1How We Got Our Bible CRR Version Part 1 Deaktop
advertisement

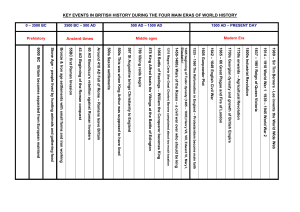
“Rose Publishing” Bruce L. Shelly Kent Powderly “Bible” “τὰ βιβλία” (“tà biblía”) meaning "the books" 1 Key Points The Bible is inspired by God. 2 Timothy 3:16-17 2 Peter 1:20-21 2 Timothy 3:16–17 (NIV84) “All Scripture is God-breathed and is useful for teaching, rebuking, correcting and training in righteousness, so that the man of God may be thoroughly equipped for every good work.” 2 Peter 1:20–21 (NLT) “Above all, you must realize that no prophecy in Scripture ever came from the prophet’s own understanding, or from human initiative. No, those prophets were moved by the Holy Spirit, and they spoke from God.” Old Testament: Clay 39 books Written approximately 1500-400 BC Stone Leather New Testament: papyrus 27 books Written approximately AD 45-100 The oldest New Testament fragment (from John 18) that we have today was copied in Greek on a papyrus codex (folded book) around AD 110-130. 3 Key Points The Old Testament was written mainly in Hebrew, with some Aramaic. A sample of Aramaic letters. The letter “aleph” in Hebrew script. The New Testament was written in Greek. A sample of Greek letters. The letter “alpha” in Koine Greek dialect. Matthew 5:18 (ESV) “For truly, I say to you, until heaven and earth pass away, not an iota, not a dot, will pass from the Law until all is accomplished.” In Aramaic the “iota” is highlighted in red. 4 Key Points The books of the Bible were collected and arranged and recognized as inspired sacred authority by councils of rabbis and councils of church leaders based on careful guidelines. (The “Cannon” of Scripture) 5 Key Points Before the printing press was invented, the Bible was copied by hand, very accurately. In many cases it was copied by special scribes who develop intricate methods of counting words and letters to insure that no errors were made. 6 Key Points The Bible was the first book ever printed on the printing press with moveable type on Gutenberg’s Press, in 1455, it was the Latin Bible (Vulgate). 7 Key Points There is much evidence that the Bible we have today is remarkably true to the original writings. Of the thousands of copies made by hand before AD 1500, more than 5,300 Greek manuscripts from the New Testament alone still exist today. Isaiah 40:8 (ESV) “The grass withers, the flower fades, but the word of our God will stand forever…” 55:11 “…so shall my word be that goes out from my mouth; it shall not return to me empty, but it shall accomplish that which I purpose, and shall succeed in the thing for which I sent it.” AUTHOR DATE Homer 850 B.C. EARLIEST TIME SPAN NUMBER ACCURACY 643 95% 1,350 8 not enough copies Euripedes 440 B.C. A.D. 1100 1,500 9 not enough copies 1,300 8 not enough copies Herodotus 450 B.C. A.D. 900 Thucydides 420 B.C. A.D. 900 Plato 380 B.C. A.D. 900 1,300 7 reconstruct Aristotle 350 B.C. A.D. 1100 1,400 5 reconstruct Caesar 60 B.C. A.D. 900 950 10 reconstruct Catullus 50 B.C. A.D. 1500 1,600 3 Tacitus A.D. 100 A.D. 1100 1,000 20 original NT A.D. 60 A.D. 130 100 14,000 99.5% AD 500 The Masoretes • The Masoretic Jews develop a meticulous system of counting the number of words in each book of the Bible to make sure it was copied accurately. • Any scroll found to have an error is buried according to Jewish law. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 ow We Got the ible A Time Line of Key Events in the History of the Bible Original Manuscripts 1500 BC - AD 100 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 1500-400 BC Old Testament Events are written down in Hebrew (Aramaic) over many centuries. In Exodus, the LORD tells Moses to write in a book. Other writers, inspired by God, include leaders, kings and prophets. Together, these writings on leather scrolls and other materials are called the Hebrew Scriptures or Old Testament. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 450 BC Ezra According to Jewish tradition, Ezra, a priest and scribe, collects and arranges some of the books of the Hebrew Bible and updates the language. (450 BC) 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 Nehemiah 8:8 (NIV84) “They (Ezra & the Scribes) read from the Book of the Law of God, making it clear and giving the meaning so that the people could understand what was being read.” 250-100 BC The Septuagint The Septuagint (70) is the first Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible. It was translated in 250-100 BC by Jewish scholars in Alexandria, Egypt. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 250-100 BC The Septuagint The 53 books of this translation are arranged by subject. 1500 BC Torah History Poetry Prophecy 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 Papyrus 200 BC The papyrus plant is cut into strips and pressed into sheets of writing material and can be made into a scroll or a codex. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 Papyrus 200 BC A papyrus codex is a bound volume made from sheets folded and sewn together, sometimes with a cover. They are used more than scrolls after AD 1-100. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 45-100 Followers of Jesus Followers of Jesus write eye-witness reports (Gospels), history, letters to other believers, and the Revelation. • • • • Matthew Mark Luke John 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 • • • • Paul James Peter Jude AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 Luke 1:1–4 (NIV84) “Many have undertaken to draw up an account of the things that have been fulfilled among us, just as they were handed down to us by those who from the first were eyewitnesses and servants of the word… Therefore, since I myself have carefully investigated everything from the beginning, it seemed good also to me to write an orderly account for you, most excellent Theophilus, so that you may know the certainty of the things you have been taught.” John 21:24–25 (NIV84) “This is the disciple who testifies to these things and who wrote them down. We know that his testimony is true. Jesus did many other things as well. If every one of them were written down, I suppose that even the whole world would not have room for the books that would be written.” AD 45-100 Followers of Jesus The writers quote from all but eight of the Old Testament books. Examples: Psalm 118:22-23 & Matthew 21:42 Isaiah 52:7 & Romans 10:15 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 “The stone the builders rejected has become the capstone; the LORD has done this, and it is marvelous in our eyes.” Psalm 118:22-23 “Jesus said to them, “Have you never read in the Scriptures: The stone the builders rejected has become the capstone; the Lord has done this, and it is marvelous in our eyes.” Matthew 21:42 Romans 10:14–15 (NKJV) How then shall they call on Him in whom they have not believed? And how shall they believe in Him of whom they have not heard? And how shall they hear without a preacher? 