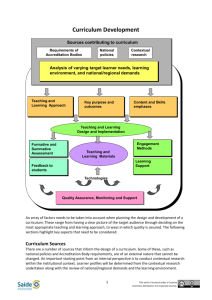
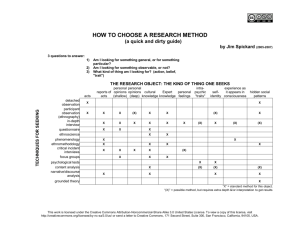
Chapter 6 - BC Open Textbooks
advertisement

Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6 Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Learning Objectives Understand • Different competitive moves commonly used by firms • When and how do firms respond to competitive actions taken by their rivals • Cooperate strategies to create mutual benefits (joint ventures, strategic alliances, etc.) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves 3 Merck executives must decide • what competitive moves to make • how to respond to rivals’ competitive moves, & • what cooperative moves to make Interestingly, other companies, such as Roche, will be a potential ally in some instances & rival in others This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Making Competitive Moves The study of competitive moves draws from military history, including Sun Tzu’s classic book, The Art of War Business strategists are familiar with a number of competitive moves that may help guide their firms to victory. • First Mover Advantage • Disruptive Innovations • Footholds • Blue Ocean Strategy • Bricolage This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves First Mover – Advantage or Not? This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves First Mover Advantage A first-mover advantage exists when making the initial move into a market allows a firm to establish a dominant position that other firms struggle to overcome Recall - a strategic resource is an asset that is valuable, rare, difficult to imitate, and non-substitutable. • Often requires significant R&D, & product testing costs • A first-mover cannot be sure that customers will embrace its offering, making a first move inherently risky • First movers must be willing to commit sufficient resources to follow through on their pioneering efforts This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves First Movers This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Good News – Real disruptions usually takes some time to catch on. Container shipping needed both ships, railcars and trucks equipped to deal with containers and container ports to load them Bad News – very hard to identify what might be invented soon… This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves First Mover – How to Fail…. • Does the product/service provide a truly sustainable competitive resource • Or is Innovation easy to copy, or worse improve on... • Can company preferably continue to improve product, or at a minimum, match product improvements (which are almost surely going to appear) • Failure to market aggressively (it’s new, consumers will not know its value for them) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Disruptive Innovations,1902 Can you think of any? This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Disruptive • • • • Big change! Affects whole market or industry Very hard to predict, but usually slow to develop Market is always evolving, difficult to pick out which are truly disruptive amongst market ‘noise’ • Includes creating brand new market where none existed before (i.e. Smart phone apps) • As market emerges or develops, other firms must decide how to respond, embrace or compete This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves (Relatively) Recent Disruptions! • • • • • • Energy Efficient light bulbs Kindle (Gaming) Electric & Driverless cars E-cigarettes iphone apps/mobile computing/texting Robots - vacuum cleaners, lawn mowers too! • Social Media - U-Tube, Facebook, Pinterest, etc. • Modern Container Shipping This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Foothold (Beach-head) Strategy Value often far exceeds small size & costs of maintenance Test market & faster expansion if things go well Can deter competitors & make harder to predict next move This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves • Carl von Clausewitz’s 19th military strategy “aim at the sharp end of spear where rivals are weak or uninterested in what you are doing” • Opens single store entering country as a showcase & establish brand This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Walmart’s disruptions centered on supply mgmt • Current data - Bar codes, satellites, inventory • Relentless focus on prices • Distribution system The first Walmart store opened July 1962 in Rogers, Arkansas & expanded in small towns underserved by large department stores This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Blue Ocean Strategy Involves creating a new, untapped market rather than competing with rivals in an existing market Creating a brand new market place • Coffee Shops, Women’s underwear stores • Transportation - Mom Vans / SUV / Electronic • Voluntourism This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Traditional Circus! Circus • Rides, side-shows & big tent • Mobile • Increased competition from all other forms of entertainment • High costs (animals, travel) • Star performers • But, Animal Activists, This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Focus on Adults Combine Theatre, ballet & Acrobat Keep the clowns! Dramatic experience / theme, org. music This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Build a Better Mouse Trap? Good luck with that… This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Bricolage • Most innovation are improvements to existing products (including new uses) • Many others, Bricolage, are joining two products or services together to create something new • And, A few are true Blue Ocean events! This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Innovative vs Incremental Regional Hub Model This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Baking Soda How many uses can you think of? • Use as an antacid • Underarm deodorant • Keep cut flowers fresh longer (add teaspoon to vase) • Put out small fires on rugs, upholstery, clothing & wood • Put open container in fridge to absorb odors • Turn baking soda into modeling clay by adding 1 1/4 cups of water to 1 cup of cornstarch • Wipe your windshield with it to repel rain Other ideas - http://lifehackery.com/2008/07/22/home-4/ This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Key Takeaways Firms can take advantage of a number of competitive moves to shake up or otherwise get ahead in an everchanging business environment. • First mover advantage • Disruptive Innovation • Blue ocean thinking • Foothold • Bricolage This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves For teaching in two 90minute classes/wk, possible break point This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves 6.2 - Responding to Other’s Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Speed and Multipoint Competition This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Mutual Forbearance This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Fighting Brands This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Making Cooperative Moves • In addition to choosing their own firm’s strategic actions, executives also have to decide whether and how to respond to rival’s moves • Research indicates that three factors determine the likelihood that a firm will respond to a competitive move: awareness, motivation, & capability -> This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Razor Wars! This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves PS – Competitors… Just how do we know what they’re up to anyways? Corporate Intelligence • gathering data & information • Everything from dumpster diving to satellite monitoring • Media monitoring, press releases, comp. websites! This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves (the absence of) Speed Kills… (6.2.1) • In hyper-competitive world, firms must cope with rapidfire barrage of attacks from rivals • head-to-head advertising campaigns, price cuts, innovation & attempts to grab key customers • Speed is essential in responding (or competitor may capture market…) • Jack Welsh - success in most competitive rivalries “is less a function of grandiose predictions than it is a result of being able to respond rapidly to real changes as they occur. That’s why strategy has to be dynamic and anticipatory.” This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves So…We Meet Again (6.2.2) • With multipoint competition, firms faces same rival in multiple markets. Competitive moves in one market can affect other markets • Cigarette makers R. J. Reynolds (RJR) & Philip Morris compete in many countries • In early 1990s, RJR introduced lower-priced cigarette brands. Philip Morris cut USA prices to protect market share which started a price war, ultimately hurt both • 2nd, Philip Morris started competing in Eastern Europe where RJR had established a strong position. • Combination of moves forced RJR to protect its market share in USA & neglect Eastern Europe This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Mutual forbearance Mutual forbearance occurs when rivals do not act aggressively because each recognizes that the other can retaliate in multiple markets • In late 1990s, Southwest Airlines & United competed in some but not all markets • United announced plans to compete on other routes • Southwest threatened to retaliate in shared markets & United backed down • Recognizing & acting on potential forbearance can lead to better performance through firms not competing away their profits, while failure to do so can be costly This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Responding to Disruptive Innovation (6.2.3) • When rival introduces disruptive innovation, firm have 3 choices • 1st, executives may believe that innovation will not replace established offerings entirely & choose to focus on traditional business models, ignoring disruption • For example, traditional bookstores did initially consider Amazon to be a competitive threat until online sales began to grow • 2nd, firm counter challenge by attacking along a different dimension • For example, Apple responded to direct sales of cheap computers by Dell & Gateway by adding power and versatility • 3rd possibility is to simply match competitor’s move • Merrill Lynch, for example, confronted online trading by forming its own Internet-based unit. Here the firm risks cannibalizing its traditional business, but executives may find that their response attracts an entirely new segment of customers This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Price Wars & Fighting Brands (6.2.4) • Lowering prices, price wars, can be effective strategy in the short term • But, may create long-term problem of trying to return to original price level, with new consumer expectations • Creation of fighting brand is one strategy that can prevent/reduce this problem • Fighting brand is a lower-end lower-cost brand that a firm introduces to try to protect the firm’s market share without damaging the firm’s existing brands. