Ch 1 Guided Notes
advertisement
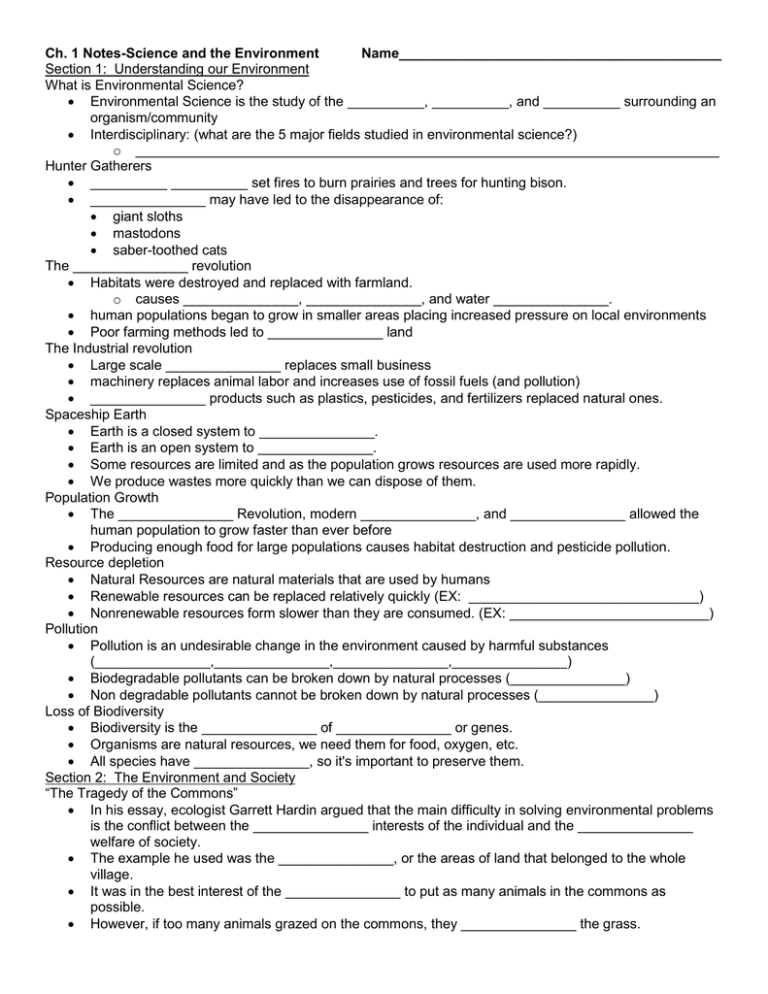
Ch. 1 Notes-Science and the Environment Name__________________________________________ Section 1: Understanding our Environment What is Environmental Science? Environmental Science is the study of the __________, __________, and __________ surrounding an organism/community Interdisciplinary: (what are the 5 major fields studied in environmental science?) o ____________________________________________________________________________ Hunter Gatherers __________ __________ set fires to burn prairies and trees for hunting bison. _______________ may have led to the disappearance of: giant sloths mastodons saber-toothed cats The _______________ revolution Habitats were destroyed and replaced with farmland. o causes _______________, _______________, and water _______________. human populations began to grow in smaller areas placing increased pressure on local environments Poor farming methods led to _______________ land The Industrial revolution Large scale _______________ replaces small business machinery replaces animal labor and increases use of fossil fuels (and pollution) _______________ products such as plastics, pesticides, and fertilizers replaced natural ones. Spaceship Earth Earth is a closed system to _______________. Earth is an open system to _______________. Some resources are limited and as the population grows resources are used more rapidly. We produce wastes more quickly than we can dispose of them. Population Growth The _______________ Revolution, modern _______________, and _______________ allowed the human population to grow faster than ever before Producing enough food for large populations causes habitat destruction and pesticide pollution. Resource depletion Natural Resources are natural materials that are used by humans Renewable resources can be replaced relatively quickly (EX: ______________________________) Nonrenewable resources form slower than they are consumed. (EX: __________________________) Pollution Pollution is an undesirable change in the environment caused by harmful substances (_______________,_______________,_______________,_______________) Biodegradable pollutants can be broken down by natural processes (_______________) Non degradable pollutants cannot be broken down by natural processes (_______________) Loss of Biodiversity Biodiversity is the _______________ of _______________ or genes. Organisms are natural resources, we need them for food, oxygen, etc. All species have _______________, so it's important to preserve them. Section 2: The Environment and Society “The Tragedy of the Commons” In his essay, ecologist Garrett Hardin argued that the main difficulty in solving environmental problems is the conflict between the _______________ interests of the individual and the _______________ welfare of society. The example he used was the _______________, or the areas of land that belonged to the whole village. It was in the best interest of the _______________ to put as many animals in the commons as possible. However, if too many animals grazed on the commons, they _______________ the grass. Once the grass was destroyed, everyone suffered because no one could raise animals on the commons. The commons were eventually replaced by _______________ fields owned by individuals. Owners were now _______________ not to put too many animals on their land, because _______________ wouldn’t allow them to raise as many animals next year. Hardin’s "Tragedy of the Commons" can be applied to our natural _______________. Hardin’s point is that someone or some group must take responsibility for maintaining a resource or it will become _______________. The solution is to override the short-term interests of the individual and improve the environment for everyone long term. Supply and Demand The Law of Supply and Demand states that as the _______________ for a good increases, the _______________ of the good also increases. Costs and Benefits The cost of environmental solutions can be high. A cost-benefit analysis _____________ the cost of the action against the benefits one expects from it. Ex: _______________ Developed and Developing Countries The unequal distribution of wealth and resources around the world influence the environmental problems in a society _______________ countries have higher incomes, slower population growth, industrial economies, and stronger social support. _______________ countries have lower average incomes, agriculture-based communities, and rapid population growth. Consumption Trends Developed nations use ______% of the world’s resources, but only make up ______% of the world’s population. Also create more _______________ and _______________ per person than in developing countries. Higher quality of life=more consumption/waste Ecological Footprints _______________ footprints show the area of Earth needed to support one person. Land for _______________, _______________, _______________ products, and _______________. forests needed to absorb air pollution A sustainable world _______________ - human needs are met so that a population can survive indefinitely. Our current world is not sustainable because developed countries are using resources faster than they can be replaced.