Implementing CLT in a local ESP context
advertisement

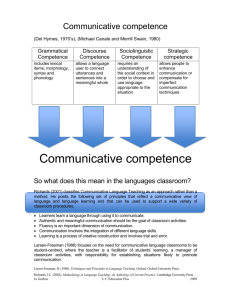
Second International Conference on Teaching English for Specific Purposes “Synergies of Language Learning” Faculty of Electronic Engineering, University of Niš, Serbia, 22-24 May, 2015 IMPLEMENTING CLT IN A LOCAL ESP CONTEXT Basim Faraj University of Benghazi Al Marj, Libya BACKGROUND Learning foreign languages is increasing dramatically Accordingly, foreign Language teaching has been developed and many theories and approaches have been suggested Grammar-translation – Direct method – Reading method – Audio-lingual method – Universal grammar – Systemicfunctional grammar – Monitor theory ..etc Communicative Language Teaching (CLT ) has been introduced to the field as a natural upgrade to all of what have been done previously in language teaching. “CLT” PERSPECTIVE Communicative language teaching (Littlewood, 1981) The focus was on learners’ message and fluency Often taught through problem-solving activities and tasks which required students to transact information Immersion program – teaching some non-language-related subject, such as history or politics, in the L2 Learners could become quite fluent in an L2 through exposure without explicit instruction. According to Savignon (2005), she stated that “The essence of CLT is the engagement of learners in communication to allow them to develop their communicative competence”. COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE (CANAL, 1983) Linguistic competence, it develops the students` knowledge about new vocabulary and syntactic features of different word classes. Discourse competence, The pieces of reading and listening used in the program has some discourse markers which also help students to develop their discourse competence. Socio-cultural competence, students interact with each other to share ideas; this interaction needs a certain socio-cultural competence to be successful. (possibility with native speakers) Strategic competence, it helps students to use their own strategies to guess the meaning of the new words they encounter. “CLT” PERSPECTIVE Brown (2001), six interrelated characteristics as a description of CLT the focus on all components of communicative competence learners should use target language for meaningful purposes fluency and accuracy are complementary principles learners should use the target language productively and receptively learners should develop their lifelong language learning strategies the role of the teacher is to facilitate and guide the learning process. LEARNING CONTEXT (TARGET POPULATION) The program is designed for first year medical students in Libya. Students are all Libyans (Culture and 1st language background) 18-20 years old Their level of English proficiency is nearly intermediate Almost all the students have basic computer skills. Importantly, they all have the same level of difficulty dealing with their academic medical subjects which are taught in English. NEEDS ANALYSIS “Discipline-specific language study has long been linked to an expectation that learners’ needs should be analyzed in order to select language components that match what students require to succeed in their academic studies.” (Kimball, 1998) Based on my recent needs analysis study, three major aspects have been considered in this project. 1. 2. 3. Technology-enhanced language learning Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) Medical terminology USING TECHNOLOGY IN LEARNING ENGLISH AS PERCEIVED BY MEDICAL STUDENTS No 19 statement Do you think that using technology such as computers may assist in learning English for medical studies? Agree Disagree 84.5% 10.3% To some extent 3.4% I do not know 1.7% 3.40% 1.70% 10.30% Agree Disagree To some extent I do not know 84.50% TECHNOLOGY PERSPECTIVE Apparently, the Internet increases the motivation on the part of students and reduces the stress of in-class language sessions (Lai & Kritsonis, 2006). It enhances different language skills by practicing in a real environment, and accessing various authentic materials which help in learning process. TECHNOLOGY PERSPECTIVE This web-based program could be regarded as a simple presentation of using technology in language education. Our purpose is to show our colleagues that; 1. Using new techniques in teaching could be quite helpful for our students; particularly, when we design programs ourselves. 2. The process of designing such programs is quite easy, flexible, straightforward and does not need any professional work at all. TECHNOLOGICAL TOOLS The program is simply a website (Google sites) English for medical purposes Word office & pdf for reading articles, assignments & hyperlinks to other sources. YouTube for audio-visual files Hot potato for exercises Discussion board and blogs for class communication & homework submission. TEACHING APPROACH Focusing on teaching all language skills (skills integration) Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) has been adopted as the main approach of teaching. The teacher`s role is managing on-class activities just to ensure that students are fully engaged in the lesson. THE COURSE “ENGLISH FOR MEDICAL STUDENTS” The program in general is ESP (EMP). It consists of six different skills: Reading, Writing, Listening , Speaking, Vocabulary and Grammar. Medical terminology is considered heavily here because of its significance in (EMP) particularly for those who are new in the field in which all materials are delivered in English. Also, it is divided into different themes all related to the field of Medicine. Ex. Human body, Infection, Heart disease etc. Each theme is covered over one session (4 weeks) INTEGRATION The Web-based program is fully integrated into the course. In each two-hour class, students should spend one hour learning directly from the website. The rest of class time is for practicing and exercises. Two (subject matter) reading articles, One relevant audio-visual material. List of new terminology of the weekly topic. A sufficient number of exercises to ensure the students’ understanding. STORYBOARD Home page Discussion board Introduction Session 1 (Human body) Overview Announcement Academic Reading Academic Writing Reading articles Audio-visual clip Blog Class contact Vocabulary Oral presentation Listening to lectures New vocabulary list Exercise Homework CONCLUSION “while these technological innovations facilitate computer-based learning activities……, they are ultimately tools in the hands of course authors who must use them creatively to maximize the students' language learning experience and to enhance their language acquisition for communicative purposes.” (Chen, Belkada, and Okamoto, 2004) Thank you Any Questions and/or Comments!!