SOL Preparation USVA History 2014
advertisement

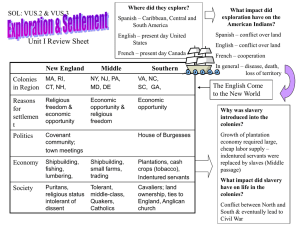
SOL Preparation for US/VA History Getting ready for the SOL There are less than 80 questions on the SOL Exam They are multiple choice questions Some include maps & graphs You have unlimited time in which to complete the test Answer all questions, leave no question unanswered The secret is in preparation, what is important to know People and events shape our history We will identify as many important people and events as possible in order to be prepared to respond successfully on the SOL Follow the slides and link the person or event with important knowledge The slides, like the test follow a chronological sequence Let’s Begin Columbian Exchange Diseases Disease kills a large segment of the indigenous population of America Jamestown Virgina 1st permanent English settlement Jamestown Colony 1607 Tobacco Mayflower Compact Compact allows for the concept of majority rule Part of today’s political decision making policy Triangle Trade Triangle Trade 13 Colonies Colonial Settlement Massachusetts & Puritans Rhode Island – dissenters Pennsylvania – Quakers Maryland – religious toleration for Catholics Plantation System Agricultural system in the South. Cash crops like tobacco & cotton fuel slavery Proclamation of 1763 & the Appalachian Mountains After French & Indian War, bares western settlement beyond Appalachian Mountains By the English Very Important Virginians Virginia Declaration of Rights (George Mason) Reiterated the notion that basic human rights should not be violated by governments Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom (Thomas Jefferson) Outlawed the established church—that is, the practice of government support for one favored church Bill of Rights James Madison, a Virginian, consulted the Virginia Declaration of Rights and the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom when drafting the amendments that eventually became the United States Bill of Rights Thomas Paine Wrote critical works Common Sense and The Crisis Inspires the cause for the American Revolution Shots heard around the World Lexington & Concord Declaration of Independence July 4, 1776 - Philadelphia Declaration of Independence Written by Jefferson Ideas of John Locke (Natural Rights) Life, liberty and pursuit of happiness Taking Sides Benjamin Franklin Inventor, scientist, and statesman Helped to gain funds and support for the American cause Yorktown, Virginia 1781 Last battle of the American Rev French fleet make the difference Articles of Confederation Powers to declare war, make peace, sign treaties, borrow money, coin money, and establish a postal service weak: no power to tax, control interstate or foreign trade, approval of states (no executive power to enforce the law) Constitutional Convention meets a meeting, planned to revise the Articles of Confederation, turns into a opportunity to write a new constitution Virginia Plan (large states) N. J. Plan (small states) Federalist The Federalists favored a strong national government that shared some power with the states. They argued that the checks & balances in the Constitution prevented any one of the three branches from acquiring preponderant power. They believed that a strong national government was necessary to facilitate interstate commerce & to manage foreign trade, national defense, and foreign relations. Constitutional Convention Great Compromise, a House based on representation determined by pop. and a Senate with two rep. from each state three-fifths compromise Checks and Balances Constitution provides for separation of powers: Executive - veto Legislature - impeachment Judiciary - judicial review George Washington Cabinet Two-Terms Warns against alliances Marbury vs. Madison Federal Courts have the power of judicial review over the Congress McCulloch v. Maryland Jefferson Buys From France In 1803 Lewis & Clark The Eli Whitney & the Cotton Gin Robert Fulton The Claremont Invented the steamboat Transportation improves with speed and two way traffic Monroe Doctrine President Monroe warns all European powers not to interfere with affairs in the Western Hemisphere. directed at the French, Spanish, Portuguese, Russians and the English, claims in the America’s. Missouri Compromise of 1820 Allows slavery south of the 36’ 30’ & admits MO as a slave state Sets the guidelines for the future admission of slave states Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 & “Bleeding Kansas” Seneca Fall Convention Women’s rights convention held in Seneca Falls, NY The beginning of the women’s suffrage movement Notable women: Eliz. Cady Stanton & Susan B. Anthony Frederick Douglas Black Abolitionist Urged Lincoln to recruit former slaves to fight in the Union Army Fredrick Douglas & Harriet Tubman and The Underground Railroad William Lloyd Garrison Publisher of the abolitionist newspaper, The Liberator Believes that slavery is a violation of Christian principles and must be ended Brigham Young and the Mormons go west Salt Lake City, Utah Texas Independence and the Alamo Struggle for independence in 1836 Clay’s Compromise of 1850 Argument for Popular Sovereignty in territories Let the people decide Territorial disputes and California admission Party of Lincoln Dred Scott Decision 1857 Supreme Court Case Ruled to be propriety and cannot sue in court Overturns the Missouri Compromise of 1820 Uncle Toms Cabin Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1852 Sparks that ignite the Civil War The Election of Lincoln causes Southern States to withdraw from the Union Lincoln’s important speeches Emancipation Proclamation frees the slaves in 1862 Ends slavery in the United States 1863 Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address “with malice towards none, with charity for all…to bind up the nations wounds” Civil War SOL Objectives Industrial development of the North After the war, passage of the th th th 13 , 14 , and 15 amendments. Established freedoms for former slaves Homestead Act, 1862 Promontory Point, Utah Carving up China U.S. in China Open Door Policy of free trade in China with out conflict Inventions/Innovations Bessemer/steel process Edison/electric light & phonograph…1000 patents Bell/telephone Wright Brothers/airplane Ford/assembly line Henry Ford’s Assembly Line Captains of Industry John D. Rockefeller and Standard Oil…(Ida Tarbell) Andrew Carnegie & Steel Social Darwinism – “survival of the fittest”…a law of nature and a law of God Philanthropy grows Progressives The Progressive Era the period from 1893 – 1920 Belief, values, & reform effort by those who have only the publics well-being to guide them. Jane Addams and Hull House (settlement house) Sherman Anti-Trust Act Prevents any business structure that “restrains trade” (monopolies) Clayton Anti-Trust Act expands Sherman Anti-Trust Act; outlaws price fixing, exempts unions from Sherman Act Unions fight for change Knights of Labor (Terrance Powderly) American Federation of Labor founded by Samuel Gompers Important Strikes: Haymarket Square, Homestead Strike, & Pullman Strike Threats of Immigration Immigration of 1880’s provides a cheap supply of labor for America’s Industrial Revolution Eastern Europeans Chinese Exclusion Act National Origins Act of 1920’s sets quotas Progressive Presidents The Progressive Movement used government to reform problems created by industrialization. Theodore Roosevelt’s “Square Deal” & Woodrow Wilson’s “New Freedom” The Big Four at Wilson’s 14 points the Treaty of League of Versailles Nations Blames Germany for the war (War Guilt Clause) Mandate System Black Migration During the late 19th and early 20th century, African Americans began the “Great Migration” to Northern cities in search of jobs and to escape poverty and discrimination in the South. Hawley-Smoot Tariff Highest protective tariff to date Wildly prohibitive duty on imported goods resulted with 25 nations passing laws to restrict purchases American goods Trade collapses…Bank Panic Stock Market crash of 1929 Over-speculation on stocks using borrowed money that could not be repaid. When the stock market crashed in 1929, stock prices collapsed, millions were left unemployed Banks failed The Great Depression Causes of the depression The New Deal: This program changed the role of the government to a more active participant in solving problems. Roosevelt rallied a frightened nation in which one in four workers was unemployed. (“We have nothing to fear, but fear itself.”) The New Deal FDR closes the banks Orders 4 billion dollars to federal banks to sure up the money supply Government involvement vs. laissez-faire approach to recovery Wagner & Social Security Acts The Wagner Act said that employers had to bargain with their workers Creates the NLRB to insure fair labor practices Social Security Act, 1935 provides relief to the nations elderly FDR & the “New Deal” Master