Scientific Method Notes
advertisement

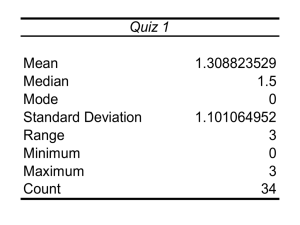
What is science? Agenda for Thursday Sept 4th 1. Nature of science/scientific method Resources Your User Name: kendricknovak Your Password: password You can log on at http://my.hrw.com Novak’s teacher website Questions What is science? Why do we do science? How do we do science? Nature of Science • Science – body of knowledge based on the study of nature – Biology, Physics, Chemistry, Earth Science • Process based on inquiry that seeks to develop explanations 7 things Science does • • • • • • • Relies on evidence Expands knowledge Challenges accepted theories Questions results Tests claims Peer Review Uses metric system The Scientific Method involves a series of steps that are used to investigate a natural occurrence. Problem/Question Observation/Research Formulate a Hypothesis Experiment Collect and Analyze Results Conclusion Communicate the Results Steps of the Scientific Method 1. Problem/Question: Develop a question or problem that can be solved through experimentation. Steps of the Scientific Method 2. Observation/Research: Make observations and research your topic of interest. Steps of the Scientific Method 3. Formulate a Hypothesis: Predict a possible answer to the problem or question. Example: If soil temperatures rise, then plant growth will increase. Steps of the Scientific Method 4. Experiment: Develop and follow a procedure. Include a detailed materials list. Experimental Design • Control group – used for comparison, baseline – may be a “no treatment” group – exposed to same conditions as experimental group, except for the variable being tested – All experiments should have a control group • Experimental Group – group that gets tested • 1 factor changes at a time • Many trials Experimental Design • Independent (manipulated) variable – a factor that’s intentionally varied by the experimenter – tested factor • Dependent (responding) variable – the factor that may change as a result of independent variable • depends on the outcome of the independent variable • What you want to measure • Constant – remains same in every test experiment Data • Information gathered during an experiment – Qualitative – observations – Quantitative – numbers Steps of the Scientific Method 5. Collect and Analyze Results: Modify the procedure if needed. Confirm the results by retesting. Include tables, graphs, and photographs. Steps of the Scientific Method 6. Conclusion: Include a statement that accepts or rejects the hypothesis. Make recommendations for further study and possible improvements to the procedure. Steps of the Scientific Method 7. Communicate the Results: Be prepared to present the project. Paper, presentations Think you can name all seven steps? Collect Formulate Communicate Observation/Research Problem/Question and Experiment Conclusion Analyze a Hypothesis the Results Results What is qualitative data? What is quantitative data? Agenda for Friday Sept 5th 1. Types of graphs 2. Outside lab What type of graph to use • • • • • Line graph. Pie Chart. Bar Graph. Area Graph. X-Y Plot. Leaf Lab Directions Part A 1. Make 10 observations of the tree/leaf/outside Part B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Each person acquire 1 leaf. Measure (in cm) from base of leaf to tip of leaf. Record you and your partners lengths in data table Compile class data Record class data Make graph Observations and inferences • Inference - using observations, prior knowledge/experiences, and details from context to make connections and come up with ideas. • Deduction – make a conclusion from something known or assumed Models • A representation of an object or event – Technology • Computer simulated model • Hands on exploration Hypotheses, Theories, Laws • hypothesis – a suggested explanation; • a proposal based on reason that predicts a possible correlation between multiple phenomena (incidents, events, observations, etc.) Laws • law – notes only that something happens; • happens consistently and across the universe • usually simply stated • frequently can be stated mathematically Example: • Newton’s 2nd Law: a = f/m Theories • theory – explains why something happens; • A framework about a class or group of phenomena • Note – Theories are never “proven” – they are confirmed by overwhelming data; all theories, like all ideas in science, are subject to correction Four areas of Bias • Representation of data • Funding of Research • Cultural Bias • Testing Representation of Data • Graphical/statistical 12.5 14 12 12 11.5 10 11 8 10.5 6 10 4 9.5 2 9 0 1 2 1 2 Funding of research • Who is funding the research? –Bp or Exxon oil • (Global climate change) –Tobacco industry (risks of smoking) –Audubon Society • (Location of pipeline / Arctic drilling) –Greenpeace Cultural Bias • Questionnaires or surveys: –Surveys written in English given to non-English language speakers Testing • Subjects used for testing –Animals / Humans for cosmetics or pharmaceuticals Scientific Method practice Mr. Novak is working on a science project. His task is to answer the question: "Does Plantgro (a commercial plant product) affect the speed of plant growth". Q: Describe how Mr. Novak would perform this experiment. Identify the control group, and the independent and dependent variables in your description. Agenda for Friday Dec 13th 1. Quiz 2. Read article Julie soaked six different kinds of seeds in water for 24 hours. Then she planted the seeds in soil at a depth of 1 cm. She used the same amount of water, light, and heat for each kind of seed to see how each seed would grow. What 4 factors are being controlled? What is the independent variable? Agenda for Monday Dec 16th 1. Alka Seltzer lab part 1 What is the difference between a theory and a law? Agenda for Tuesday Dec 17th 1. Alka seltzer lab part 2 Test Friday Period 5 Data 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ave Groups 1/2 A lot 51.4 56.5 55.6 56.15 69.2 67 Groups 3/4 200 mL 46.8 72 52 52 40 Groups 5/6 A little 48 34.6 28.7 26.1 20 20.7 61 1 2 3 4 5 6 Groups 7/8 Hot 18.9 19.5 23.8 24.6 25.8 24.9 Groups 9/10 Room Temp 52 50 56 65 57 90 Groups 11/12 Cold 75.3 63.3 80 86.2 94.9 122.5 Ave Period 3 Data 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ave Groups 1/2 A lot 50.9 42.4 48 55.2 50.9 59.8 Groups 3/4 200 mL 55 54.3 49.6 49.4 49.1 48 Groups 5/6 A little 46.6 42.2 43.8 50.3 46.4 63.7 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ave Groups 7/8 Hot 27 26 25 17.1 23.1 24.9 Groups 9/10 Room Temp 57.2 36.5 38.17 30.6 36.19 34.3 Groups 11/12 Cold 95 108 123 104 101 115 1 2 3 4 5 6 Groups 13/14 Stirred 45 38 53 47 36 33 Groups 15/16 Not stirred 43 81 100 94 81 72 Ave What is the difference between control and constants? Agenda for Wednesday Dec 18th 1. Scientific method practice 2. Design Bridge Test Friday List the 4 areas of bias. Agenda for Thursday Dec 19th 1. Build and Test Bridge Test Tomorrow **I will look at stamps*** TEST • Scientific method – Independent/dependent variable – Control group/experimental – Constants • Areas of bias • Observation/inferences • Qualitative/quantitative Engineering points • some lessons about design: – Build the simplest thing that could possibly work. “simple” DOES NOT equal“stupid”. – Go with the strengths of the material you’re given.