Week 4, Lesson 3 - Plant Adaptations (continued).
advertisement

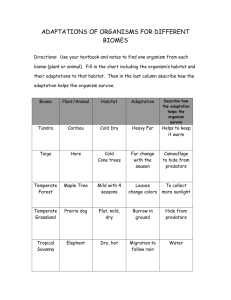
Plants Week 4 Directions 1.Prepare your desk for science. • Leave your plant quiz (signed) on your desk. 2.Use voice level 2 (conversation) to discuss this question: What is an adaptation? What would happen if plants didn’t adapt? Why is this important to the survival of a plant species? If you have OLD homework or quizzes to turn in, please put them on the desk up front. Targets & Warm Up Targets: Students will discover how plants adapt to various environments. Warm Up: What biomes did we discuss yesterday? What plant adaptations did your group discover as you read yesterday? Adaptation A change that living things go through to fit better with their environment. Biome A biome is a large geographical area of distinctive plant and animal groups, which are adapted to that particular environment. Each biome consists of many ecosystems whose communities have adapted to the small differences in climate and the environment inside the biome. Biomes Plant Text Vocabulary Dense • Very thick; so thick that it is difficult or impossible to see through Vegetation • The plants of an area or a region; plant life Canopy • The upper (top) layer of the forest Moisture • Presence of a liquid, especially water, often in small amounts Your Task 1. There will be 4 groups of 5 to 6 people. 2. Each group will rotate from station to station. 3. The group will read (out loud) the text about how plants adapt to a specific biome. 4. After reading, each group will discuss the adaptations that they read about. Table of Contents Date Title Plant Adaptations Page 9 Once you are finished with the Table of Contents, go to page 9 and add the title and date to the top of the page. Desert Plants • • • • Capture water with special roots and leaves Use leaves to get water Store water in roots, leaves, stems, or fruits Change size and texture of leaves to hold on to moisture Desert Plants Tundra Plants • Grow close together and to the ground • Able to grow under snow • Carry out photosynthesis in cold temperatures • Produce flowers quickly • Have small leaves to hold on to moisture Tundra Plants moss lichen Tropical Rainforest Plants • Some plants below the canopy can grow in the shade • Some plants below the canopy work to reach the sunlight • Example: Strangler fig Tropical Rainforest Plants: Strangler Fig • Seeds are deposited on branches of host trees • Seeds sprout and send a long root to the ground • Root gets bigger, branches and leaves grow up and create a canopy that blocks sunlight from the host tree • More roots are sent out and wrap around the host to strangle and kill it! Tropical Rainforest Plants: Strangler Fig Deciduous Forest • When it gets colder, the tree closes off the area between the stem and the tree to prevent damage to the leaves. • The leaves fall off and then grow back when it is warm. Deciduous Trees Abscission: the process by which a plant drops one or more of its parts, such as a leaf, fruit, flower, or seed Plant Adaptation Questions 1. Why do plants need to adapt? What causes a plant’s adaptation? 1. How are plant adaptions in the tundra and desert similar? How are they different? THINK QUESTION: Natural selection says, “Only the fittest survive.” – What does this mean? How does this relate to plant adaptations? Targets (Revisited) Targets: Students will discover how plants adapt to various environments. Plants Mangrove tree Barrel cactus Water lily Orchid Bromeliad Aloe plant Cattail Birch tree Pitcher plant Venus flytrap Fir tree Palm tree Ocotillo Bengal bamboo Bougainvillea Arctic moss Labrador tea White oak tree Homework Subject Science Homework None Due Date None