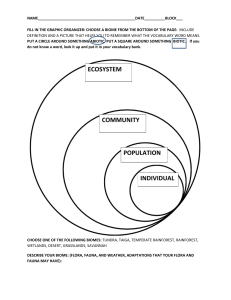
RESEARCH CHARTS Complete the charts below to help us to produce comparisons of animal characteristics common in each biome. (We will draw our conclusions based upon evidence in our charts back at school.) ANIMAL GROUP I: REPTILES Animal Biome Body Color Covering Panther Chameleon (Rainforest) Aldabra Tortoise (Near primates) Emerald Tree Boa (Rainforest) African Rock Python (Elephant Crossing) Other Interesting Fact/Adaptation ANIMAL GROUP II: BIRDS Animal African Penguin (Northern Trek) Scarlet Macaw (Rainforest) Stellars Sea Eagle (Near Waterfowl Lake) Ostrich (Savannah) Biome Body Color Covering Other Interesting Fact/Adaptation ANIMAL GROUP III: MAMMALS Animal Wolf (Northern Trek) Fennec Fox (Savannah) African Lion (Savanna) Polar Bear (Northern Trek) Harbor Seal (Northern Trek) Biome Body Color Covering Other Interesting Fact/Adaptation ANIMAL GROUP IV: HOOFED MAMMALS Animal Grants Zebra (Savanna) Bactrian Camel (Northern Trek) Reindeer (Northern Trek) Black Rhino (Savannah) Biome Body Color Covering Other Interesting Fact/Adaptation ANIMAL GROUP V: PRIMATES Animal Biome Body Color Covering Interesting Facts/Adaptation Orangutan (Rainforest) Western Lowland Gorilla (primate bldg.) Mongoose Lemur (primate bldg.) Tamarin (Golden Lion) (Rainforest) Questions: Region: Northern Trek 1. Find the Grizzly Bear. This bear is a sub species of the Brown bear, and lives mostly in Alaska and Canada where winters can be very harsh. Which of these adaptations is not especially important when surviving in winter? A. hibernating C. big nose B. long, dense, fur D. fat layers 2. Think of how the Grizzly bear may use its claws. These bears are omnivores, eating a variety of plants and other animals like fish and small mammals. What purpose would their claws serve? A. swimming C. hunting prey B. digging D. Both B and C 3. Find the Bactrian Camel. What special physical adaptations do they have to help them be successful in the desert?? 4. Why did eagles almost disappear? Region: Rainforest 1. Humans are classified as apes, and are part of the primate order (group). Other closely related ape members include chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. Find and observe the orangutans. Describe at least 4 similarities we share in common in the space below. Include both physical and behavioral adaptations. 2. Take a close look at the beak of the roseate spoonbill. It eats small animals like minnows. How is the shape of its beak a useful adaptation for feeding??? 3. River otters are known for living in aquatic habitats. What are 2 adaptations allow them to do this? 4. What is a useful adaptation that rainforest animals use to escape torrential storms and seasonal flooding? 5. How much of the world’s oxygen does the rainforest provide through photosynthesis among its many plants. ________________ Region: Near Wildfowl Lake….Birds of Prey zone 1. Many bird species that are scavengers have no feathers on their heads. What would a likely reason for this adaptation be?? A. it keeps their bodies cool B. their skin is more attractive than feathers C. Easier to clean after feasting on a dead animal. Region: Savanna and Elephant Crossing 1. What animal will roll in the mud to protect itself from the hot sun? ____________________________________ 2. Describe an interesting adaptation of the African elephant. 3. How are the stripes of a zebra an advantage for its survival?