politician, the fireside chats Brain Trust…Frances Perkins Major programs: FDIC, WPA, TVA, SEC, & NRA Pump priming & government deficits Pearl Harbor - Dec. 7, 1941 “ A day that will live in infamy” FDR U.S. declares war on Japan the next day Japanese-American Interment Camps during WW II th 6 , D-DAY June 1944 Liberation of Europe Manhattan Project & the Atomic Bomb Project to develop the atomic bomb in New Mexico More WW II stuff Term: island hopping, how the U.S. moved across the Pacific to defeat the Japanese The battle of El Alimien in North Africa Midway, the turning point in the Pacific Nuremberg Trials Soviet occupation of Eastern Europe Cold War The Berlin Airlift The Marshall Plan Truman Doctrine – policy of containment Berlin Wall erected in 1961 NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization & Collective Security The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was formed as a defensive alliance among the United States and western European countries to prevent a Soviet invasion of Western Europe. Soviet allies in Eastern Europe formed the Warsaw Pact and for nearly 50 years both sides maintained large military forces facing each other in Europe. Mao & Communist China By 1949, Communist forces control mainland China Break from the Soviets 1950’s Population shift to the suburbs Baby Boom Russia launches “Sputnik” Eisenhower wars of the “military industrial complex” in his farewell address McCarthyism & the Red Scare HUAC-the House Un-American Committee roots out Communist in government Red Scare Senator Joseph McCarthy played on American fears of communism by recklessly accusing many American governmental officials and citizens of being communists based on flimsy or no evidence. This led to the coining of the term McCarthyism, or the making of false accusations based on rumor or guilt by association. Jonas Salk finds a cure for polio Brown vs. Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas 1954 Plessy vs. Ferguson reversed Virginia closes public schools open private ones Thurgood Marshall and the NAACP Rosa Parks and the Montgomery Bus Boycott & The Little Rock Nine st 1 Televised Presidential debates, 1960 John F. Kennedy and the New Frontier Americas first Catholic President Peace Corps & NASA Dr. Martin Luther King Non-violent protest Gandhi Fidel Castro led a Fidel Castro communist revolution that took over Cuba in the late 1950s. Many Cubans fled to Florida and later attempted to invade Cuba and overthrow Castro. This “Bay of Pigs” invasion failed. In 1962, the Soviet Union stationed missiles in Cuba, instigating the Cuban Missile Crisis. President Kennedy ordered the Soviets to remove their missiles and for several days the world was on the brink of nuclear war. Eventually, the Soviet leadership “blinked” and removed their missiles. Civil Rights Act of 1964 The act prohibited discrimination based on race, religion, national origin, and gender. It also desegregated public accommodations. Voting Rights Act of 1965 The act outlawed literacy tests. Federal registrars were sent to the South to register voters. The act resulted in an increase in African American voters. Vietnam War Gulf of Tonkin Tet Offensive Vietnamization July, 1969 President Kennedy’s dream fulfilled Man lands on the moon June 17, 1972 Role of the Washington Post Saturday Night Massacre Tapes reveal cover-up Congress moves toward impeachment Roe vs. Wade 1973 Supreme Court Case legalizes abortion in the United States The Arab The Energy Crisis Embargo of 1973 drove up gas prices U.S. conservation Speed limits set at 55 Alaskan Oil pipeline built A Conservative Shift Tax Cuts Supply-side economics (trickle down theory) Recession & Recovery Sandra Day O’Connor 1st Woman appointed to the Supreme Court of the United States Fall of the Soviet Union 1989, satellite nations forced democratic elections Berlin Wall comes down East & West Germany reunited Pro-democracy China, 1989 student protest leads to a violent crackdown on Chinese citizens Human Rights at issue World’s Hot Spots – The Middle East Persian Gulf Ongoing Middle East conflict Oil OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) Operation Desert Shield Desert Storm…Kuwait is liberated after Iraq invasion UN effort led by the United States (Persian Gulf War, 1991) The End This does not include everything, but it does cover a sufficient amount of material that should insure your success on the Virginia SOL exam Good Luck!!!