Multidimensional Arrays
advertisement

Multidimensional Arrays in Java
Vidhu S. Kapadia
The Basic Definitions
• What is an Array?
• An array is a fixed size sequential collection of elements of
identical types.
• They are created with either a new operator or array initializes
• The storage space for arrays is allocated from the garbagecollected heap.
• The element in an array are indexed by the integers 0 to n- 1,
where n is the size of the array
Declaring an Array
• Using the new operator
new Type [ ]
Here the size of the array must be specified, and all the elements in the
array are initialized to the default initial values based on the types of
elements.
int ia1 = new int [3];
//creates an integer array of size 3; all elements are initialized to 0
Point pa [ ] = new Point [10];
//creates an array of points of size 10; all elements are initialized to
null
Declaring an Array
• Using the one-dimensional array initializer
{v0, v1, …..,vn-1}
The values for v0, v1, …..,vn-1 are the initial values of the
elements in the array. The size of the array is determined by the
number of initial values provided in the array initializer
Int ia2 [ ] = {1, 2, 3};
// Creates an array of size 3; elements are initialized to 1, 2, and 3
respectively
What are Multidimensional
Arrays
• A multidimensional array is treated as an
array of arrays.
– Let a be a k-dimensional array; the elements of a can
be accessed using the following syntax:
a [ i1 ] [ i2 ]…[ ik ]
where n1, n2, ….., nk
Multidimensional Arrays
• Applying what we learned about simple
arrays to multidimensional array, we get the
following:
A k-dimensional array can be created with
either of the following methods:
– Using the new operator
– Using the k-dimensional initializer
Creating k-dimensional Array
Using the new operator
• Using k-dimensional array
initializer
new Type [ n1] [n2]…[nk]
•
Size of each dimension is n1,
n2, …,nk, respectively.
•
All the elements in the array are
initialized to default initial values
based on the type of the
elements
•
{I1, I2, ...., Ik}
where each I1, I2, ...., Ik
is a
(k-1)- dimensional array initializer.
Examples…
•
Using the new operator, the following
example is of creating and initializing
a two-dimensional array.
double mat1[ ][ ] = new double[4][5];
This creates a 4 x 5 two-dimensional
array. All elements are initialized to
0.0.
•
Using k-dimensional array initializer,
the following example is of creating
and initializing a two-dimensional
array.
int mat2[ ] [ ] = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}};
This creates a 2 x 3 twodimensional array. The elements
are initialized as:
mat2[0][0]=1
mat2[0][1]=2
mat2[0][2]=3
mat2[1][0]= 4
mat2[1][1]= 5
mat2[1][2]= 6
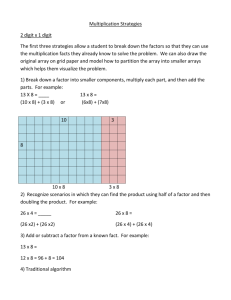
Illustrating Two-Dimensional
Array
Processing Multidimensional
Arrays
•
Multidimensional arrays are often processed using for statements.
To process all the items in a two-dimensional array, a for statement
needs to be nested inside another.
int[ ][ ] A = new int[3][4];
The following loop stores 0 into each location in two dimensional array
A:
for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++)
{
for (int column = 0; column < 4; column++)
{
A [row][column] = 0;
}
}
An Example:
• Using a mathematical function in the Java
Math class and handling of two–dimensional
arrays, the following example calculates the
max – min value.
public class MaxMin{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
double mat[ ] [ ]= { {2.3, 5.1, 9.9},
{8.3, 4.5, 7.7},
{ 5.2, 6.1, 2.8}}
int n = mat.length;
int m= mat[0].length;
double maxmin = 0.0;
Running the program
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
produces the following
double min = mat[j][0];
result:
for (int i = 1; I <n ; i ++){
The max-min value is 4.5
min = Math.min(min,mat[i][j]);
}
if (j==0){
maxmin = min;
}else{
maxmin = Math.max(maxmin, min);
}
}
System.out.println(“The max-min value is” + maxmin);
}
}
Keep in mind that…
• Computer memory is linear –
• In accessing a multidimensional array you are really
accessing a one-dimensional array in memory.
• You can simulate multidimensional arrays by packing
them into a one-dimensional array.
• The two manners of packing the one-dimensional array
are row-major order, where the array is filled one row at
a time; and column-major order, where columns are
placed into the array.
Interesting Tidbits about Arrays
in Java
• One of the main differences between the arrays in Java
and those in C/C++ is that the Java arrays are ALWAYS
bounds-checked at run time.
• Array bound-checking will automatically detect a major
source of faults in programs, that is exceeding the bounds
of arrays while accessing or manipulating their elements.
• There is no limit on the number of dimensions that an
array type can have. However, arrays of dimension three
or higher are fairly uncommon.
References
• Jia, Xiaoping. Object Oriented Software Development using
Java- 2nd edition, Adison Wesley 2003
• The historical collection classes – Arrays, IBM. April, 16,
2006, http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/java/library/jarrays/
• Array initialization, The Code Guru. April, 16, 2006,
http://codeguru.earthweb.com/java/tij/tij0053.shtml