ppt file for this lecture (click to file)
advertisement
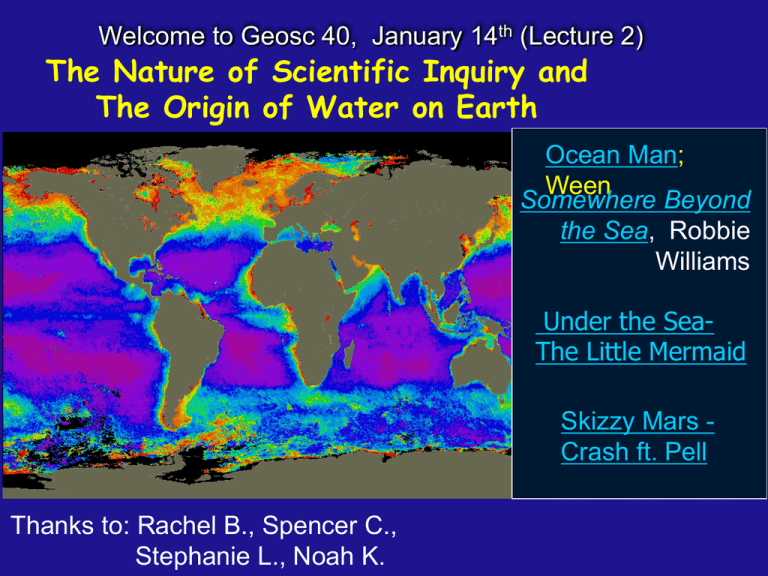
Welcome to Geosc 40, January 14th (Lecture 2) The Nature of Scientific Inquiry and The Origin of Water on Earth Ocean Man; Ween Somewhere Beyond the Sea, Robbie Williams Under the SeaThe Little Mermaid Skizzy Mars Crash ft. Pell Thanks to: Rachel B., Spencer C., Stephanie L., Noah K. Geosciences 40: The Sea Around Us Course Web Page: www3.geosc.psu.edu/geosc040 Geosciences 40: The Sea Around Us Course Web Page: www3.geosc.psu.edu/geosc040 How is the class going to work? What should I study? The Nature of Scientific Inquiry and The Origin of Water on Earth Can the North Brazil Current Help Us Understand Atlantic Water Flow? Why the Sea is Salty Seawater is essentially an NaCl solution Average seawater salinity is 35 ppt (35 g/kg), but it varies from place to place 30 ppt Surface water salinity 37 ppt Water reservoirs The oceans contain nearly all of Earth's surface water (>97%) • lakes & rivers = 0.01% of available water • ice (glaciers and ice caps) & groundwater = 2.5% • atmosphere (water vapor) = <0.001% Ah, but the oceans contain only a small portion of Earth’s total water -most of Earth’s water is in its interior! Origin of Water in the Oceans How Science Gets Done And How Concepts Evolve The Scientific Method is Based on Empirical Observations, Skepticism and Repeated Measurements Belief-Based vs. Empirical • Truth is based on authority (of texts, selfproclaimed or selected leaders, legends, etc.) and is generally inviolable. • Truth is based on application of a standardized method and repeated tests to confirm a result, and is subject to change as new methods are developed and new results discovered. In other words, theories evolve… Belief-based vs. empirical approaches to knowledge Belief system The Source Of Authority? Definitions are simply decrees. They are not based on Science The Theory of Evolution is Based on The Scientific Method A theory based on scientific principles and rigorously tested by skeptical scientists for over a century and a half! Marone’s Theory of Learning and Grades • Come to class • Read the materials on the course web site • Be curious • Ask questions you’ll get an A in this course and live happily ever after… Empirical* system: Parameter “Y” Measurements Observations Hypotheses Theories Parameter “X” Scientific Method “Correlations” *empirical means “experiential” or “searching for interrelationships” Scientific method: definitions FACT : observation repeatedly confirmed HYPOTHESIS: testable statement about the natural world (a working model) THEORY: a set of verified hypotheses that explain how things work. A theory explains most or perhaps all of the observations, but ‘the jury is still out,’ for one reason or another. LAW: generalization of how some aspect of natural world behaves under stated circumstances; repeatedly-verified explanation of some aspect of the natural world 1. Initial observation of materials/phenomena/behavior THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 2. Development of questions/establishment of constraints 3. Formulation of models to explain your observations MULTIPLE WORKING HYPOTHESES 4. Testing of hypotheses through observation/experiment; COLLECTION OF DATA (MEASUREMENTS) 5. Analysis of data, evaluation/interpretation of results (ELIMINATE HYPOTHESES) 6. Formulate conclusions. Scientific Method Hypotheses and Theories must be falsifiable. That is, we can never “prove” a hypothesis, we can only disprove it We must accept some uncertainty until substantial observations and tests have been conducted. Some problems do not yield easily and answers are complex (for example--the origin of water