Name: AP Environmental Science Science, Systems, Matter, and
advertisement

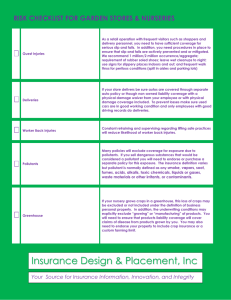
Name: ________________________ AP Environmental Science Science, Systems, Matter, and Energy 18 September 2012 Read pp. 28-34 and complete the following: 1. _______________ is an attempt to discover order in the natural world and use that knowledge to make predictions about what is likely to happen in nature. 2. List the six steps that scientists often take in trying to understand nature. I._________________________________________________________________________________ II.________________________________________________________________________________ III.________________________________________________________________________________ IV._______________________________________________________________________________ V. ________________________________________________________________________________ VI._______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Which of the following statements about the scientific process is inaccurate? a. Scientists tend to be highly skeptical of new data and hypotheses. b. Scientists use a peer review process to ensure that other scientists’ work is rigorous and logical. c. Experiments must be reproducible so that scientists can corroborate the results. d. Technological developments can be useful to humans, but have not place in the advancement of scientific understanding. e. Scientific theories are not hunches, but rather well-tested and widely accepted scientific hypotheses. 4. Consider this situation: A soil scientist working at a soybean farm discovers that following the application of a new fertilizer the nitrogen levels in the soil increase by 12%. Subsequent applications of the fertilizer on three other farms increased the soil nitrogen levels by 11.8%, 12.1%, and 11.9% respectively. The soil scientist reports his findings to the fertilizer company. They decide to advertise to customers that the fertilizer will increase soil nitrogen levels by 12% with every application. Is the company using inductive or deductive reasoning to make their claim? Defend your answer. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the difference between sound science and junk science? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6. A ________________ is a set of components that function and interact in some regular and theoretically understandable manner. 7. Explain the differences between inputs, throughputs and outputs in a system. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 8. A _________________________ occurs when an output of matter, energy, or information is fed back into the system as an input and leads to changes in that system. A _______________ feedback loop causes a system to change further in the same direction, while a ________________, or corrective, feedback loop causes a system to change in the opposite direction. 9. Consider this situation: The polar ice caps reflect sunlight energy back into outer space. As the earth’s temperature warms, the polar ice caps melt. As they melt, less ice and snow remains to reflect sunlight energy; therefore, energy that would have been reflected is now absorbed. This absorbed heat energy warms the planet further. Is this an example of a positive feedback loop or a negative feedback loop? Defend your answer. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Consider this situation: The Environmental Protection Agency has done little testing to determine the health effects of various pesticides and fertilizers when these chemicals are used together. Members of the non-profit Pesticide Action Network (PAN) are concerned about this lack of testing. Why might PAN be especially concerned? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Read pp. 38-47 and complete the following: 11. Which of the following forms of matter has the highest quality? a. coal b. bauxite (aluminum ore) c. methane gas leaching from a landfill d. seawater e. automobile emissions 12. The ____________________________________ states that while chemicals may be changed from one physical or chemical form to another, they can never be created or destroyed by the change. 13. What three factors determine the severity of a pollutant’s harmful effects? a._____________________________________ b. ____________________________________ c. _____________________________________ 14. Match the term in column B with its definition in column A. Column A a. A pollutant that is broken down completely or reduced to acceptable levels by natural physical, chemical, or biological processes. b. A measure of how long a pollutant will stay in the air, water, soil, or body. c. A pollutant that natural processes cannot break down. d. A pollutant that takes decades or longer to degrade. e. A complex chemical pollutant that living organisms, usually bacteria, can break down into simpler chemicals. Column B _____ persistence _____ degradable pollutants _____ biodegradable pollutants _____ slowly degradable pollutants _____ non-degradable pollutants 15. Strontium-91 has a half-life of 9.5 hours. How many hours will it take for 20 grams of this isotope to decay to 2.5 grams? a. 9.5 hours b. 90.5 hours c. 28.5 hours d. 76 hours e. 17.5 hours 16. Contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 17. ___________________ is the ability to do work and transfer heat. 18. Compare and contrast the two major types of energy: kinetic energy and potential energy. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 19 TRUE or FALSE: Heat and electromagnetic radiation are two types of moving or kinetic energy. 20. ________________________ is a measure of an energy source’s ability to do useful work. 21. Review Figure 2-13.Which of the following sources has the highest energy quality? a. natural gas b. wood c. geothermal energy d. normal sunlight e. nuclear fission 22. State the law of conservation of energy (also known as the first law of thermodynamics.) __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 23. State the second law of thermodynamics. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 24. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. In nature, food chains are limited in length because the amount of useful energy available to predators declines as you go up the food chain. b. LED light bulbs are preferred over incandescent light bulbs because they are 100% efficient. c. We can never recycle or reuse high-quality energy to perform useful work. d. The cheapest and quickest way to get more energy is to not waste it in the first place. e. It is unavoidable to waste some heat and some matter to the environment whenever we manufacture something. 25. Review Figures 2-15 and 2-16.Compare and contrast high-throughput economies and low throughput economies. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________