Beginning Civil Rights Movement Answers
advertisement
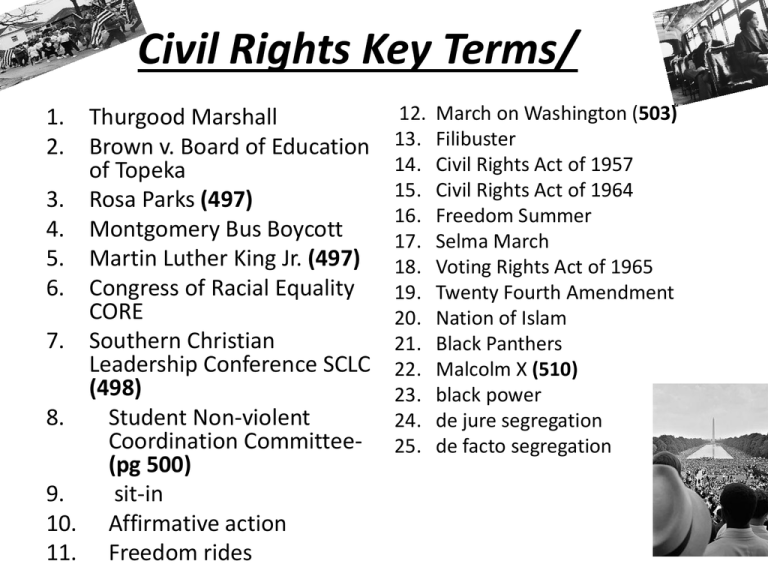
Civil Rights Key Terms/ 1. 2. Thurgood Marshall Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka 3. Rosa Parks (497) 4. Montgomery Bus Boycott 5. Martin Luther King Jr. (497) 6. Congress of Racial Equality CORE 7. Southern Christian Leadership Conference SCLC (498) 8. Student Non-violent Coordination Committee(pg 500) 9. sit-in 10. Affirmative action 11. Freedom rides 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. March on Washington (503) Filibuster Civil Rights Act of 1957 Civil Rights Act of 1964 Freedom Summer Selma March Voting Rights Act of 1965 Twenty Fourth Amendment Nation of Islam Black Panthers Malcolm X (510) black power de jure segregation de facto segregation PROJECT DUE TOMORROW! CARDS NEED TO BE IN A ZIPLOC BAG WHEN TURNED IN! Prezis need to be emailed to me! PROJECT DUE NOW! CARDS NEED TO BE IN A ZIPLOC BAG WHEN TURNED IN! Turn your Project into your class Box at the front. They are labeled per class except 1st you are the blue one! Prezis need to be emailed to me! Pg 698-699 • Complete the Work Sheet you have 25 Minutes • When you are finished you should work on your vocabulary African American Migration: African Americans Migrated to large northern cities. Out of their communities prominent doctors, & lawyers rose up who had influence over politics. The New Deal: While Roosevelt was in office African Americans working for the federal government increased significantly. Rise of the NAACP: They worked to change segregation laws. Thurgood Marshall and Oliver Hill were a part of the legal team that fought against the separate but equal clause that they would eventually help defeat. WWII: African Americans gained voting rights in Northern cities. It also opened people’s eyes to the racism and discrimination. Agenda: Beginning Civil Rights Movement IF YOU DIDN’T TURN IN YOUR PROJECT YOU HAVE UNTIL END OF TODAY THEN I CONTACT PARENTS! FYI: Vocab Quiz Friday Spiral Check Feb. 25 next Thursday Beginning Civil Rights pg. 273-276 • Person 3 Reads 1st today • You will read and complete the questions in each of the squares over each topic. – You MUST read the acting as an armature • You MUST answer the question at the bottom ON YOUR OWN Brown vs. Board of Education: What was the problem that started the Montgomery Bus Boycott: What was the problem that started the situation? separate but equal or “segregated” African Americans weren’t allowed to sit in the “white” section of the bus Little Rock Arkansas 1957: What was the What was the problem problem that started that started the the situation? situation? Lack of voting rights in the South situation? Schools were Civil Rights Act of 1957: Govern Faubus surrounded the allwhite Little Rock High School to prevent 9 African-Americans from going to school. What people were involved and what was their role in the situation? What people were involved and what was their role in the situation? What people were involved and what was their role in the situation? Rosa Parks refused to President Eisenhower Linda Brown & surrender her bus in 1957s passed the other African seat to a white Civil Rights Act. American students passenger in were denied Montgomery AL. admission to an all Martin Luther King white public school. Junior developed a Thurgood Marshall boycott of the city’s argued the case public buses. before the Supreme Court. Chief Justice Earl Warren wrote the unanimous decision of the court. What people were involved and what was their role in the situation? Governor Faubus attempted to stop the “Little Rock Nine” from attending school. President Eisenhower had to send federal troops to Little Rock to ensure their safety. How was the problem resolved? How was the problem resolved? How was the problem resolved? How was the problem resolved? The Court ruled that “segregated” schools were illegal. That separate but equal was illegal and that the schools must desegregate. The Court ruled that segregation on the public buses violated the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment. Created the Civil Rights Commission & established a Civil Rights Division in the U.S. Justice Department. It also provided federal courts power to register AfricanAmerican voters. Set pattern for later legislation. The students were allowed to attend school when the courts forced Faubus to reopen the school. Agenda: Civil Rights Protest FYI: Vocab Quiz Canceled Spiral Check Feb. 25 next Thursday Agenda: Civil Rights Protest/ SCLC-Voting Rights FYI: Spiral Check Feb. 25 next Thursday Civil Rights Test Tuesday March 1 Civil Rights Protests Get this out and start filling it in!! Chapter 21 Section 3 Sit-Ins Tactic: to sit down in a public place until served. Outcome: Sparked violent reactions/ but helped the civil rights movement gain momentum Freedom Rides Integration at “Ole Miss” Birmingham, 1963 Tactic: Whites & African Americans attempted to desegregate transportation on Freedom Rides Tactic: James Meredith wanted to transfer to University of Mississippi and the NAACP filed claim that he was turned down on racial grounds Tactic: King and SCLC marched on Birmingham leading to violence by the city officials and jailing of the protestors. Outcome: Interstate commission banned segregation in interstate transport Outcome: Supreme Court upheld Meredith claim. Kennedy had to send troops to allow Meredith to attend class. Outcome: As the nation watched it eventually helped lead to desegregation of city facilities and fairer hiring practices. Betty Frieden: wrote the Feminine Mystique challenged the belief that educated suburban housewives were happy doing nothing more than cleaning their