Chapter 2 Review of Computer Network Technology
advertisement

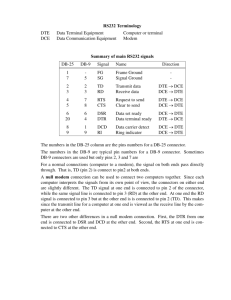
Chapter 2 Review of Computer Network Technology Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Network Topology Local Area Networks Network Node Components Internet TCP/IP Protocols Refer to net-inrtro.ppt 5. Transmission Technology 1. Network Topology - LAN Topology DTE DTE DTE DTE DTE Ethernet DTE DTE Bus DTE DTE DTE Star DTE Figure 2.1(c) Star Topology Figure 2.1(a) Bus Topology DTE DTE DTE DTE DTE Ring DTE DTE DTE DTE DTE DTE DTE Ethernet Hub Token Ring Hub Figure 2.1(b) Ring Topology Figure 2.1(d) Hub Configurations A Campus Network Of LANs 10.1.1.2 10.1.1.3 10.1.1.4 10.1.1.5 Ethernet 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.1 Bridge 10.1.2.6 Ethernet 10.1.2.0 10.1.2.2 10.1.2.3 10.1.2.4 10.1.2.5 FDDI Ring 10.10.0.0 External Network Router Router Half-Router Router Half-Router Ethernet 10.3.1.0 10.1.2.1 Router ATM ELAN 10.4.1.0 Token-ring 10.2.1.0 1. Network Topology - WAN Topology N1 N2 N1 N3 N5 N2 N6 N3 N4 N4 N5 N6 Figure 2.2(a) Mesh Topology Mesh Tree Figure 2.2(b) Tree Topology 2. Local Area Network Type of LANs Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Half-duplex Vs Full-duplex Switched Ethernet VLAN (Virtual LAN) Token Ring FDDI Ethernet • IEEE 802.3 standard • 10 Mbps data rate • CSMA/CD • Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection • Analogy of a hollow pipe • Back Off Algorithm • Packet Size: 64 ~ 1500 bytes • Segment length and drop cable length Ethernet Table 2.1 Ethernet LAN Topology Limits TYPE DESCRIPTION SEGMENT LENGTH DROP CABLE 10Base2 Thin coax (0.25”) 200 meters Not allowed 10Base5 Thick Coax (0.5”) 500 meters Twisted pair: 50 meters 10Base-T Hub topology N/A Twisted pair: 100 meters 10Base-F Hub topology N/A 2 km 10Base-T : 10 Mbps, Baseband, Twisted Pair Fast Ethernet Network Data Link LLC MAC Sublayer Physical Convergence Layer PMD Sublayer LLC Logical Link control MAC Medium Access Control PMD Physical Medium Dependent Figure 2.4 100Base-T Fast Ethernet Protocol Architecture LAN - IEEE 802.x Network 802.1 (HLI) 802.5 802.4 Physical MAC 802.2 802.3 Data Link LLC 802.1: HLI HLI: High Level Interface 802.2: LLC LLC: Logical Link Control 802.3: Ethernet MAC: Medium Access Control 802.4: Token Bus 802.5: Token Ring Fast Ethernet 100 Mbps 100Base-T PMD (Physical Medium Dependent) sublayer – to be consistent with IEEE 802.3 UTP Category 5 Gigabit Ethernet IEEE 802.3z 1 Gbps Packet size: 512 bytes Table 2.2 Gigabit Ethernet Topology Limits 9 micron SingleMode 50 micron Single Mode 50 micron Multimode 62.5 Balance micron Shielded Multimode Cable UTP 1000BASE-LX 10 km 3 km 550 m 440 m - - 1000BASE-SX - 550 m 260 m - - 1000BASE-CX - - - 25 m - 1000BASE-T - - - - 100 m Full-Duplex Ethernet Half-Duplex Full-Duplex Coaxial Cables can not support full-duplex. UTP + Hub with full-duplex support 10Base-T, 100Base-T, 100Base-F ↓ 10Base-Tx, 100Base-Tx, 100Base-Fx Switched Ethernet DTE DTE DTE Switched Hub = Multi-Port Bridge DTE Switched hub DTE DTE DTE DTE Virtual LAN DTE 1 DTE 2 Router DTE 3 Switched Hub Port for Subnets 200.100.150.1 & 200.100.160.1 DTE 4 VLAN VLAN 200.100.150.1 200.100.160.1 Figure 2.10 Virtual LANs DTE 5 Advantages of VLAN Performance Formation of Virtual Workgroups Simplified Administration Reduced Cost Security Token Ring DTE 4 IEEE 802.5 3 to 1 ACK DTE 1 DTE 1 has token control Token Ring DTE 3 1 to 3 MSG DTE 2 Figure 2.11 Token Ring LAN Dual Ring TR LAN DTE 4 DTE 1 Redundant Ring Primary Ring DTE 3 DTE 2 Figure 2.12(a) Token Ring Dual Ring Management Failure Recovery in TR LAN DTE 4 DTE 4 DTE 1 DTE 3 DTE 1 DTE 3 Failed Station DTE 2 Figure 2.12(b) Token Ring DTE Isolation DTE 2 Figure 2.12(c) Token Ring Segment Isolation FDDI • • • • • Fiber Distributed Date Interface Uses fiber optics medium Modified token ring protocol Data rate 100 Mbps Up to 500 DTEs in a single segments of 100 km without repeaters • Ideal for campus backbone network • Single and dual attached stations (SAS and DAS) • Dual attached stations load share the two rings Dual Ring FDDI Network DAS SAS SAS DAS SAS Single Attached Station DAS Dual Attached Station Figure 2.13(a) Dual Ring FDDI Network Configuration LAN Data Rate Race E’Net 10Mbps FDDI 100 Mbps Fast E’Net 100Mbps ATM 155.52 Mbps Gbit E’Net 1 Gbps Duplex E’nets ATM OC-n 3. Network Node Components • • • • • • • Hubs Bridges Remote bridges Routers Gateways Half bridge / half router Switches Basic Network Nodes ATM Switch ATM ATM Switch Figure 2.14(a) Switch Local LAN Ethernet