Farm and Food Prices - Derived Demand
advertisement

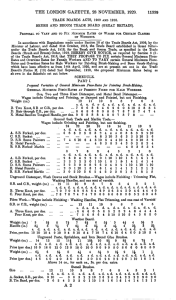
Farm and Food Prices Derived Demand AG BM 102 Introduction • Consumers rarely buy directly from farmers • Instead farmers sell to marketing service providers, who process, store, transport, and otherwise add utility, and who sell to the consumer • Hence, retail demand is not farm demand Eggs • Farmers sell nest run eggs to packer • The packers wash, candle, inspect, and sort the eggs • The eggs are sold to the supermarket • The consumer buys the eggs • These marketing services cost about 50 cents per dozen Egg Demand Quantity Doz/cap/yr. 17 18 19 20 Retail Price $/doz. $1.30 $1.20 $1.10 $1.00 Marketing Cost Farm Price $0.50 $0.50 $0.50 $0.50 $0.80 $0.70 $0.60 $0.50 21 22 23 $0.90 $0.80 $0.70 $0.50 $0.50 $0.50 $0.40 $0.30 $0.20 24 25 $0.60 $0.50 $0.50 $0.50 $0.10 $0.00 Egg Demand $1.40 $1.20 DR $/doz. $1.00 $0.80 DF $0.60 MC $0.40 $0.20 $0.00 16 18 20 Doz/capita 22 24 Farm Egg Supply Quantity Price 17 $0.00 18 $0.10 19 $0.20 20 $0.30 21 $0.40 22 $0.50 23 $0.60 Egg Market $1.40 $1.20 DR $1.00 $/doz. PR PF $0.80 DF $0.60 MC $0.40 $0.20 SF $0.00 16 18 20 Doz/capita 22 24 Some Points about Graph • Equilibrium where DF and SF cross • This is P = $0.40/doz and Q = 21 doz./cap. • At this quantity Mc = $0.50 and PR = $0.90 • No incentive to move • Farm price = Retail price – marketing cost Demand Equations QR 30 10 PR QF 25 10 PF Elasticities b( P / Q ) 1 1 R b( PR / Q) 10(0.90 / 21) 0.428 F b( PF / Q) 10(0.40 / 21) 019 . Some Notes • Farm Demand is derived from retail demand • When farm market is in equilibrium it defines retail market as well • Farm demand elasticity is always less elastic than retail • Farmer is separated from consumer by marketing sector • If marketing costs rise, farm price goes down and retail price goes up Flexibility The percent change in price in response to a 1 % change in quantity Flexibility • Applies especially to the demand for agricultural products • Useful in recognizing that quantity is predetermined and prices adjust to clear market • Strawberries, tomatoes, other non-storable products f % change P / % change Q P c dQ f d (Q / P) (1 / b)(Q / P) 1 / Calculate Flexibility fF 1 / ( 019 . ) 5.25 fR 1 / ( 0.428) 2.33 Since the farm level flexibility is greater farm prices move more as the quantity supplied increases