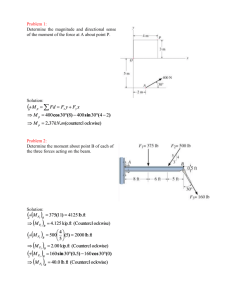
Solution
advertisement

Jun 2011 Chapter 9 Sinusoidal SteadyState Analysis مذكرات شرح وتمارين محلولة امتحانات سابقة للعديد من المواد أدناه متاحة مجانا على الموقعين المذكورين أدناه .احذر الطبيب الشاب والحالق المسن أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Example 9.1: Finding the Characteristics of a Sinusoidal Current A sinusoidal current has a maximum amplitude of 20 A. The current passes through one complete cycle in 1 ms. The magnitude of the current at zero Lime is 10 A. a) What is the frequency of the current in hertz? b) What is the frequency in radians per second? c) Write the expression for 𝑖(𝑡) using the cosine function. Express ∅ in degrees. d) What is the rms value of the current? Solution: a) From the statement of the problem, 𝑇 = 1 ms; Hence 𝑓 = 1⁄𝑇 = 1000 Hz. b) 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝑓 = 2000 𝜋 rad⁄s. c) We have 𝑖 (𝑡) = 𝐼𝑚 cos(𝜔𝑡 + ∅) = 20 cos(2000𝜋𝑡 + ∅) 𝑖(0) = 10 A. But Therefore 10 = 20 cos ∅ and ∅ = 60𝑜 . Thus the expression for 𝑖(𝑡) becomes: 𝑖(𝑡) = 20 cos(2000𝜋𝑡 + 60𝑜 ). d) The rms value of a sinusoidal current is 𝐼𝑚 ⁄√2. Therefore the rms value is 20⁄√2, or 14.14 A. ،احذر ضياع وقتك بشكل منتظم .أقصد ضياع عمرك برغبة منتظمة أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Example 9.2: Finding the Characteristics of a Sinusoidal Voltage A sinusoidal voltage is given by the expression 𝑣 = 300 cos(120𝜋𝑡 + 30𝑜 ). a) What is the period of the voltage in milliseconds? b) What is the frequency in hertz? c) What is the magnitude of 𝑣 at 𝑡 = 2.778 ms? d) What is the rms value of 𝑣? Solution: a) From the expression for 𝑣, 𝜔 = 120𝜋 rad⁄s. Because 𝜔 = 2 𝜋⁄𝑇 , 𝑇 = 2 𝜋⁄𝜔 = 1 60 s = 16.667 ms. b) The frequency is 1⁄𝑇 = 60 Hz. c) From (a), 𝜔 = 2𝜋⁄16.667; Thus, at 𝑡 = 2.778 ms, 𝜔𝑡 ≈ 1.047 rad or 60𝑜 . Therefore, 𝑣 (2.778 ms) = 300 cos(60𝑜 + 30𝑜 ) = 0 V. d) 𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠 = 300⁄√2 = 212.13 V. احذر عدوك مرة وصديقك ألف مرة فإن .