Packets Bridge Routing Filter Bridge External LAN Ethernet Packets Figure 2.14(b) Bridge Router Local Network IP Packets Routing Filter External Network IP Packets Router Figure 2.14(c) Router Gateway IP Network Packets Format change Gateway X.25 Network Packets Networked Components Dial-up Network Half Router Router Switched Hub External Network Gateway ATM Switch Hub Bridge External Network Remote Bridge Workstation Hub Figure 2.15 Networked Components Router Hub Hubs • Hub is a platform with multiple ports • Function dependent on what is housed • LAN multi-port repeater • Switched LAN bridge (switched hub) DTE DTE DTE DTE Patch Panel Hub Wiring Closet Hub 1 Backplane Interconnection Hub 2 Figure 2.16(b) Stacked Hub To DTEs Stacked Hub Bridges Bridge Local Bridge Remote Bridge Simple Multiport Multiport Multi-protocol Refer to Figure 2.17, page 77 Bridges Operates at Layer 2, the data link layer. Allows networks with different physical signaling, but with compatible data link addressing schemes, to communicate. Helps reduce traffic on a backbone LAN by filtering any information coming from one segment to another that does not need to be forwarded through the backbone. A common use for a bridge is to allow users on an Ethernet LAN and a Token Ring LAN to communicate with each other. Bridges Remote Bridges Used to connect remote LANs Transparent Bridges Used to connect LANs of the same types Use a Spanning Tree Algorithm for routing Backward learning Routing Table of ports associated with destination addresses Source Routing Bridges Used to network token-ring LANs Source is aware of the entire path to the destination. Routers • Routers operate at network layer • Routes packets between nodes of similar network protocols • Routing table used to route packets • DLC and Physical layers could be different under the same common network layer protocol A Router Configuration Network A Protocol P Network B Protocol P Router Router Protocol interface TP TP NP NP NP NP DP DP DP' DP' Phy Phy Phy' Phy' Physical medium A Physical medium B Figure 2.21 Router Configuration Gateway • Gateway is router connecting two networks with dissimilar network protocols • Gateway does the protocol conversion at the network layer Protocol Converter • Protocol converter does the conversion at the application layer Gateway Configuration Network A Protocol P Network B Protocol Q Gateway Gateway TP Protocol interface TP NP NP NP' NP' DP DP DP' DP' Phy Phy Phy' Phy' Physical medium Figure 2.22 Gateway Configuration Tunneling Using Multiprotocol Routers • Tunneling is transmission of packets (via multiprotocol routers) by encapsulation • In Figure 2.24, packets are encapsulated and transmitted through X.25 network in a serial mode IP Tunnel Multiprotocol Router IP Multiprotocol Router Figure 2.24 Tunneling Using Multiprotocol Routers Ethernet Ethernet X.25 Half-Bridge/Half-Router •Half-bridge (half-router) is point-to-point communication • Uses PPP protocol • Helps low-end users to communicate with ISP on dial-up link saving the expense of dedicated link Serial Output Router PPP/MP Bridge Ethernet • Router encapsulates packets in PPP frames and puts serial outputs to the bridge, and vice-versa Switches • Switches are embedded in bridges and routers • Switched network used in WAN • Two types of switched networks • Circuit-switched • Packet-switched • Datagram service • Virtual circuit Pkt3 Pkt2 Pkt1 DTE A Pkt1 Pkt3 Pkt2 B Pkt2 A Pkt3 Pkt1 Pkt2 D DTE Z Pkt2 C Figure 2.26(a) Datagram Configuration Pkt1 Pkt3 Pkt2 DTE A Pkt2 Pkt1 Pkt3 B A Pkt3 D C Figure 2.26(b) Virtual Circuit Configuration Pkt2 Pkt1 DTE Z 5. Transmission Technology Transmission Technology Medium Wired LAN WAN Mode Wireless LAN Mobile Digital Satellite Analog Transmission Media Media Wireline Transmission Electric Conductors Twisted Pair • UTP • STP Coaxial Cable • Thin • Thick Wireless Transmission Optical Fiber Mono-mode Radio Multi-mode Laser Links Infrared Microwave Satellite Transmission TDM Channel Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) channel 24 Time Bandwidth Transmission Modes channel 1 channel 2 User 24 User 1 User 2 User 3 User 4 Time Packet Multiplexing Packet Multiplexing Bandwidth Figure 2.27(a) T1 Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Transmission User 1 User 2 User 3 User 4 User 5 Time Figure 2.27(c) Cell Transmission (ATM) 1 4 Time U se r U se r 1 5 U se r 3 5 2 r1 U se U se r U se r 4 3 r1 U se U se r U se r 1 Cell Multiplexing U se r Cell Multiplexing Bandwidth Figure 2.27(b) Packet Transmission ( X.25)