Module 5: Leading
advertisement

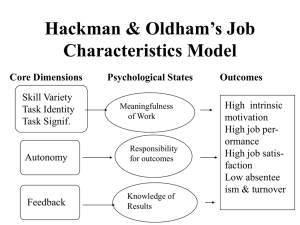
Module 5: Leading Section 2: Motivating and rewarding employees Learning objectives • Describe the motivation process • Define needs and explain the hierarchy of needs theory • Differentiate Theory X from Theory Y • Describe the motivation-hygiene theory and equity theory • Explain the key relationships in expectancy theory • Describe how managers can design individual jobs to maximize employee performance • Describe the effect of workforce diversity on motivational practices Learning objectives (Contd.) • Define leader and explain the difference between managers and leaders • Summarize the conclusions of trait theories of leadership • Be familiar with Fiedler contingency model • Describe the path-goal model of leadership • Explain situational leadership • Describe characteristics of charismatic leaders and visionary leaders • Explain four specific roles of effective team leaders • Identify five dimensions of trust Motivation and individual needs • Motivation: the willingness to exert high levels of effort to reach organizational goals, conditioned by the effort’s ability to satisfy some individual needs • Need is defined as an internal state that makes certain outcomes appear attractive The Motivation Process Unsatisfied Need Search Behavior Reduction of Tension Tension Drives Satisfied Need Classical theories of motivation • Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory • Theory X and Theory Y • Herzberg’s Two-factor Theory Early theories of motivation Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self Esteem Social Safety Physiological Little Ambition Theory X Workers Dislike Work Avoid Responsibility Self-Directed Theory Y Workers Enjoy Work Accept Responsibility Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory Hygiene Factors • Quality of supervision • Salary and benefits • Company policies • Working conditions • Relations with others • Security and status High Job Dissatisfaction Motivators • Career advancement • Recognition • Work itself • Responsibility • Advancement •Growth 0 Job Satisfaction High Contemporary theories of motivation • • • • Three-needs theory Equity theory Job characteristics model Expectancy theory Need for Achievement (nAch) The Theory of Needs Need for Power (nPow) Need for Affiliation (nAff) David McClelland Equity Theory Employee’s Perception Ratio Comparison* Outcomes A < Inputs A Outcomes A Inputs A *Where Inequity (Under-Rewarded) Inputs B = Inputs A Outcomes A Outcomes B Outcomes B Equity Inputs B > Outcomes B Inequity (Over-Rewarded) Inputs B A is the employee, and B is a relevant other or referent. Skill Variety Task Identity The Job Characteristics Model Task Significance Autonomy Feedback Examples of High and Low Job Characteristics Characteristics Examples Skill Variety • High variety The owner-operator of a garage who does electrical repair, rebuilds engines, does body work, and interacts with customers • Low variety A bodyshop worker who sprays paint eight hours a day Task Identity • High identity A cabinetmaker who designs a piece of furniture, selects the wood, builds the object, and finishes it to perfection • Low identity A worker in a furniture factory who operates a lathe to make table legs Task Significance • High significance Nursing the sick in a hospital intensive-care unit • Low significance Sweeping hospital floors Autonomy • High autonomy A telephone installer who schedules his or her own work for the day, and decides on the best techniques for a particular installation • Low autonomy A telephone operator who must handle calls as they come according to a routine, highly specified procedure Feedback • High feedback An electronics factory worker who assembles a radio and then tests it to determine if it operates properly • Low feedback An electronics factory worker who assembles a radio and then routes it to a quality control inspector who tests and adjusts it The Job Characteristics Model Core Job Dimensions Skill variety Task identity Task significance Critical Psychological States Experienced meaningfulness of the work Autonomy Experienced responsibility for outcomes of the work Feedback Knowledge of the actual results of the work activities Employee Growth Need Strength Personal and Work Outcomes High internal work motivation High-quality work performance High satisfaction with the work Low absenteeism and turnover The