انقلب الصديق فهو أعلم بالمضرة أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Example 9.7: Combining Impedances in Series and in Parallel The sinusoidal current source in the circuit shown in Fig. 9.18 produces the current 𝑖𝑠 = 8 cos 200,000𝑡 A. a) Construct the frequency-domain equivalent circuit. b) Find the steady-state expressions for 𝑣, 𝑖1 , 𝑖2 and 𝑖3 . Solution: a) The phasor transform of the current source is 8| 0o ; the resistors transform directly to the frequency domain as 10 and 6 Ω; the 40 𝜇H inductor has an impedance of 𝑗8 Ω at the given frequency of 200,000 rad⁄s; and at this frequency the 1 𝜇F capacitor has an impedance of – 𝑗5 Ω. Figure 9.19 shows the frequency-domain equivalent circuit and symbols representing the phasor transforms of the unknowns. b) The circuit shown in Fig. 9.19 indicates that we can easily obtain the voltage across the current source once we know the equivalent impedance of the three parallel branches. Moreover, once we know 𝐕, we can calculate the three phasor currents 𝐈𝟏 , 𝐈𝟐 , and 𝐈𝟑 . To find the equivalent impedance of the three branches, we first find the equivalent admittance simply by adding the admittances of each branch. .احرص أن يكون في أي عمل تعمله شيء من اإلبداع أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Continued (Example 9.7): 1 = 0.1 S 10 1 6 − 𝑗8 𝑌2 = = = 0.06 − 𝑗0.08 S 6 + 𝑗8 100 1 𝑌3 = = 𝑗0.2 S −𝑗5 The admittance of the three branches is: 𝑌 = 𝑌1 + 𝑌2 + 𝑌3 = 0.16 + 𝑗0.12 = 0.2| 36.87o The impedance at the current source is: 1 𝑍 = = 5|− 36.87o 𝑌 The Voltage 𝐕 is 𝑌1 = 𝐕 = 𝐙𝐈 = 40|− 36.87o V Hence 40|− 36.87o 𝐈𝟏 = = 4|− 36.87o = 3.2 − 𝑗2.4 A 10 40|− 36.87o 𝐈𝟐 = = 4|− 90𝑜 = −𝑗4 A 6 + 𝑗8 𝐈𝟑 = 40|− 36.87o 5|− 90o = 8| 53.13o = 4.8 + 𝑗6.4 A We check the computations at this point by verifying that 𝐈 𝟏 + 𝐈𝟐 + 𝐈𝟑 = 𝐈 Specifically, 3.2 − 𝑗2.4 − 𝑗4 + 4.8 + 𝑗6.4 = 8 + 𝑗0 The corresponding steady-state time-domain expressions are 𝑣 = 40 cos(200,000𝑡 − 36.87o ) V 𝑖1 = 4 cos(200,000𝑡 − 36.87o ) A 𝑖2 = 4 cos(200,000𝑡 − 90o ) A 𝑖3 = 8 cos(200,000𝑡 + 53.13o ) A احصل على الصالحيات التي تحتاجها .فالصالحيات مثل الحرية تكتسب وال توهب أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Assessment 9.7: A 20 Ω resistor is connected in parallel with a 5 mH inductor. This parallel combination is connected in series with a 5 Ω resistor and a 25 𝜇F capacitor. a) Calculate the impedance of this interconnection if the frequency is 2 krad⁄s. b) Repeat (a) for a frequency of 8 krad⁄s. c) At what finite frequency does the impedance of the interconnection become purely resistive? d) What is the impedance at the frequency found in (c)? Solution: a) 𝑤 = 2000 rad⁄s −1 = − 20 Ω 𝑤𝐶 20(𝑗10) = 20‖ 𝑗10 + 5 + 𝑗20 = + 5 − 𝑗20 (20 + 𝑗10) 𝑤𝐿 = 10 Ω 𝑍𝑥𝑦 = 4 + 𝑗8 + 5 − 𝑗20 = (9 − 𝑗12) Ω −1 =−5Ω 𝑤𝐶 b) 𝑤𝐿 = 40 Ω 𝑍𝑥𝑦 = 5 − 𝑗5 + 20‖ 𝑗40 = 5 − 𝑗5 + [ (20)(𝑗40) ] 20 + 𝑗40 = 5 − 𝑗5 + 16 + 𝑗8 = (21 + 𝑗3) Ω c) 𝑍𝑥𝑦 20(𝑗𝑤𝐿) 𝑗106 20𝑤 2 𝐿2 𝑗106 =[ +5− ] + (5 − )= 20 + 𝑗𝑤𝐿 25𝑤 400 + 𝑤 2 𝐿2 25𝑤 The impedance will be purely resistive when the 𝑗 terms cancel, i.e., 400𝑤𝐿 106 = 400 + 𝑤 2 𝐿2 25𝑤 Solving for 𝑤 yields 𝑤 = 4000 rad⁄s d) 𝑍𝑥𝑦 20𝑤 2 𝐿2 = + 5 = 10 + 5 = 15 Ω 400 + 𝑤 2 𝐿2 اختر وزارة لتصبح وزيرها لمدة يوم ماذا ستقرر؟،واحد بوزراة هامة أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Assessment 9.8: The interconnection described in Assessment Problem 9.7 is connected across the terminals of a voltage source that is generating 𝑣 = 150 cos 4000𝑡 V. What is the maximum amplitude of the current in the 5 mH inductor? Solution: The frequency 4000 rad⁄s was found to give 𝑍𝑥𝑦 = 15 Ω in Assessment problem 9.7. Thus, 𝐕 150| 0o 𝐈𝒔 = = = 10| 0o A 𝑍𝑥𝑦 15 o 𝐕 = 150| 0 , Using current division, 𝐈𝑳 = 20 (10) = 5 − 𝑗5 = 7.07|− 45o A 20 + 𝑗20 𝑖𝐿 = 7.07 cos(4000𝑡 − 45𝑜 ) A, 𝐼𝑚 = 7.07 A اذا اردت السعاده فال .تتوقع الشكر لما تفعله أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.24: Find the admittance 𝑌𝑎𝑏 in the circuit seen in Fig. P9.24. Express 𝑌𝑎𝑏 in both polar and rectangular form. Give the value of 𝑌𝑎𝑏 in millisiemens. Solution: First find the admittance of the parallel branches 𝑌𝑝 = 1 1 1 1 = + + = 0.375 − 𝑗0.125 S 6 − 𝑗2 4 + 𝑗12 5 𝑗10 𝑍𝑝 = 1 1 = = 2.4 + 𝑗0.8 Ω 𝑌𝑝 0.375 − 𝑗0.125 𝑍𝑎𝑏 = − 𝑗12.8 + 2.4 + 𝑗0.8 + 13.6 = 16 − 𝑗12 Ω 𝑌𝑎𝑏 = 1 1 = = 0.04 + 𝑗0.03 S = 40 + 𝑗30 mS = 50| 36.87o mS 𝑍𝑎𝑏 16 − 𝑗12 ازهد في الدنيا يُحبك هللا وازهد .فيما عند الناس يُحبك الناس أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.25: Find the steady-state expression for 𝑖𝑜 (𝑡) in the circuit in Fig. P9.25 if 𝑣𝑠 = 750 cos 5000𝑡 mV. Solution: 𝑍 = 400 + 𝑗(5)(40) − 𝑗 𝐈𝒐 = 750| 0o × 10−3 500|− 36.87o 1000 = 500|− 36.87o Ω (5)(0.4) = 1.5| 36.87o mA 𝑖𝑜 (𝑡) = 1.5 cos(5000𝑡 + 36.87o ) mA ماذا:استفد من كل مشكلة بسؤالك نفسك .