Practice Problems: Codominance and Incomplete
advertisement

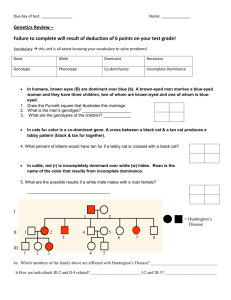
Practice Problems: Codominance and Incomplete dominance 1. A cross between a blue blahblah bird & a white blahblah bird produces offspring that are silver. The color of blahblah birds is determined by just two alleles. a) What are the genotypes of the parent blahblah birds in the original cross? b) What is/are the genotype(s) of the silver offspring? c) What would be the phenotypic ratios of offspring produced by two silver blahblah birds? 2. A white-feathered bird mates with a black-feathered bird of the same species. All of the offspring have grey feathers. Name this phenomenon and use a Punnett square to explain it. 3. The color of fruit for plant "X" is determined by two alleles. When two plants with orange fruits are crossed the following phenotypic ratios are present in the offspring: 25% red fruit, 50% orange fruit, 25% yellow fruit. What are the genotypes of the parent orange-fruited plants? 4. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios that result from the each of the following crosses of the bird species in question #2. (a) grey x white (b) black x grey (c) grey x grey 5. In a species of bird different from the one in questions #2 and #4, crossing a black-feathered bird with a white-feathered bird yields offspring that possess both white and black feathers. Explain the type of inheritance observed. Use a Punnett square. Questions on Incomplete Dominance, Co-Dominance & Multiple Alleles 1. An AB mother has an AB child. What are the possible of the father? 2. Assign each of the following children to the right parents: Children O A B AB genotypes Parents AB x O AxO A x AB OxO 3. Suppose a man marries a woman with blood type AB. The type is A. What possible blood types could their children man’s have? 4. Two babies were mixed up in the hospital. The blood types babies and the parents were determined. Which baby the Browns? Explain your reasoning. of the belongs to Baby #1: type O Baby #2: type A Mr. Brown: type AB Mrs. Brown: type B Mr. Smith: type B Mrs. Smith: type B 5. A white-feathered bird mates with a black-feathered bird of the same species. All of the offspring have grey feathers. Name this phenomenon and use a Punnett square to explain it. 6. A man has type A blood and his wife has type B. The woman bears a child with type O. He accuses her of infidelity, saying that this proves he is not the father of the child. Is there any justification for his suspicions on the basis of this evidence? Explain your reasoning. 7. Suppose a man with type A blood marries a woman with type AB blood. What blood types would you expect to find among the children? Could you tell whether the man was homozygous or heterozygous? 8. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios that result from the each of the following crosses of the bird species in question #5. (a) grey x white 9. (b) black x grey (c) grey x grey A woman sues a man for the support of her child. She has type B blood and her child has type O. The man has type B. Could the man be the father? Explain your reasoning. 10. A wealthy elderly couple die together in an accident. Soon a man shows up to claim their estate, contending that he is their long lost son. Other relatives dispute his claim. Hospital records show that the deceased couple had blood types AB and O. The claimant to the fortune has type O blood. Do you think that the claimant is an imposter? Explain your reasoning. 11. In a species of bird different from the one in questions #5 and #8, crossing a black-feathered bird with a white-feathered bird yields offspring that possess both white and black feathers. Explain the type of inheritance observed. Use a Punnett square.