Radio Transmitter & Receiver Tutorial: EKT313 Problems
advertisement

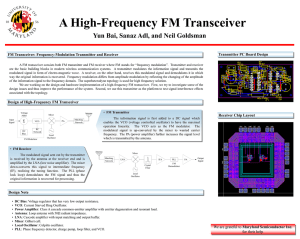
Tutorial 4 EKT 313 EKT313 Electronic Communication Systems PPKKP TUTORIAL 4 Radio transmitters 1. Discuss the four basic requirements of a transmitter. 2. What circuits are typically part of every radio transmitter? 3. What is the name given to the bias for a class C amplifier produced by an input RC network? 4. Name the capacitor and the process used for fine-tuning in an emitter follower crystal oscillator. 5. Why are crystal oscillators used instead of LC oscillators to set a transmitter frequency? 6. How is the output frequency of a frequency of a PLL synthesizer changed? 7. What is the purpose of the loop filter in a PLL? 8. What are parasitic and how are they eliminated in a power amplifier? 9. Compare the differences between class D and Class E amplifier. 10. Explain how a feed forward power amplifier reduces distortion. 11. How is impedance matching handled in a broadband linear RF amplifier? 12. An antenna will be connected to class C amplifier that has a supply voltage of 36 V and a collector current of 2.5 A. Calculate the RF output power if the efficiency of the amplifier is 80% and find the turns ratio of the transformer to match 6 Ω amplifier impedance with the 72 Ω antenna load. 13. An FM transmitter has an 8.6 MHz crystal carrier oscillator and frequency multipliers of 2,3 and 4. What is the output frequency? 14. A PLL frequency synthesizer has an ouput frequency of 162.7 MHz. The reference is a 1 MHz crstal oscillator followed by a divider of 10. What is the main frequency divider ratio? 15. Using the principles of PLL frequency synthesizers, create a synthesizer that will generate all the AM radio broadcast frequencies from 1MHz to 10 MHz in 100 KHz increments. This unit will be used as the carrier source in an AM broadcast transmitter. . 16. Design an LCC T network that will match 5Ω internal resistance to a 52 Ω load at 54 MHz. Assume Q of 12. Sahadah ahmad Page 1 Tutorial 4 EKT313 Electronic Communication Systems PPKKP Communication Receivers 1. Define the terms sensitivity, selectivity and image frequency. 2. With the aid of the block diagram of a simple receiver, explain the basic superheterodyne principle. 3. What are the advantages that the superheterodyne receiver has over the TRF receiver? Are there any disadvantage? 4. With the aid of circuit diagram , explain the operation of practical diode detector circuit, indicating what changes have been made from the basic circuit. How is AGC obtained from this detector. 5. What is the difference between forward AGC and reverse AGC? 6. Name the three main sources of selectivity for receivers implemented with ICs. 7. Design a receiver with no separate IF filter and using only single detector. Besides that propose a low cost filter at the mixer output for selectivity in your design. Sahadah ahmad Page 2