OPTICAL DETECTORS AND FIBER OPTIC RECEIVERS.
advertisement

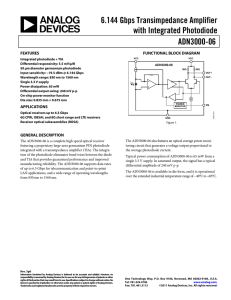
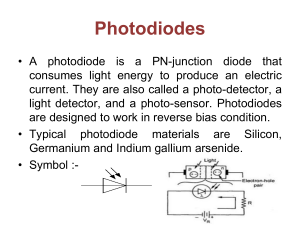
OPTICAL DETECTORS IN FIBER OPTIC RECEIVERS. Presenter: Julius Munyantwali. Introduction. A fiber optic receiver is an electro-optic device that accepts optical signals from an optical fiber and converts them into electrical signals. Consists typically of : -Optical detector -Low-noise amplifier -Other circuitry. Block diagram of fiber optic receiver. Optical Detectors. These are transducers that convert optical signals into electrical signals. Transducers are devices that convert input energy of one form into output energy of another. An optical detector does so by generating an electrical current proportional to the intensity of the incident optical light. Optical Detector Requirements. Compatible in size to low-pass optical fibers for efficient coupling and packaging. High sensitivity at the operating wavelength of the source. Low noise contribution. Maintain stable operation in changing environmental conditions. Semiconductor Photodiodes. Generate current when they absorb photons. The amount of current depends on ; -Wavelength of the light and responsivity of the photodiode -Size of the photodiode active area relative to the fiber core size -Alignment of the fiber and photodiode. Optical detector materials. Si,GaAs, GaAlAs – 850nm Ge, InP, InGaAs -1300nm and 1550nm. Materials determine the responsivity of the detector which is the ratio of the output photocurrent to the incident optical power. It’s a function of the wavelength and efficiency of the device. PIN Photodiode. Semiconductor positive-negative structure with an intrinsic region sandwiched between the other two regions. Normally operated by applying a reverse-bias voltage. Dark current can also be produced which is a leakage current that flows when a reverse bias is applied without incident light. PIN Photodiode. Response time factors. Thickness of the active area. -Related to the amount of time required for the electrons generated to flow out of the detector active area. Detector RC time constant. -Depends on the capacitance of the photodiode and the resistance of the load. Schematic of a Photodiode. Advantage of PIN photodiodes. The output electrical current is linearly proportional to the input optical power making it a highly linear device. Low bias voltage(<4v). Low noise Low dark current High-speed response AVALANCHE Photodiodes. An APD internally amplifies the photocurrent by an avalanche process when a large reverse-bias voltage is applied across the active region. The gain of the APD can be changed by changing the reverse-bias voltage. AVALANCHE Photodiode. Light Emitters As Detectors. LEDs and lasers can also be used as light detectors making them half-duplex fiber optic communication devices. They can be used alternately as light emitters and detectors allowing transmission of information in either direction over the fiber. In order for the LED to operate as a full-duplex, the temperatures at both ends should be carefully chosen. Ping-Pong(Full-Duplex) LED. Questions And Comments.