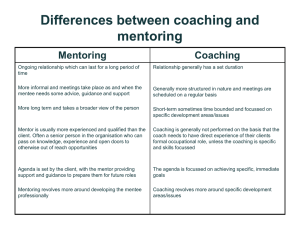
Define and illustrate issues on relevant leadership styles
advertisement

LEADERSHIP, MOTIVATION AND SUPERVISORY DEVELOPMENT SKILLS FOR MANAGERS AND SUPERVISORS LEADERSHIP, MOTIVATION AND SUPERVISORY DEVELOPMENT SKILLS COURSE OBJECTIVES COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Understand that management in all business and organisational activites is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively. Management is “ the art of getting things done through people.” (Mary Parker Follet, 1868-1933). State various functions of management comprising planning, organising, staffing, leading or directing, and controlling an organisation ( a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal. (Henri Fayol, 1841-1925) Explain the meaning of leadership as a process of influencing a group of people to move towards its goal setting or goal achievement. (Stogdill,1950) COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Understand four factors of leadership i.e. leader, followers, communication, and situation to create synergistic team effort in an organisation .(Bolma dan Deal, 1991) Define and illustrate issues on relevant leadership styles: - bureaucratic leader (Weber, 1905) - charismatic leader (Weber, 1905) - autocratic leader (Lewin, Lippitt dan White,1939) - democratic leader (Lewin, Lippitt dan White, 1939) - laissez-faire leader (Lewin, Lippitt dan White, 1939) COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Define and illustrate issues on relevant leadership styles: - people-oriented leader (Fiedler, 1967) - task-oriented leader ( Fiedler, 1967) - servant leader (Greenleaf, 1977) - transaction leader (Burns, 1978) - transformation leader (Burns, 1978) - environment leadership ( Carmazzi, 2005) Understand leadership models: - Bolman dan Deal’s Four Framework Approach 1991), structure, human resource , politic or symbol. COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Understand leadership models: -Managerial Grid (Blake and Mouton, 1985) to determine leadership position either as a country club style, middle of the road style, produce or perish style, team style or impoverished style. -Know principles and importance of emotional intelligence leadership, emotional quotient (EQ) with emphasis on affective aspects (supplement to the cognitive aspects, intelligence quotient, IQ) as the dominant aspects to the development of an effective team. (Daniel Goleman, 1998). The best leaders grasp emotional competencies, i.e. self-awareness, social awareness, self-management, and social skill. COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Understand Emotional Intelligence Leadership (EQ) aspects of coercive, authoritative, affiliative, democratic, pacesetting and coaching Understand Situational Leadership Model which describe leadership styles in terms of the amount of Task Behaviour and Relationship Behaviour and categorised into four behaviour types i.e. S1, Telling, S2, Selling, S3, Participating, S4, Delegating. Understand basic concept of human motivation in an organisation by knowing human needs models (Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Herzberg’s Hygiene and Motivational Factors COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Identify core topics in motivation which includes inspiration with dreams, setting targets and goals (SMART goals), persistence, comfort zone, overcoming fear, desired outcomes as a medium to make decisive decision. Understand in detail on the basic concepts of Performance Management System (PMS) i.e Balanced Scorecard, KPI and Competencies (Kaplan dan Norton, 2000) (Towers Perin, 2003) COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Understand in detail on the basic concepts of Performance Management System (PMS) i.e Balanced Scorecard, KPI and Competencies (Kaplan dan Norton, 2000) (Towers Perin, 2003) Identify three Performance Management Cycles involving Performance Planning, Performance Review/Assessment and Performance Reward Recognise the main outcome of the PMS in terms of productivity and performance which forms three categories of employees in an organisation i.e. high flyers, average workers and poor performers. COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of the course, participants would be able to : Know Mentoring strategies that is the process of educating and coaching and role model to the high performers. Know Coaching startegies to the avergae perfor,ers so as to motivate and inspire them to be a peak performer. Know