PowerPoint Presentation - Diabetes
advertisement

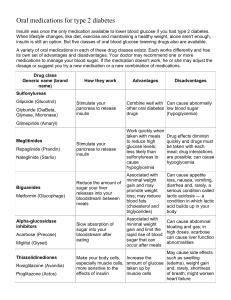
Woods Charter School Diabetic Training What you’ll learn from this presentation • What Senate Bill 911 requires • Diabetes--- Type 1 and Type 2 • How to recognize and treat: – High blood sugar (Hyperglycemia) – Low blood sugar (Hypoglycemia) LAW SENATE BILL 911 Diabetes is considered a disability; therefore… • Diabetes is covered under many federal and state mandates and laws • It is important to understand what diabetes is in order to: Comply with legal mandates and laws Facilitate care for students with diabetes NC Bill 911 We all need to work together Parents are required by law to • Provide pertinent information needed to develop a diabetes care plan for the student • Communicate with the school staff, including the bus drivers, about any changes or developments concerning the student’s diabetes care regimen The School is required by law to: • Provide diabetes training and education to school staff • Train two or more Diabetes Care Mangers (DCM’s) Responsibilities of the Diabetes Care Manager • • • • • Plan and participate in conferences with the student, parents, and school staff to develop an individualized diabetes care plan Assist student with diabetes care and maintenance Be accessible in case of an emergency Be up-to-date on diabetes information about individual student and diabetes in general Have open lines of communication with those involved with student, including: – Teachers – Substitute teaches – Parents – School nurse – Bus drivers – Other members of school staff that may be involved with care of student Basic Facts about Diabetes Mellitus • • • Diabetes is a major contributor to the development and risk of: – Cardiovascular disease – Heart Attacks – Stroke – Blindness – Kidney failure – Amputations Normal growth and development in children may be delayed or stunted There are two types of Diabetes, and both types have a problem with the balance between glucose (sugar) and insulin (anti-sugar) Insulin Versus Glucose • Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas • Insulin interacts with glucose to maintain the right balance of glucose in the body • Carbohydrates are metabolized into glucose • Glucose is required by the body’s cells for energy • Insulin and glucose have an inverse relationship – If one is up the other is down • The Goal is to find the right BALANCE between Glucose and Insulin Type 1 Diabetes • Commonly known as juvenile or childhood diabetes • The pancreas does not produce insulin • Type 1 Diabetics are INSULINDEPENDANT • They must have daily injections of insulin • Type 1 accounts for 10% of all cases of diabetes cases in the US – 1 in 400 children have Type 1 diabetes • Usually discovered during childhood or before the age of 30 Type 2 Diabetes • The pancreas does not produce enough insulin or does not use the insulin properly, they are INSULIN RESISTANT • More common in adults, but there is a rising epidemic of children developing Type 2 diabetes • Those most at risk: – Hispanics – African-Americans – Native Americans – A family history of diabetes – Obesity – Apple shaped bodies are more prone to diabetes than pear shaped bodies Managing Diabetes When diabetes is kept in control complications can be prevented and controlled Type 1 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes • Require daily insulin injections • Maintain a balance between • – Amount of insulin taken, – Food intake (especially carbohydrates), and – Exercise • The balance in measured by self monitoring blood sugar readings If caught early, Type 2 can usually be managed by lifestyle modifications including: – – – – Weight loss Healthier eating habits Oral medications Regular exercise Treatment of Diabetes • Self monitoring of glucose levels – Place a drop of blood on a test strip that is read by a blood glucose monitor – Important assessment for anyone with diabetes – Usually done during the school day • Insulin – Type 1 diabetes requires insulin by injection using one or a combination of • Insulin pump, • Syringe, or • Pen device – Type 2 (insulin only in later stages) • Exercise and diet control by carbohydrate counting are important for both types of diabetes Insulin • Most students require at least two injections a day unless they are using an insulin pump • There are many combinations of insulin used depending on activity level, time of day, etc. – Some work faster while some last longer • Insulin pumps are battery operated devices that automatically deliver insulin – Insulin pumps are the size of a pager Carbohydrate Counting • • Type 1 diabetics need to “Carb Count” to balance insulin with food and activity Type 2 diabetics need to “Carb Count” to record what they eat in an effort to eat a balanced diet and promote weight loss – The goal for Type 2 diabetics is to ward off the need for insulin injections with lifestyle modifications Regular Exercise • It is recommended for 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercise daily • Promotes weight loss • Helps increase self esteem Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Too much glucose (sugar) Not enough insulin (The feeling one gets when one eats too much) Not enough glucose (sugar) Too much insulin (The feeling one gets when they are very hungry) Hyperglycemia Too Much Glucose Too much sugar in the blood Happens when Eat too much food Don’t exercise enough Body trying to compensate for Illness or Physical and/or mental stress Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia Usually these are the first signs of developing diabetes Frequent urination Extreme hunger or thirst Extreme fatigue Dry itchy skin Blurred vision Frequent infections Slow healing wounds Teachers and school staff are key in identifying students with these symptoms Treating Hyperglycemia • Drink water or other calorie free/ caffeine free liquid to dilute the blood and sugar – This will also help hydrate the body • Seek immediate medical assistance if person unable to eat or drink If high blood sugar goes untreated for a long period of time Diabetic Ketoacidosis can result Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) • • • High blood sugar that goes untreated for a long period of time Signs and symptoms include: – Nausea – Vomiting – High levels of ketones in urine and blood Life threatening, so if you suspect DKA get immediate medical attention CAUTION: Students with insulin pumps use rapid acting insulin, so they may develop DKA very rapidly if pump is not working properly Hypoglycemia Not enough sugar • Also called “low” or “insulin reaction” • Usually symptoms occur when blood sugar below 70-80 on blood glucose reading • Usual causes: – – – – Too much insulin Increased activity Eating too few carbohydrates Too much time between snacks and meals Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia Early signs Hunger Shakiness Dizziness Sweating Fast heartbeat Drowsiness Irritable, sad, or angry Nervous Pale, clammy skin Important to recognize these symptoms before late signs develop Late Signs Feeling sleepy Being unusually stubborn Lack of coordination Tingling or numbness in tongue Personality change Passing out Seizure Recognizing Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) Frequent causes: • Late or missed meals • Exercise or activity • Change in school schedule (be on the lookout) – Fire drill – Assemblies – End of grade testing – Anything that may cause stress or alters normal patterns Treating Hypoglycemia Sometimes it is hard to tell the difference between high and low blood sugar, but remember YOU WILL NOT HURT ANYONE BY GIVING THEM FOOD If you suspect low blood sugar: 1. If possible, test their blood sugar with a glucose monitor 2. Give juice or another source of easily ingested carbohydrates 3. Wait 30 minutes and test blood sugar again, or reassess signs and symptoms • If blood sugar is still low, give more carbohydrates and start over with testing blood sugar Hypoglycemia Busters What to give someone with low blood sugar: 2-4 glucose tablets 4 oz of apple or orange juice 4-6 oz of regular soda 4-8 Life Savers 2 tablespoons of raisins 3-4 teaspoons of sugar or syrup 1 cup of low fat milk 2 teaspoons of cake gel/icing • Resist the urge to give them too much food or drink as this can cause them to have too much sugar in their blood resulting in hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) If early signs of hypoglycemia develop into late signs: • The student may have seizures or become unconscious • A medication called Glucagon must be given by a trained staff member • Try not to let this become an emergency, be on the lookout for early signs of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) Bus Drivers have Important Responsibilities • When a student is acting unusual, always assume they have low blood sugar and treat according to diabetes care plan • Students should be allowed to monitor, treat, and eat snacks while on the school bus. Thank you for completing this Power Point presentation Please complete the google test by August 31, 2010