Chapter 8
Budgetary Planning
PowerPoint Authors:
Susan Coomer Galbreath, Ph.D., CPA
Charles W. Caldwell, D.B.A., CMA
Jon A. Booker, Ph.D., CPA, CIA
Cynthia J. Rooney, Ph.D., CPA
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Role of Budgets in the Planning and
Control Cycles
A budget is a comprehensive financial
plan for achieving the financial and
operational goals of an organization.
Planning
Developing
objectives for
acquisition
and use of
resources.
Control
Steps taken by
management to
ensure that
objectives are
attained.
8- 3
Planning and Control Cycle
8- 4
Planning Process
Strategic
Plan
Long-term
Objectives
Short-term
Objectives
Tactics
8- 5
Benefits of Budgeting
Thinking Ahead
Communication
Motivation
Forcing managers to
look ahead and state
their goals for the future
Communicating
management's
expectations
and priorities
Providing motivation for
employees to work
toward organizational
objectives
Providing lead time to
solve potential problems
Promoting cooperation
and coordination
between functional
areas of the organization
Providing a benchmark
for evaluating
performance
8- 6
Behavioral Effects of Budgets
Budget Problems
Solution
• Perceived unfair or
unrealistic goals.
• Reasonable and
attainable budgets.
• Poor managementemployee
communications.
• Employee participation in
budgeting process.
8- 7
Behavioral Effects of Budgets
Budget Problems
• Building budget slack
into budgets.
• A “use-it-or-lose-it”
mentality.
Solution
• Different budgets for
planning and for
performance evaluation.
• Continuous, or rolling
budgets.
• Zero-based budgeting.
8- 8
Components of the Master Budget
8- 9
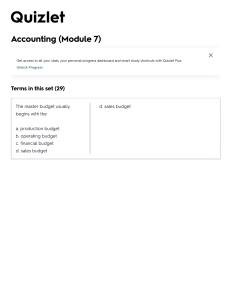
Sales Budget
Sales
Budget
Estimated
Unit Sales
Estimated
Unit Price
Analysis of economic and market conditions
+
Forecasts of customer needs from marketing personnel
8- 10
Production Budget
The production budget is directly related to the sales budget
and to the quantity of inventory the company wants to have on
hand at the beginning and end of each period. The
relationship between budgeted production, sales, and
inventory is summarized in the following formula:
8- 11
Raw Materials Purchases Budget
Next, we must determine what quantity of raw materials to
purchase to use for the production budget. Budgeted material
purchases will depend on budgeted production needs, as well
as on the planned levels for beginning and ending raw
materials inventory. The relationship between budgeted raw
material purchases, budgeted production, and raw materials
inventory is summarized in the following formula:
8- 12
Cash Budget
Our focus is on cash flows that arise from operating
activities and are directly related to the operating budgets
for Cold Stone Creamery. The relationship between
budgeted cash collections and budgeted cash payments
from operating activities and cash balances is summarized
in the following formula:
8- 13
Budgeting in Non-Manufacturing
Firms
The primary operating budget for a merchandiser is a
merchandise purchases budget, which is similar in form
to a raw materials purchases budget for a manufacturer.
Since a merchandising company does not manufacture, it does not
have raw material, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead budgets.
8- 14
End of Chapter 8
8- 15