Motivating Potential Score Motivating = Potential Score (MPS) Skill + Task + Task X Autonomy X Feedback Variety Identity Significance High MPS Increases 3 Motivation Performance Satisfaction and Decreases Absence Turnover Expectancy Theory Individual Effort 1 Individual Performance 2 Organizational Rewards 3 1. Effort-performance relationship 2. Performance-rewards relationship 3. Rewards-personal goals relationship Individual Goals An Integrative Model of Motivation High nAch Ability Task complexity Individual Effort Individual Performance Objective Performance Evaluation System Equity Comparison O O IA IB Organization Rewards Reinforcement Goals Direct Behavior Personal Goals Dominant Needs Leaders and leadership • Leaders are people who are able to influence others and who possess managerial authority • Leadership is an influence process; therefore, leaders are people who, by their actions, encourage a group of people to move toward a common or shared goal. Trait Theories of Leadership Ambition and Energy Desire to Lead Honesty and Integrity SelfConfidence Intelligence Job-Relevant Knowledge Behavioral approach to leadership • Behavioral theories of leadership • Ohio State University studies • The University of Michigan studies Continuum of Leader Behavior Manager sells decision Autocratic Consultative Manager presents ideas Manager presents tentative decision Participative Democratic Employees make decision Laissez-faire Employee-Centered Leadership Boss-Centered Leadership Manager makes decision Formal Studies of Behavioral Styles Ohio State Initiating Structure Consideration University of Michigan Employee-Orientation Production-Orientation The Managerial Grid 1 (1,9) (9,9) Concern for People 2 3 4 5 (5,5) 6 7 8 9 (9,1) (1,1) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Concern for Production 7 8 9 Contingency approach to leadership • • • • Fiedler model Path-goal theory Leader-participation model Situational leadership Fiedler’s LPC Scale 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... ......................…. Pleasant Friendly Rejecting Helpful Unenthusiastic Tense Distant Cold Cooperative Supportive Boring Quarrelsome Self-assured Efficient Gloomy Open ........................... .......................... . ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... ........................... .....................…. Unpleasant Unfriendly Accepting Frustrating Enthusiastic Relaxed Close Warm Uncooperative Hostile Interesting Harmonious Hesitant Inefficient Cheerful Guarded Findings of the Fiedler Model High Performance People-Oriented Task-Oriented Low Favorable • Category • Leader-Member Relations • Task Structure • Position Power Moderate I II Good High Strong Unfavorable Good III Good IV Good V Poor VI Poor VII Poor VIII Poor High Weak Low Strong Low Weak High Strong High Weak Low Strong Low Weak The Path-Goal Theory Environmental Situational Factors Leader Behavior Outcomes Subordinate Situational Factors Leader Participation Model Employee Involvement Continuum Increased Leader Control 1 2 3 4 Increased Employee Involvement 5 Contingency Variables in the Revised LeaderParticipation Model Quality Requirement Commitment Requirement Leader Information Problem Structure Commitment Probability Goal Congruence Employee Conflict Employee Information Time Constraint Geographic Dispersion Motivation Time Motivation Development The Situational Leadership Model Relationship Behavior High relationship and low task Low relationship and low task Style of Leader S3 S2 Participating Selling Delegating Telling Task Behavior S4 High S1 Moderate High task and high relationship High task and low relationship Low R4 R3 R2 R1 Able and willing Able and unwilling Unable and Willing Unable and unwilling Emerging approach to leadership • Charismatic leadership • Visionary leadership • Transactional and transformational leadership Charismatic Leadership • Self-confidence • Vision and articulation • Strong convictions • Extraordinary behavior • Image as a change agent • Environmental sensitivity Visionary Leadership Explain the Vision Express the Vision Extend the Vision Transactional Leaders Transformational Leaders Leadership Styles Motivation versus Inspiration Coaches Liaisons Team Leader Roles Conflict Managers TroubleShooters What Is Trust? • Integrity • Competence • Consistency • Loyalty • Openness Three Types of Trust DeterrenceBased KnowledgeBased IdentificationBased