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Fighting Brands – GM & Geo • By late 1980s, GM challenged by small, inexpensive Japanese cars • GM wanted to recapture lost sales, without harming existing brands, Chevrolet, Buick, & Cadillac, by putting their names on low-end cars • Solution – Geo brand • Interestingly, several Geo models produced in joint ventures – Metro & Tracker joint venture with Suzuki • By 1998, market revolved around higher-quality vehicles, Geo brand discontinued This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Fighting Brands - Airlines • Some fighting brands are rather short lived. • Two major airlines experienced similar futility. • In response to the growing success of discount airlines such as Southwest, AirTran, Jet Blue, and Frontier, both United Airlines and Delta Airlines created fighting brands. • United launched Ted in 2004, discontinued 2009. • Delta’s Song only lasted from 2003 to 2006. • Southwest’s acquisition of AirTran in 2011 created a large airline that may make United and Delta lament that they were not able to make their own discount brands successful. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Key Takeaways When threatened by the competitive actions of rivals, firms possess numerous ways to respond, depending on the severity of the threat including: • Multipoint competition • Mutual forbearance • Responses to disruptive innovation • Fighter brands • Speed of response This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves 6.3 Making Cooperative Moves This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Making Cooperative Moves • In addition to competitive moves, firms can benefit from cooperating with each other • Cooperative moves such as forming joint ventures and strategic alliances may allow firms to enjoy successes that might not otherwise be reached • Share (rather than duplicate) resources • Learn from each other’s strengths This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Four types of Cooperative Moves • Joint venture is a cooperative arrangement that involves two or more firms each contributing to the creation of a new entity • Strategic alliance is a cooperative arrangement between two or more organizations that does not involve the creation of a new entity • Co-location occurs when goods and services offered under different brands are located very close to each other • Co-opetition refers to a blending of competition and cooperation between firms This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Joint Ventures Cooperative arrangement that involves 2 or more firms each contributing to the creation of a new entity. • The partners share decision-making authority, control of the operation, & any profits This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Advantages & Disadvantages of Joint Ventures • Advantages • Enter related businesses or new geographic markets or gain new technological knowledge • Access to resources, specialized staff & technology • Sharing of risks with a venture partner • Disadvantages • Time and effort to build the relationship, challenges: • The objectives of the venture are not 100% clear and communicated to everyone involved. • There is an imbalance in levels of expertise, investment or assets brought into the venture by partners. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Strategic Alliances Cooperative arrangement between 2 or more orgs that does not involve creation of new entity This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Advantages & Disadvantages of Strategic Alliances • Advantages • Allowing each partner to concentrate on activities that best match their capabilities. • Learning from partners & developing competences that may be more widely exploited elsewhere. • Better use of resources & competencies to survive • Disadvantages • Potential to reduce future opportunities - unable to enter into agreements with partner’s competitor • Lack of commitment to the partnership • Risk of sharing too much knowledge and the partner company becoming a competitor This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Co-location • Similar goods are located close to each other • Fast food, hotels, auto-malls (cars) • The Mall This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves “Co-opetition” a blending of competition & cooperation between 2 firms This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves Dis/Advantages Co-location & Co-opetition • Co-location Advantage • A bigger set of customers may be attracted to a set of colocated firms than (sum of) individual locations • Co-location Disadvantage • co-location can be very expensive • Co-opetition Advantage • reduction of transaction costs & other savings and increasing expectation among customers • Co-opetition Disadvantage • competition and cooperation may not be always successful between two firms This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves In Conclusion, This chapter has considered various competitive and cooperative strategies commonly used by firms • When and how can firms respond to competitive actions taken by their rivals, and the industry in general • Various cooperate strategies to create mutual benefits (joint ventures, strategic alliances, etc.) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY). Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves