Herbs & Spices - Stewburner Storeroom
advertisement

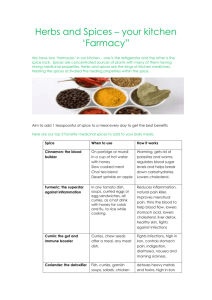
Food Prep: Herbs & Spices - CS1(SS) Foster Learning Objectives Identify fresh herbs and spices visually Discuss the characteristics and origins of herbs/spices Discuss the different market forms Explain the different uses of herbs/spices Herbs Fresh herbs are always preferable because their flavor profiles are more complex and complete Usually, the Navy stocks dried herbs for shelf life (endurance) and to prevent waste (spoilage) Dried herbs are dehydrated, and this concentrates their flavor (consider in usage) Rule of thumb: 1 tsp of dry = 3 tsp of fresh Dried herbs can be added at anytime during cooking depending on desired result (and product) Fresh herbs take very little time to release flavor, should be added at the end of cooking process Dried herbs have a 6 month shelf life when in airtight containers Herb Identification Oregano Market Forms: Fresh or Dried, Leaf or Ground Characteristics: Pungent herb, similar to marjoram but stronger. Native to Italy and Mexico, grown domestically (U.S.). Uses: Italian & Mexican food, tomato sauces, soups sauces, stews meats salads and marinades. Mint Market Forms: Herb leaf, fresh or dried. Characteristics: Aromatic herb with cool flavor. Spearmint and peppermint are most common. Uses: Lamb, fruits, tea, fruit beverages, peas, carrots, potatoes, jellies, soups, sauces. Herb Identification Basil Market Forms: Herb Leaf, Fresh or Dried Characteristics: Aromatic green leaf, member of mint family. Can be grown fresh in warm weather. Uses: Tomato dishes, pesto, egg dishes, salads, marinades, fish, compound butters Tarragon Market Forms: Fresh, dried or pickled leaf. Characteristics: Delicate green herb that is both mint & licorice-like. Small oblong leaf. Uses: Bearnaise sauce, tarragon vinegar, chicken fish, salads, dressings, eggs Herb Identification Thyme Market Forms: Fresh or dried herb leaf, crushed or ground. Characteristics: Tiny brownish green leaf, very aromatic. Uses: Soups, chowders, stocks, sauces, meats, poultry, salads, dressings. Bay Leaves Market Forms: Whole leaf herb. Characteristics: Stiff, dark green, oblong leaf. Pungent aroma. Reminiscent of sassafras. Comes from Laurel tree. Uses: Stocks, sauces, soups, stews, braised meats. Herb Identification Rosemary Market Forms: Whole leaf herb, fresh or dried. Characteristics: Light green leaf resembling pine needles, very aromatic. Once grown, very healthy and strong even in cold weather. Uses: Lamb, fish, beef, sauces, soups, stews, salads, marinades. Parsley Market Forms: Fresh leaf herb in bunches, dried. Characteristics: Green leaf, curly or flat with delicate sweet flavor. Excellent source of Vitamin C. Uses: Garnish, fried, stews, sauces, salads, vegetables, potatoes. Herb Identification Cilantro Market Forms: Leaf herb, dried or fresh. Characteristics: Light green aromatic leaf. Shape of flat parsley but much more pungent flavor. Leaf from coriander seed. Uses: Salads, salsa, sauces, soups, eggs, dressings. Sage Market Forms: Whole, rubbed or ground herb leaf, fresh or dried. Characteristics: Pungent grey green herb with fuzzy leaves, oblong shape. Uses: Stuffings, meat, poultry, soups, stews, salads, fish. Spices Spices are plant derivatives (bark, seeds, flowers, fruit, etc.) Whole spices have a longer shelf life than ground Whole spices have a 3 – 6 month shelf life Ground spices incorporate uniformly and release flavor faster Ground spices have a shelf life of 3 months maximum. Ground spices are best added at the end of the cooking process Spice Identification Black Pepper Market Forms: Whole “peppercorns” – black, white or green, cracked, medium or fine ground. Characteristics: Small hard