houses. Friedan helped form the National Organization of Women. New Attitudes: feminist objected to beauty contest, sexist language and the use of sex object in advertising Gains in Women’s Rights Jarrett pages 298-300 Affirmative Action: universities receiving federal support couldn’t discriminate on the basis of sex in admissions policy. Title IX: banned sex discrimination in education institutions. Guaranteed girls in school the same opportunities as boys Equal Pay Act: required companies to pay women the same wages as men for the same work Cesar Chavez Chapter 23 Section 2 Actions In 1960 the Latino’s began to organize against discrimination the Chicano movement. In 1968 10,000 Mexican American students walked out of 5 Los Angeles high schools to protest their unequal treatment In 1960 Cesar Chavez and Dolores Huerta began to organize the Mexican field hands into the United Farm Workers or UFW. In 1965 they had 1700 members Boycotted the grape and lettuce farmers to gain rights for the field hands. Achievements In 1975 California passed a law requiring collective bargaining between growers and union representatives. In 1961 voters in San Antonio elected Henry B Gonzalez to Congress. In 1970 Jose Gutierrez the political party La Raza Unida was created. Agenda: MLK vs Malcom X Sit with your group you were assigned yesterday! FYI: Spiral Check Feb. 25 TOMORROW Civil Rights Test Tuesday March 1 Mendez v. Westminster, 1947 Facts of the case: 1945 California sent Mexican-American children to separate public schools. The Mexican American parents challenged this practice in the U.S. District Court saying it violated the Fourteenth Amendment, which guaranteed equal protection of the laws. Supreme Court Decision: The court ruled they had not violated any specific law as CA also segregated Chinese or Japanese children, but not a law based on Mexican American students. Delgado v. Bastrop ISD, 1948 Facts of the case: Delgado based on Mendez v Westminster School District decided that segregation of Mexican American children was illegal without a state law was illegal. Supreme Court Decision: The U.S. District court agreed and ordered Bastrop to stop segregation of Mexican American Students Hernandez v Texas 1954 Facts of the case: Hernandez was convicted of murder in TX by an all white jury. He sued TX for violating the 14th Amendments equal protection clause. TX claimed Mexican’s were white and therefore not entitled to special protection Supreme Court Decision: The court ruled that Mexican-Americans were a separate class and entitled to protection and Hernandez had a right to trial where members of his class were not excluded. White v Regester 1973 Facts of the case: In 1970 TX changed the TX legislature district boundaries. Bexar and Dallas counties gained members, but it would eliminate the opportunity for Mexican Americans & African Americans to be elected. Supreme Court Decision: The court ruled the TX didn’t have the right to discriminate by setting up multi-member districts. Edgewood ISD v Kirby 1984 Facts of the case: The U.S. Supreme Court ruled in 1971 that children don’t have a right to an education under the U.S. Supreme Court. Civil Rights activist then filed suit against Kriby the TX Education Commissioner on behalf of Edgewood ISD a large Mexican-American populated school district. They claimed the states funding methods violated the TX Constitution. Supreme Court Decision: The court ruled that the district was correct and the state must develop a more equitable funding method. Question: Martin Luther King Southern Christian. He was a Baptist minister. Influenced by the teachings of Mohammed. Became a member of Nation of Islam (preached black separatism and self-help) after spending time in jail. Non-violent protesting. Speaking out for non-violence Passive resistance Use what he called "Weapons of love:" Montgomery Bus Boycott (1955) March in Washington (1963) Won the Nobel Peace prize in 1964. Religion: Describe the religious outlook of King and Malcolm X Approach to Civil Rights/ Equality for Blacks: Describe the methods each leader used to instruct his followers when fighting for equal rights? Key Events: List a number of the events of the life of each person that were instrumental in making a person a leader. Death: Desribe the circumstances of the deaths of King and Malcolm X Early Life : What events in the youth and early adulthood of two men determined their destiny? Effects: Describe the effects each leader had on the Civil Rights Movement and the perception of blacks in America. Malcolm X April 4th, 1968 Death caused violent riots by blacks across the nation. "I have been to the Mountain Top speech" predicted his death one day before. Suspicious of whites; willing to use "any means necessary" to achieve equality. Was a segregationist until his pilgrimage to Mecca. Joined Black Muslims under Elijah Mohammed. Travelled the world to learn about other black cultures. Assassinated by members of the Black Muslim movement. Many scholars believe in an international conspiracy as he represented a threat to the Black Muslims after breaking with Elijah Mohammed. Decided to go into the ministry. Attended Morehouse College (GA) Montgomery Bus boycott put him as leader of the movement. ● Growing up in Michigan his parents were targets of local white supremacists- house burned down, father killed in an alleged streetcar accident and his mother committed to a state mental hospital. ● Imprisoned for drug use and distribution. Led to a conversion to spirituality. Perception has changed towards larger freedom. His death led to passage of civil rights legislation Gave people strength and courage. Encouraged protest and instilled black pride.