15 And how shall they preach unless they are sent? As it is written: “How beautiful are the feet of those who preach the gospel of peace, Who bring glad tidings of good things!” (Is. 52:7) AD 100 New Testament The original writings are copied and circulated so that by approximately AD 150 there is wide enough use of them to speak of the “New Testament” (“New Covenant”). 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 200-300 Early Translations Earliest Translations: Latin Coptic (Egypt) Syriac (Syria) Early Coptic Translation 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 200-300 Church Fathers Church fathers accept the writings of the Gospels and Paul’s letters as “canonical” (from a Greek word referring to the rule of faith and truth) or forming a “cannon”. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 397 The Canon The 27 books of the New Testament are formally confirmed as canonical by the Synod of Carthage in AD 397, thus recognizing three centuries of use by followers of Christ. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 400 Jerome Jerome starts translating the Scriptures into Latin in AD 410 and finishes 25 years later. This translation, called the Latin “Vulgate”, remains the basic Bible for many centuries. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 Jerome AD 1900 AD 2000 The Latin Vulgate Vulgate AD 400 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 Sources Used: Ancient Greek and Hebrew Copies AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 400 Bible Copies Fine quality animal skins from calves or antelope (vellum) and sheep or goats (parchment) are used for over 1,000 years to make copies of the Bible. (AD 300-1400) 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 600 The Bible in Britain Christianity reaches Britain (England) before AD 300, but Anglo-Saxon pagans drive Christian Britons into Wales (AD 450-600). 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 Britain AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 800-900 The Bible in Britain Alfred The Great, King of Wessex (AD 871-901) translates portions of Exodus, Psalms, and Acts into Anglo-Saxon. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 955-1020 The Bible in Britain Aelfric (AD 955-1020) translates portions of the Latin Old Testament into Anglo-Saxon. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 A Portion of Psalm 50 in Anglo-Saxon AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1300 The Bible in Britain Normans (French) conquer England (AD 1066) and make French the official language. No English translation of the Bible is produced until the 1300s. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1300 The Wycliffe Bible The first translation of the whole Bible into English is named after John Wycliffe, an English priest , scholar, and diplomat. John Wycliffe 1330-1384 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1300 The Wycliffe Bible His followers, derisively called Lollards (“mumblers”), include Wycliffe’s criticisms of the church in the preface to the Wycliffe Bible. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 Wycliffe Bible, AD 1384 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 Wycliffe AD 1380 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 Sources Used: The Vulgate AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 John 1:1-5 (Middle English) “In the bigynnyng was the word, and the word was at God, and God was the word. This was in the bigynnyng at God. Alle thingis weren maad bi hym, and withouten hym was maad no thing, that thing that was maad. In hym was lijf, and the lijf was the liyt of men; and the liyt schyneth in derknessis, and derknessis comprehendiden not it.” AD 1408 The Wycliffe Bible In AD 1408, in England, it becomes illegal to translate or read the Bible in common English without permission from a bishop. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1428 The Wycliffe Bible In AD 1415, the Wycliffe Bible is banned and burned. Forty years after Wycliffe’s death, in AD 1428, his bones are exhumed and burned for heresy. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1455 The Printing Press The first book ever printed was the Vulgate translation of the Bible. Gutenberg and The First Printing Press 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 The Gutenberg Bible was often illuminated by artists who hand paint letters and ornaments on each page. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 The last words of John Hus were that, “in 100 years, God will raise up a man whose calls for reform cannot be suppressed.” Jan Hus 1369-1415 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1517 Martin Luther Martin Luther nailed his famous 95 Theses of Contention (a list of 95 issues of heretical theology and crimes of the Roman Catholic Church) onto the church door at Wittenberg. 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 Martin Luther AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1496 Thomas Linacre “Either these (Greek Manuscripts) are not the Gospel… or we are not Christians” 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 AD 1496 John Colet Oxford Professor (Son of the Mayor of London) 1500 BC 500 BC AD 1 AD 500 AD 1000 AD 1500 AD 1900 AD 2000 St. Paul’s London Hebrews 4:12 (NASB95) “For the word of God is living and active and sharper than any two-edged sword, and piercing as far as the division of soul and spirit, of both joints and marrow, and able to judge the thoughts and intentions of the heart.”