berry. Black: pungent, aromatic. White: milder. Adds sharp tang to all foods. Green: packed in mild brine. Uses: Widely used with just about all foods including green in sweets. Red Pepper Flakes Market Forms: Dried flakes. Characteristics: Hot, spicy, powerful. Uses: Mexican, Cajun, Ethnic foods, salsas, gumbos, etc. Spice Identification Cayenne Pepper Market Forms: Ground spice, seed Characteristics: Ground hot red pepper, very powerful. native of French Guiana. Uses: In small amounts: soups, sauces, fish, eggs Chili Powder Market Forms: Ground spice, blend Characteristics: Blend of ground cumin, chili pepper, oregano, allspice. Can be mild or hot. Uses: chili, stews, sauces, ground meats. Spice Identification Onion Powder Market Forms: dried powder Characteristics: mild, flavorful Uses: soups, sauces, stews Garlic Market Forms: Fresh, whole bulb. Dried: granulated, powder or mixed with salt. Characteristics: Strong, aromatic, member of the onion family. Uses: Used widely in cooking. Spice Identification Ginger Market Forms: Spice, fresh whole, dried powder, candied, crystallized or pickled. Characteristics: Light brown knobby root from tropical plant. Uses: Baked goods, desserts, fruits, curry dishes, pickling, chutney, Chinese, Caribbean & Japanese cuisine. Cinnamon Market Forms: Stick or ground spice. Characteristics: Aromatic bark from cinnamon or cassia tree. Reddish brown color. Native of East India. Uses: Preserves, stewed fruits, breads, pastries, desserts, ham, hot beverages. Spice Identification Nutmeg Market Forms: Whole or ground spice. Characteristics: Sweet, aromatic kernel of nutmeg fruit. Grown in Netherlands and East/West Indies. Uses: Baked goods, pies, cream sauces, soups, chicken, veal, vegetables, desserts, breads. Allspice Market Forms: Whole or ground spice. Characteristics: Small brown berry. Flavor resembles a combination of cinnamon, clove & nutmeg. Native to W. India. Uses: Sausages, braised meats, poached fish, cooked fruits, puddings, pies, relishes. Spice Identification Cumin Market Forms: Whole or ground seed, spice. Characteristics: Small seed resembling caraway, but lighter in color. Grown in Mexico and Syria. Uses: Chili and curry powder blends. Sausage, meats, salsa, egg & cheese dishes. Curry Powder Market Forms: Ground blend, spice. Characteristics: Mixture of approx. 20 spices, peppery, yellow in color. Includes tumeric, cumin, coriander, ginger, clove, cinnamon. Can vary from mild to very hot. Uses: Curry dishes, vegetables, soups, sauces, fish, meat, rice. Spice Identification Paprika Market Forms: Ground spice. Characteristics: Ground from dried sweet red pepper. Spanish: bright & mild. Hungarian: darker, more pungent. Uses: Asset to bland pale food. Fish, seafood, meats, salads, sauces, dressings, garnish. Cloves Market Forms: Whole or ground spice. Characteristics: Dried flower bud of tropical clove tree, pungent, sweet in flavor. Native of Indonesia. Uses: Whole: Marinades, stocks, sauces, braised meats, hams & pickling. Ground: pastries, fruits and cakes. Questions? Review What is the rule for dry to fresh herb usage? - 1 tsp. dry = 3 tsp. fresh What type if preferable? - Always fresh, if practical When should you add dry herbs to food? - Anytime, according to the recipe and desired end result Fresh? - The end, flavor disperses very rapidly Review - What spice is a dried flower bud native of Indonesia? Cloves. Small seed resembling caraway native of Mexico & Syria? Cumin. Small brown berry native of W. India? Allspice Review Light brown bulbous root of a tropical plant? - Ginger Aromatic green leaf that is grown in warm weather? - Basil Pungent, grey/green herb with fuzzy leaves? - Sage Stiff, oblong dry leaf of a Laurel tree? - Bay leaves Questions?