Counselling strategies by confronting and solving problems faced by the poor performers and finding ways to enhance their performances. COURSE OUTLINES DAY ONE 8.30 am-9.00am: Registration of participants 9.00am-10.30am: Briefing from the Organiser, Orientation and Course Introduction Major Functions and Roles of Supervisors and Managers I: The myth of the supervisor A New Paradigm of Management Key Management Functions The Supervisor’s Role 3 Techniques for Staying on Top DAY ONE 9.00am-10.30am: Major Functions and Roles of Supervisors and Managers II : The Art and Science Management Skills of the Effective Manager The Six Challenges Roles of A Manager and Supervisor 10.30am-11.00am: Tea Break DAY ONE 11.00 am – 1.00 pm: Developing Leadership Skills I: Definition of leadership and its Concepts -Definition -The supervisor’s role -Terminology in Leadership Dynamics -Differences Between A Manager and A Leader -Understanding The Four (4) Main Leadership Styles Styles 1-Autocratic Styles 2-Democratic Styles 3-Participative Styles 4-Delegating DAY ONE 11.00 am – 1.00 pm: Developing Leadership Skills I Selecting and Applying The Appropriate Leadership Style to Achieve the Desired Leadership Impact Leadership Style: Situational Leadership (Hersey and Blanchard) Key Characteristics of Transformational Leadership (Burns) Leadership Self-Assessment Activity Factors That Influence The Time Taken To Develop A Subordinates 1.00pm-2.15pm : Lunch Break DAY ONE 2.15 pm – 5.00 pm: Developing Leadership Skills II Selecting and applying the appropriate leadership style to achieve the desired leadership impact Exercise : Empower others You The Delegator Delegating Leadership Style Appropriate for Various Development Levels The Four Leadership Styles: Supportive Behaviour What does a style 1,2,3 and 4 leader do? DAY ONE 2.15 pm – 5.00 pm: Developing Leadership Skills II Summary of Leadership Styles. The Five Qualities of A Smart Leader The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People LEADERSHIP MODELS Exercise : Measuring Your EQ. Exercise: Leadership Matrix Survey -Managerial Grid Exercise: Attitudes Toward Employees 10 Ways to Cultivate Leadership Skills that Build Respect. 7 Keys to Effective Supervision. DAY TWO 9.00 am – 10.30 am: Motivating Subordinates towards Higher Performance I What is motivation? Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Theory Measuring Your Role Competencies (Mc Clelland Three Needs Profiling) Theory X and Y (Mc Gregor) Motivation Exercise: What Working People Want Three Elements from Motivation Seven Rules of Motivation (Captain Bob Webb) Develop Your Dreams Setting Your Goals DAY TWO 11.00am-1.00pm : Effective Performance Management I The Concept of Performance Management Performance Management System, PMS Cycle Introduction to the concept of Balanced Scorecard and KPI (Kaplan and Norton) Step 1: Performance Planning (What and How component) The concept of Competencies Observing Behaviour Exercise : Recording Evidences DAY TWO 11.00am-1.00pm : Effective Performance Management II Step 2: Performance Review Coaching and Feedback Step 3:Performance Rewarding 1.00pm-2.00pm- Lunch Break DAY TWO 2.00pm-5.00pm : Developing An Excellent Personality of Employees : Coaching, Counseling and Mentoring I Adults Learning Model: Pedagogy and Andragogy Three Types of Learning: cognitive, affective and psychomotor ( Benjamin Bloom) Performance Coaching -Definition (Hahne dan Schultze) (Bittel dan Newstorm) (Schon -GROW Model -Exercise : My Coaching Practices DAY TWO 2.00pm-5.00pm :Developing An Excellent Personality of Employees : Coaching, Counseling and Mentoring II Counseling -The concept and definition (Rugby) (Asian Institute of Management, Manila) (ITD, UK) -The qualities of the leaders to conduct counselling session -Counselling Steps -Exercise: Counselling by confronting employees (Micki Holliday) DAY TWO 2.00pm-5.00pm :Developing An Excellent Personality of Employees : Coaching, Counseling and Mentoring III Mentoring The basic concept and definition (Bozeman and Feeney) - Needs and target group for mentoring session (Delong and Vijayaraghavan) DAY TWO 2.00pm-5.00pm :Developing An Excellent Personality of Employees : Coaching, Counseling and Mentoring III Mentoring -Types of Mentoring(Buell) - Style, Focus and characteristics of Mentoring ( Harris and Krogh) 4.30-5.00ptg: Course Evaluation Course Ends. -Lecture -Group Discussions -Case Studies -Simulation and “Role Play” Course Methodologies: Target Group : -Senior Officers -Supervisors -Managers