smth’ to learn the name of functions that are related to ‘smth’. HELP: Type ‘help function_name’ to learn how that function works, its inputs and outputs. Everything is a Matrix Each variable in MATLAB is a matrix. For example: >> a=1; >>size(a) ans= 1 1 Creating Matrices >> a = [ 1 2 2 1 ] a=1221 >> b= [1; 2; 2; 1] b= 1 2 2 1 Accessing a Matrix >> a=[1 2; 3 4] a= 12 34 >> a(2,1) ans= 3 Matrix Operations Matrix operations like, Matrix addition, subtraction, multiplication Determinant of a matrix Inverse of a matrix Transpose of a matrix Element by element multiplication, division … are defined in MATLAB. Flow Control-IF >> if a+b==5 m=1; elseif a+b==3 m=2; end >> Flow Control-Switch >> switch (rem(n,4)==0) + (rem(n,2)==0) case 0 M=0 case 1 M=1 otherwise M=2 end Loops >> a = [ 0.8 0.1; 0.2 0.9 ] >> x = [ 1; 0 ] >> for i = 1:20 x = a*x end Avoid using Loops in Matlab. M-Files: Scripts And Functions Scripts: Do not accept input arguments or return output arguments.They operate on data in the workspace. M-Files: can accept input arguments and return output arguments.Internal variables are local to the function. Read & Write Files Load, Save,Saveas Textread … There are many other functions for file operations. Check File I/O part in Mathwork’s Help. Function Definition Name of the function and the file should be the same. function[output1,output2]=example(input) Example – Generating Random Numbers Generate random numbers of size 5x3 (5 rows, 3 columns); >> a=randn(5,3); Example-Distributions Parameter Estimation Examples: Normal Distribution >>[mu,sigma]=normfit(data); Binomial Distribution >> phat=binofit(data,n) … Example-Probability Density Function Pdf gives the probability density function for a specified distribution >> Y=pdf(name,X,A) Where name is the name of the distribution, X is the data and A is the parameters for the given distribution. Example-Maximum Likelihood Estimation mle gives the maximum likelihood estimation >> mle(data); >> mle(data,’distribution’,dist) Where dist is the name of the distribution Graphical Representation Generally ‘plot’ is used for drawing graphics. >>plot(x) ; plots the columns of x versus their index. Many options are provided for this function. Refer To http://www.mathworks.com/access/hel pdesk/help/helpdesk.html Course Web Page: www.ceng.metu.edu.tr/courses/secon dprog/ceng564/