أستفيد من هذه المشكلة وماذا تعلمت أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.26: The circuit shown in Fig. P9.26 is operating in the sinusoidal steady state. Find the value of 𝑤 if 𝑖𝑜 = 100 sin(𝑤𝑡 + 81.87o ) mA 𝑣𝑔 = 50 cos(𝑤𝑡 − 45o ) V Solution: 𝐕𝒈 = 50|− 45o V; 𝑍= 𝐈𝒈 = 100|− 8.13o mA 𝐕𝒈 = 500|− 36.87o Ω = 400 − 𝑗300 Ω 𝐈𝒈 2.5 × 106 𝑍 = 400 + 𝑗 (0.04𝑤 − ) 𝑤 2.5 × 106 ∴ 0.04𝑤 − = − 300 𝑤 ∴ 𝑤 2 + 7500𝑤 − 62.5 × 106 = 0 ∴ 𝑤 = − 3750 ± √(3750)2 + 62.5 × 106 = − 3750 ± 8750 𝑤 > 0, ∴ 𝑤 = 5000 rad⁄s استمر في إبداعك مهما .تحدث الناس عن إخفاقاتك أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.27: Find the steady-state expression for 𝑣𝑜 in the circuit of Fig. P9.27 if 𝑖𝑔 = 200 cos 5000𝑡 mA. Solution: 𝑍𝐿 = 𝑗(5000)(48 × 10−3 ) = 𝑍𝐶 = 𝑗240 Ω −𝑗 = − 𝑗80 Ω (5000)(2.5 × 10−6 ) Construct the phasor domain equivalent circuit: Using current division: 𝐈= (80 + 𝑗240) (0.2) = 0.1 + 𝑗0.1 A 240 − 𝑗80 + 80 + 𝑗240 𝐕𝒐 = 240 𝐈 = 24 + 𝑗24 = 33.94| 45𝑜 𝑣𝑜 = 33.94 cos(5000𝑡 + 45o ) V ،استمع لنفسك جيدا .فأنت أفضل صديق لها أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.28: The circuit in Fig. P9.28 is operating in the sinusoidal steady state. Find the steady-state expression for 𝑣𝑜 (𝑡) if 𝑣𝑔 = 64 cos 8000𝑡 V. Solution: 1 109 = = − 𝑗4000 Ω 𝑗𝑤𝐶 (31.25)(8000) 𝑗𝑤𝐿 = 𝑗8000(500)10−3 = 𝑗4000 Ω 𝐕𝒈 = 64| 0𝑜 V 𝑍𝑒 = (2000)(𝑗4000) = 1600 + 𝑗800 Ω 2000 + 𝑗4000 𝑍𝑇 = 1600 + 𝑗800 − 𝑗4000 = 1600 − 𝑗3200 Ω 64| 0𝑜 𝐈𝒈 = = 8 + 𝑗16 mA 1600 − 𝑗3200 𝐕𝐨 = 𝑍𝑔 𝐈𝒈 = (1600 + 𝑗800)(0.008 + 𝑗0.016) = 𝑗32 = 32| 90𝑜 V 𝑣𝑜 = 32 cos(8000𝑡 + 90o ) V اضحك يضحك العالم .معك وابك تبك وحدك أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.36: a) The frequency of the source voltage in the circuit in Fig. P9.36 is adjusted until 𝑖𝑔 is in phase with 𝑣𝑔 . What is the value of 𝑤 in radians per second? b) If 𝑣𝑔 = 45 cos 𝑤𝑡 V (where 𝑤 is the frequency found in [a]), what is the steady-state expression for 𝑣𝑜 ? Solution: 109 104 (𝑗2 𝑤) 109 2 × 104 𝑗 𝑤(104 − 𝑗2 𝑤) a) 𝑍𝑔 = 4000 − 𝑗 + = 4000 − 𝑗 + 25𝑤 104 + 𝑗2 𝑤 25𝑤 108 + 4𝑤 2 109 4 × 104 𝑤 2 2 × 108 𝑤 = 4000 − 𝑗 + +𝑗 8 25𝑤 108 + 4𝑤 2 10 + 4𝑤 2 109 0.2 × 109 𝑤 ∴ = 25𝑤 108 + 4𝑤 2 108 + 4𝑤 2 = 5𝑤 2 ⟹ 𝑤 2 = 108 ⟹ 𝑤 = 10,000 rad⁄s b) When 𝑤 = 10,000 rad⁄s 4 × 104 (104 )2 𝑍𝑔 = 4000 + 8 = 12,000 Ω 10 + 4(104 )2 45| 0o ∴ 𝐈𝑔 = = 3.75| 0o mA 12,000 𝐕𝒐 = 𝐕𝒈 − 𝐈𝒈 𝐙𝟏 109 𝑍1 = 4000 − 𝑗 = 4000 − 𝑗4000 Ω 25 × 104 𝐕𝒐 = 45| 0o − (3.75 × 10−3 )(4000 − 𝑗4000) = 45 − (15 − 𝑗15) = 30 + 𝑗15 = 33.54| 26.57o V 𝑣𝑜 = 33.54 cos(10,000𝑡 + 26.57o ) V اضربوا الرأي بعضه .