equity method
advertisement

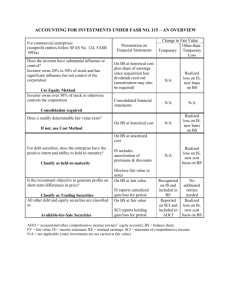
Module 7: Intercorporate Investments 1 Investment in Marketable Equity Securities - Overview Equity investments represent ownership of another company’s outstanding common stock. Marketable equity investments are actively traded on a public stock exchange. By owning shares of common stock, the investor “owns” a part of the company, represented by the percentage ownership. There are different accounting rules for: (1) less than 20 percent ownership (passive). (2) between 20 and 50 percent ownership (significant influence). (3) greater than 50 percent ownership (control). 2 (1) Less than 20 % ownership. If marketable securities, use the mark-to market method. Carries securities on balance sheet at market value. Revaluation at the end of each period based on new market price Unrealized gains (or losses) are recognized as the investment is valued up (or down). Treatment of the Unrealized G/L depends on classification of security: – (a) Trading securities. – (b) Available-for-sale securities. 3 (a) Trading Securities Trading securities held for the short term, with purpose of selling securities for profit. At purchase - record at cost to acquire. Activity during the year - record declaration of cash dividends, and recognize “Dividend Income” on the Income Statement: Dividends Receivable xx Dividend Income xx 4 (a) Trading Securities For securities on hand at the end of the accounting period - revalue to market value and record “Unrealized Gain/Loss” on Income Statement. When sold - recognize “Gain/Loss on Sale” on Income Statement for any balance since the last revaluation. 5 (b) Available-for-sale Securities Available-for-sale (AFS) securities may be held for the short term or for long term, depending on management’s intentions. At purchase - record at cost to acquire. Activity during the year - record declaration of cash dividends, and recognize “Dividend Income” on the Income Statement: Dividends Receivable xx Dividend Income xx 6 (b) Available-for-sale Securities For securities on hand at the end of the accounting period - revalue to market value and record “Unrealized Gain/Loss” on Balance Sheet (as part of Other Comprehensive Income in Stockholders’ Equity). When sold - recognize “Gain/Loss on Sale” on Income Statement for total difference between original cost and selling price. 7 (2) From 20% to 50% Investment Because investment represents significant influence of investor, we cannot account for investments the same way as Trading or AFS. Specifically, we cannot recognize “Dividend Income” as dividends are declared, because the investor can control dividend payout, and therefore control the creation of income. 8 (2) From 20% to 50% Investment The equity method increases the investment account and recognizes investor’s portion of income as investee earns it (as investee reports income to investor). The equity method decreases the investment account as investee declares dividends to the investor. Note: additional complications from equity method from cost exceeding fair value of investment (e.g., goodwill) are not addressed here for unconsolidated investments. 9 Basic Equity Method Journal Entries On investor’s books: 1. When investment purchased: L.T. Investment xx Cash, etc. xx 2. When dividends declared to investor: Dividends Receivable xx L.T. Investment xx 3. When income reported by investee to investor (from investee’s I/S): L.T. Investment xx Income from Investment xx 10 Illustration - Equity Method Company P purchases 30% of the outstanding common stock of Company S on January 2, 2009 for $400,000 cash. During 2009, Company S reported net income of $300,000 to its shareholders, and declared $100,000 dividends to its shareholders. Required: Prepare all journal entries necessary (on Company P’s books) to record this investment using the equity method of accounting. 11 Journal Entries on P’s Books: 1. Acquisition: 2. Dividends declared (100,000 x 30%) 3. Income reported (300,000 x 30%) 12 Effects of Equity method If the company had used the cost method and recognized dividend income, the amount of income would have been $30,000. Under the equity method, Company P recognized $90,000 income. The equity method often yields higher income, but the amount is less subject to manipulation. The IRS recognizes income as the cash is received (dividend income). This creates a differential basis between tax and financial accounting (more in Chapter 5, Part 2). 13 Other Cautions Regarding Equity Method The equity ignores market value for the investment account. Instead the investment account fluctuates as the investee’s equity fluctuates (income in excess of dividends). 20-50 percent is not always a valid indication of significant influence. It generates off-balance sheet financing - one line on the balance sheet may actually represent a percentage ownership in a number of assets and liabilities. (Consolidated investments show all the detail of assets and liabilities, where unconsolidated investments show only a net asset amount. 14 (3)Greater than 50% Investment If an investor has majority control, the investment is recorded using the equity method, and a parent/subsidiary relationship is established. At the end of the period, the financials of the parent and subsidiary must be combined, or consolidated, for external financial reporting. Goodwill is recognized as a separate asset in the consolidation. 15 Comprehensive Problem Prepare the following journal entries for Jackson Company for 2007. Assume there were no other investments prior to the following activities. Feb. 17 - Purchased 500 shares of Medical Company common stock for $20 per share (classified as trading securities): March 31 - Received a $1.20 per share dividend on Medical Company stock: 16 Comprehensive Problem April 1 - Purchased 30,000 of the 100,000 outstanding shares of Olde Company common stock at $10 per share. Classification of Investment? June 28 - Received a $1.00 share dividend on the Olde Company stock: 17 Comprehensive Problem Oct. 1 - Purchased 2,000 of Alpha Company common stock for $15 per share. These shares are classified as available-for-sale. Dec. 31 - Olde Company reported annual earnings of $80,000 to its investors: 18 Comprehensive Problem Dec. 31 AJEs - At the end of the year, the following market prices per share were reported: Medical Co. (trading) $25 per share Alpha Co. (AFS) $12 per share Olde Co. (equity) $11 per share AJE for Medical? AJE for Alpha? AJE for Olde? 19 Comprehensive Problem What total effect would the previous transactions have on the income statement for 2007? What effect would the previous transactions have on other comprehensive income for 2007? 20