1 - The KISMET simulation homepage
advertisement

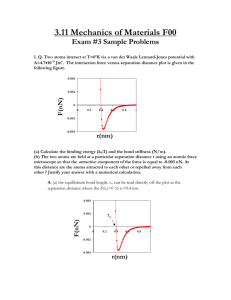
Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe Technik und Umwelt Introduction Theory Noninvasive Measurement of Elastic Properties of Living Tissue Methods Experiments Results Application Summary Dr. Heiko Maaß Institut für Angewandte Informatik Mechanical properties in medicine Introduction • Quantification of tissue mechanics Theory Methods • Quantitative evaluation of diagnostical results Experiments Results Application Summary • Monitoring of healing processes • Detection of hardenings or softenings (palpation) Application of mechanical tissue parameters Introduction • simulation of elastic tissue Theory Methods Experiments • accident research • product design Results Application Summary • biophysics The 'Karlsruhe Endoscopic Trainer' State of the art Introduction vibration 10-1000 Hz • Elastography Theory Methods • Sonoelastic Imaging Experiments Results Application • Strain Imaging deformation • Magnetic Resonance Elastography Summary measurement using Ultrasound or MR-tomography Phenomenological model Introduction Christoffel-equation: ( Cijkmn j nm c 2sound ik ) U k 0 Theory Methods general approach Experiments Results f ( ,csound ,vload , material ) Application Summary restricted to soft tissue (no bone or cartilage) Mechanical properties of biological tissue stress Introduction • non-linear Theory • inhomogeneous Methods • anisotrop Experiments • plastic Results • viscous Application • incompressible Summary • temperature dependent compression tension strain • dependent on metabolism, innervation and perfusion liver 1mm Acoustical properties of biological tissue velocity of sound Introduction 0 Theory Methods 1000 gases 3000 2000 soft tissue 4000 m/s bone, cartilage Experiments 0 e x ~ f a 25 20 15 10 5 0 4 b 3 2 c 1 0 0 5 10 15 sound frequency in MHz 20 resolution in mm Summary in cm Application damping penetration depth Results a: penetration depth b: lateral resolution c: axial resolution Non-invasive testing principle Introduction Theory Methods Experiments t Results Application Summary s Simulation of the propagation of ultrasound waves Introduction Theory Methods Experiments Results Application Summary Assembly used for the non-invasive measurement tomographical system graphic workstation Introduction Theory Methods position sensing system Experiments Results interaction Application Summary ultrasound device ultrasound head coupled with position sensor Performance of the sound speed measurement Introduction spatial orientation image overlay Theory Methods Experiments Results Application Summary liver Testing devices US Introduction Theory F Experiments Results Application Summary C = 1540 m/s F Pos Methods Introduction Theory Methods compressive stress in MPa Evaluation of the experimental series 0,06 Summary 1: origin tangential gradient 1 1 EU d 0,04 0,02 2: parametric regression 0 0 0,2 0,4 compressive strain d 0,6 2 EP d (1 P1 d P2 d2 ) 3: general regression compressive stress in MPa Application 2 0,08 Experiments Results regression analysis 3 0,1 Fat 0,1 0,08 0,06 0,04 0,02 0 Liver Muscle 3 a1 d a2 d2 a3 d3 Kidney Spleen linear 0 0,2 0,4 compressive strain d 0,6 correlation analysis Correlation analysis results Theory Methods Experiments Results Application Summary origin tangent EU in MPa Introduction 0,5 0,45 0,4 0,35 0,3 0,25 0,2 0,15 0,1 0,05 0 1500 parameter EP in MPa liver tissue 1550 1600 0,5 0,45 0,4 0,35 0,3 0,25 0,2 0,15 0,1 0,05 0 1500 1550 1600 sound speed in m/s sound speed in m/s origin tangent parametric regression 1 = EU d series intra vitam 2 = 1,2 EP d (1 _ 3d + 17d2) series post mortem Ranges of sound speed and origin gradient origin gradient in MPa (compression) Introduction Theory Methods Experiments Results Application Summary 0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 fat (soft) fat (harder) liver spleen heart muscle kidney post mortem fat liver spleen kidney intra vitam 1400 1420 1440 1460 1480 1500 1520 1540 1560 1580 1600 sound speed in m/s Simulation of soft biological tissue tension Introduction E t ( 1 a2 t a3 t 2 a4 t 3 ) Theory F(s) stress Methods Experiments Results -1,0 0 Application Summary -0,5 compression 0,5 1,0 strain t • Development and employment of testing devices • Measurement of tissue parameters intra vitam Introduction • Comparison to tisssue properties post mortem • Simulation of the propagation of sound Theory Methods • Non-invasive differenciation of fat is possible Experiments • Curve shapes are specific to the tissue kind Results Application • Curves are independent on stress velocity • Phenomenological model is not quantifiable Summary • Usage of curve approximations in complex simulations • Development of new non-invasive methods of testing Introduction Theory Methods Experiments Results Application Summary Thank you for paying attention