on Earth; the carbon cycle; global climate, earthquake prediction Chat with at least 3 people around you. Can you set up a time to go over course materials, study for exams or otherwise talk about the materials in this course? Does the person on your right live A) On campus B) Off campus The Habitable Zone Where did Earth’s Water Come From? And Why is it Still Here? Seawater Origin and Evolution Where’s Pluto? Earth: The Third Stone from the Sun (Jimi is not dead!) • The chemical evolution of Earth’s ocean and atmosphere is intimately related to the processes that formed the Earth--the water planet. • Why does Earth have liquid water whereas the other planets do not at present? Or do they? The “Goldilocks Principle” http://www3.geosc.psu.edu/geosc040/40.lecture_files/ Planetary mass Distance from sun SURFACE TEMPERATURE ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION Boiling breaks chem bonds (°C) 100° High gravity retains light volatile gases = thick atmosphere Low gravity loses all atmospheric gases 0° LIFE ZONE * Freezing stops all biochem rxns INTERNAL COMPOSITION Because of a generous portion of radioactive elements the Earth retains a liquid outer core (within Earth’s interior) of iron and nickel that provides a mechanism for generating a protective magnetic field that shields the surface from harmful solar radiation. WATER on MARS 4 BILLION YEARS AGO? 3000 km The Grand Canyon of Mars - Valles Marineris Water-formed gullies in crater Photos and mosaic JPL/ NASA NASA “Global Surveyor” mission map of ancient oceans on Mars (orbiter, 1997) The Origin of Water on Earth • Was it always here? • What about in the earliest stages of Earth’s history • Have we always had the same amount of water? • Have the oceans always been the same size? • Has ocean water always tasted the same? • There’s a lot of water out there…. • Where did it come from? Two Major Hypotheses Earth Belch –degassing of volatile chemical species (water, C02, etc. Substances easily driven off by heat Volcanic Eruptions, Hot Springs, Seafloor Vents E.T ? Comets and meteorites. Impacts big and small Seawater Origin and Evolution Is it a planet ?! ET? Comet, meteorite impact So, Where Did the Oceans Come From? So, Where Did the Oceans Come From? So, Where Did the Oceans Come From? So, Where Did the Oceans Come From? So, Where Did the Oceans Come From? Summary: Origin of Water on Earth and in the Oceans Two Major Hypotheses Earth Belch –degassing of volatile chemical species (water, C02, etc. Substances easily driven off by heat Volcanic Eruptions, Hot Springs, Seafloor Vents E.T ? Comets and meteorites. Impacts big and small The “Goldilocks Principle” http://www3.geosc.psu.edu/geosc040/40.lecture_files/ Planetary mass Distance from sun SURFACE TEMPERATURE ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION Boiling breaks chem bonds (°C) 100° High gravity retains light volatile gases = thick atmosphere Low gravity loses all atmospheric gases 0° LIFE ZONE * Freezing stops all biochem rxns INTERNAL COMPOSITION Because of a generous portion of radioactive elements the Earth retains a liquid outer core (within Earth’s interior) of iron and nickel that provides a mechanism for generating a protective magnetic field that shields the surface from harmful solar radiation. But….. Remember, Theories Evolve… NASA’s LCROSS mission in 2010 discovered “significant water on the moon.” •And, according to a paper just published in Nature Geoscience, Moon Water Differs from Earth Water •Moon rocks show that lunar water has more heavy hydrogen than does terrestrial water, indicating a cometary origin. •Could some of Earth’s water have “Houston, we have a problem” originated from comet bombardment?