ببعض يتولد منه الصواب أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.37: The frequency of the sinusoidal current source in the circuit in Fig. P9.37 is adjusted until 𝑣𝑜 is in phase with 𝑖𝑔 . a) What is the value of 𝑤 in radians per second? b) If 𝑖𝑔 = 2.5 cos 𝑤𝑡 mA (where 𝑤 is the frequency found in [a]), what is the steadystate expression for 𝑣𝑜 ? Solution: 1 = 0.2 × 10−3 S 5000 1 1200 0.2𝑤 𝑌2 = = − 𝑗 1200 + 𝑗0.2 𝑤 1.44 × 106 + 0.04𝑤 2 1.44 × 106 + 0.04𝑤 2 a) 𝑌1 = 𝑌3 = 𝑗𝑤50 × 10−9 𝑌𝑇 = 𝑌1 + 𝑌2 + 𝑌3 For 𝑖𝑔 and 𝑣𝑜 to be in phase the 𝑗 component of 𝑌𝑇 must be zero; thus, 𝑤50 × 10−9 = or 0.2𝑤 1.44 × 106 + 0.04𝑤 2 0.2 × 109 0.04𝑤 + 1.44 × 10 = = 4 × 106 50 2 6 ∴ 0.04𝑤 2 = 2.56 × 106 b) 𝑌𝑇 = 0.2 × 10−3 + ∴ 𝑤 = 8000 rad⁄s = 8 krad⁄s 1200 = 0.5 × 10−3 S 6 6 1.44 × 10 + 0.04(64) × 10 ∴ 𝑍𝑇 = 2000 Ω 𝐕𝒐 = (2.5 × 10−3 | 0o )(2000) = 5| 0o 𝑣𝑜 = 5 cos 8000𝑡 V ،اعرف الرجل من فعله ال من كالمه .واعرف محبته من عينه ال من لسانه أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.62: Use the concept of voltage division to find the steady-state expression for 𝑣𝑜 (𝑡) in the circuit in Fig.P9.62 if 𝑣𝑔 = 75 cos 5000𝑡 V. Solution: 106 𝑍𝑜 = 600 − 𝑗 = 600 − 𝑗800 Ω (5000)(0.25) 𝑍𝑇 = 300 + 𝑗2000 + 600 − 𝑗800 = 900 + 𝑗1200 Ω = 1500| 53.13o Ω 𝑍𝑜 (75| 0o )(1000|− 53.13o ) 𝐕𝒐 = 𝐕𝒈 = = 50|− 106.26o V o 𝑍𝑇 1500| 53.13 𝑣𝑜 = 50 cos(5000𝑡 − 106.26o ) V ركز, اعرف أولوياتك .واعمل من أجلها, عليها أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م Jun 2011 Question 9.63: Use the concept of current division to find the steady-state expression for 𝑖𝑜 in the circuit in Fig. P9.63 if 𝑖𝑔 = 125 cos 500𝑡 mA. Solution: 1 106 = − 𝑗 4 = − 𝑗100 Ω 𝑗𝑤𝐶 10 𝑗𝑤𝐿 = 𝑗(500)(1) = 𝑗500 Ω Let 𝑍1 = 50 − 𝑗100 Ω; 𝑍2 = 250 + 𝑗500 Ω 𝐈𝒈 = 125| 0o mA 𝐈𝒈 𝑍1 125| 0o (50 − 𝑗100) 𝐈𝒐 = = (300 + 𝑗400) 𝑍1 + 𝑍2 = − 12.5 − 𝑗25 mA = 27.95|− 116.57o mA 𝑖𝑜 = 27.95 cos(500𝑡 − 116.57𝑜 ) mA .اعمل عمال صالحا ولو بسيطا كل يوم أو بالبريد االلكترونيSMS ديناران هدية عنـد التنبيه على كـل خطـأ بمذكرات الموقع برسالة Circuits, English 123, Numerical Methods, Dynamics, Strength, Statics :عامة مواد C++, Java, MATLAB, Data Structures, Algorithms, Discrete Math, Digital Logic, Concepts :مواد كمبيوتر Mechanical Design I/II, Structural Analysis I/II, Management, CAD, Fluid Mechanics, System Dynamics :مواد تصميم , eng-hs.neteng-hs.com شرح ومسائل محلولة مجانا بالموقعين info@eng-hs.com 9 4444 260 حمادة شعبان.م