respiratory lectures
advertisement

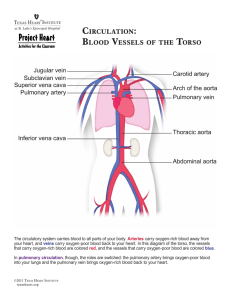
Pulmonary Circulation Characteristics • Low Resistance /Pressure • The specific structure(s) primarily responsible for the majority of control of resistance in the resting state is controversial. • Resistance more evenly distributed, but majority of resistance is normally on the arterial side (upstream) of the the capillaries. • Thin-walled arterial system (relatively little smooth muscle) • Anatomical considerations • Vessels are surrounded by bags of gas and flexible interstitial fluidfilled regions • No true arterioles?? • Alveolar and extra-alveolar vessels respond to conditions differently Influences on resistance • • Pulmonary Circulation Neural/Humoral: all the same players as in the periphery (but less effective) and a few with more specific actions • Serotonin: Arterial side vasoconstriction • Histamine:Venular side vaso(veno)constriction ***venous side can become dominant resistance Intravascular Pressure • recruitment (primary) • distension R 1/P Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (cmH2O/L•min-1) 300 Perfusion 200 Increasing Arterial Pressure 100 Increasing Venous Pressure 0 10 20 30 Arterial or Venous Pressure (cm H2O) 40 Influences on resistance • Pulmonary Circulation Neural/Humoral: all the same players as in the periphery (but less effective) and a few with more specific actions • • Serotonin: Aretrial side vasoconstriction • Histamine Venular side vaso(veno)constriction Intravascular Pressure R 1/P • recruitment (primary) • Distension ***Thus, cardiac output is considered to be the primary determinant of pulmonary vascular resistance • Lung volume (cmH2O/L•min-1) Vascular Resistance 120 100 80 60 50 100 150 Lung Volume (ml) 200 Influences on resistance Pulmonary Circulation • Lung volume • Low Volume: extra-alveolar vessels are smaller, capillaries more open • High Volume: extra-alveolar vessels are pulled open; capillaries become defromed by stretch (more oval; higher resistance) * Lung volume effects on extra-alveolar vessels is lost with positive pressure ventilation. • PO2: Local Control Decreased PAO2 causes vasoconstriction. Advantage: blood is shunted away from poorly ventilated alveoli. • Surrounding Pressure • Alveolar • Interstitial (<0) The Starling Resistor Concept Pulmonary Circulation Arterial (Pa) Pulmonary Circulation Zone 1 PA>Pa>Pv Alveolar (PA) Zone 2 Pa>PA>Pv Distance Venous (Pv) Zone 3 Pa>Pv>PA Blood Flow Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Circulation 60 mmHg 50 Pulmonary Arterial Catheter Tracing 40 30 20 10 0 Left Atrial Pressure Tracing Pulmonary Capillaries Left Atrium Pulmonary Vein