Thinking Tools Progress Stages Stage Description (what you need
advertisement

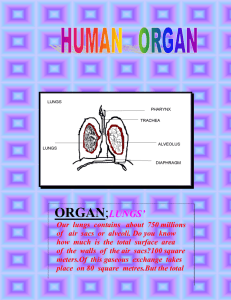
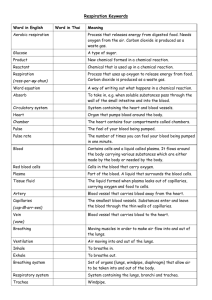
Name: Form: Science Teacher: Year 8 Thinking Tool . Answer ONE of the questions at the top of the thinking tool. Choose the question that matches what you are studying in lessons. Use the different stages to help you write a final paragraph to answer the question. There are progress stages included to help you understand how to reach your target and what you need to do to progress beyond this. Use the attached keywords to help you and use the link below to the BBC Bitesize website to research your answer if you need more support (you can use other websites if you want!) Also don’t forget to ask your class teacher for help if you feel you are struggling. http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/ Thinking Tool Question A (Casualty Topic): Explain how your body gets energy to run a race. or Question B (X-Factor Topic): Explain how the sound of a drum gets to your ears. Key Words: List the key words you think you will need to use to answer the question. Diagram: the question. sketch a diagram to show what happens and use your keywords to help answer Sequence: Put your ideas into a sequence of sentences that will help answer the question as a final paragraph. Paragraph Write your answer to the question as fully as you can. (HINT - Use cause & effect connectives e.g. consequently, because, whenever, depending upon, eventually, since/until etc.) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (Continue on another sheet of paper if you need more space!) FEEDBACK: WWW:___________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ EBI:_____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Thinking Tools Progress Stages Stage Description (what you need to do to get this stage) Recall 3 You have……….. Written a list of key words. Drawn and labelled a basic diagram Identified the basic scientific content. …to help answer the questions. 4 Recall and Vocabulary. You have……….. Written a list of key scientific words, Drawn a basic labelled diagram Described the scientific content. Structured some basic sentences. …..to help answer the question. 5 Recall, Vocabulary and Key Ideas. You have……….. Written a list of key scientific words, Drawn and labelled a diagram. Explained the scientific content. Structured some sentences using key ideas and scientific words. Linked the sentences to form a basic paragraph. …..to help answer the question. 6 Recall, Vocabulary, Key Ideas and Explanation. You have……….. Written a list of key scientific words, Drawn and labelled a detailed diagram. Analysed the scientific content. Written structured sentences using key ideas and scientific words. Linked the sentences with connectives to form a paragraph. …..to help answer the question. 7 Recall, Vocabulary, Key Ideas and Explanation. You have……….. Written a list of key scientific words, Drawn and labelled a detailed diagram. Linked the scientific content. Written structured sentences using key ideas and scientific words. Linked the sentences with connectives to form a detailed paragraph referencing your key words and scientific knowledge. …..to help answer the question. KEYWORDS FOR CASUALTY TOPIC (Question A)! Word Pronunciation absorb aerobic respiration To take in, e.g. when soluble substances pass through the wall of the small intestine and into the blood. ress-per-ay-shun air sacs alveolus Meaning Process that uses up oxygen to release energy from food. Carbon dioxide is produced as a waste gas. Groups of alveoli in the lungs where oxygen comes out of the air and goes into the blood. Carbon dioxide is also transferred from the blood to the air in these. al-vee-O-lus Small, round pocket that is grouped with other alveoli to form air sacs in the lungs. Plural = alveoli. artery Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. blood Contains cells and a liquid called plasma. It flows around the body carrying various substances which are either made by the body or needed by the body. breathing Moving muscles in order to make air flow into and out of the lungs. breathing system Set of organs (lungs, windpipe, diaphragm) that allow air to be taken into and out of the body. bronchus Tube in the lungs that connects the windpipe to the air sacs. Plural = bronchi. capillaries cap-ill-arr-ees chamber The heart contains four compartments called chambers. cilated epithelial cell sil-lee-ay-ted cilia sil-lee-a digestive system Cells with cilia that are found in the lungs. eppy-theel-ee-al circulatory system diffusion The smallest blood vessels. Substances enter and leave the blood through the thin walls of capillaries. Small hairs on the surface of some cells. System containing the heart and blood vessels. diff-you-shun The natural movement of particles from a place where there are a lot of them to a place where there are fewer of them. The group of organs that carry out digestion. exhale To breathe out. exhaled air Air that is breathed out. gas exchange Taking oxygen into the blood and getting rid of carbon dioxide into the lungs. Happens in the air sacs in the lungs. gill A series of flaps of tissue with a good blood supply just behind the head of an organism which is used to take oxygen out of water. Fish have gills. glucose A type of sugar. heart Organ that pumps blood around the body. Hydrogen carbonate An indicator that can be used to show how much carbon dioxide there is in indicator something. inhale To breathe in. inhaled air Air that is breathed in. mucus Slimy substance which traps dirt and microbes and is moved out of the lungs by cilia. plasma Part of the blood. A liquid that surrounds the blood cells. product New chemical formed in a chemical reaction. pulse The feel of your blood being pumped. pulse rate The number of times you can feel your blood being pumped in one minute. reactant Chemical that is used up in a chemical reaction. red blood cells Cells in the blood that carry oxygen. respiration ress-per-ay-shun Process that uses up oxygen to release energy from food. Carbon dioxide is produced as a waste gas. respiratory system System containing the lungs, bronchi and trachea. tissue fluid The liquid formed when plasma leaks out of capillaries, carrying oxygen and food to cells. trachea Windpipe. vein vane Blood vessel that carries blood to the heart. ventilation Air moving into and out of the lungs. word equation A way of writing out what happens in a chemical reaction. KEYWORDS FOR X-FACTOR TOPIC (Question B)! Word Pronunciation amplitude Meaning Half the height of a wave. cochlea cok-lee-a The part of the ear that changes vibrations into electrical impulses. decibel (dB) dess-i-bell Unit for measuring the loudness of a sound. eardrum frequency A thin membrane inside the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it. free-kwen-see The number of waves each second. hertz (Hz) The unit for frequency. 1 hertz means one wave per second. impulse Electrical signal carried by a nerve cell. intensity The loudness or volume of a sound. loudness How loud a sound is; the volume of a sound. noise Unpleasant sound. oscilloscope oss-ill-O-skope An instrument which shows a picture of a wave on a screen. pitch How high or low a note sounds. sound intensity meter A meter which measures the loudness of a sound. threshold of hearing The quietest sound that can be heard. vacuum A completely empty space with no particles. vibrate Move backwards and forwards. wave A way of transferring energy. Waves can be side to side or backwards and forwards movements. wavelength The distance between the top of one wave and the top of the next.