MINI- WEATHER UNIT modified from www.middleschoolscience
advertisement

MINI- WEATHER UNIT
modified from www.middleschoolscience.com
Task 1 – Finding your city
1. Find your state and city using Google Maps (link).
2. Make a dot to represent your city on your blank map (link).
3. Write the name of your city next to it.
4. Using a yellow colored pencil, color in your state on the map.
Task 2 – Start Recording your city’s weather:
1. What is your adopted city’s zip code? US Zip Codes (link)
1. Add the zip code to your map.
2. Using the zip code and weather website, find the current weather conditions
2. Record the weather for today. What time is it in your city?
Weather website (link)
Do NOT add astronomy data yet
Weather log spreadsheet for your class.
I will record the weather for TX, on the first tab of the spreadsheet
Add your information on the tab for your adopted city (add your city to the tab name)
3. Record the weather from November 23rd to today using the historical data
Task 3 – Astronomy Data:
Record today’s weather, using the weather website (link) and your weather log spreadsheet.
What is the latitude and longitude of your city?
You can find this on the weather website in the top left corner, above the current temperature.
Record the latitude and longitude on your map. (link)
On the weather website (link), scroll down to “Astronomy Data”
Find the following data for November 23rd through today:
1. Record the Actual Sunrise, Sunset, & Day Length for your city
2. Record the Moon Rise Data for your city.
Task 4
1.
2.
3.
– Time zones:
Record today’s Weather & Astronomy Data (link).
What time zone is your city in? The information is posted on the weather site, can you find it?
Using this website (link/pdf) draw lines on your blank USA map (link) to represent each time zone. Identify
and label each one.
4. Answer the following questions by adding it to your map:
How many time zones are there in the United States?
Is your city in the same time zone as Texas?
If not, what is the difference in time?
Task 5 – State Facts
1. Record today’s Weather & Astronomy Data (link)
2. Create a documnet comparing your adopted state to TX, use charts or tables, and email when completed.
Sources
Enchanted Learning (link)
NetState (link)
US Census (link)
USDA (link)
State Facts
1. State capital
2. State Nickname
3. State motto
4. Population of state
5. Largest city
Population of largest city
6. Fun Fact of your choice
7. Admission to statehood
When did the states become an official state of the union? (Month, day and year)
8. Out of the 50 states, Texas is # ______ your state is # _________ .
9. State Flag – compare the flag of Texas to your adopted state:
Image of state flag
Words/phrases/slogans?
Symbols and what they represent
10. Is there a song that mentions your state or your city?
Task 6 – Weather Symbols
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. Weather Symbols Reference Handout (link)
3. Station Models (link)
The following will be graded for accuracy:
1. Practice using weather station symbols – worksheet (pdf)
have this checked by me when done
2. Create a Weather Station Model (WSM) for your city and TX on your mini-map(pdf)
Add your city’s WSM to the classroom map of the USA (pdf) using an EXPO marker
3. On your mini-map, lightly color in any areas of precipitation according to the national radar (link) using the
colors shown.
Be sure you can see the 48 continental states on the map at once
Make a key to show areas of rain (green) and snow (blue)
have this checked by me when done
Task 7 – Isotherms
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
1. WSM
2. Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
Climate Comparison & Map Skills
1. Find the following information and create a chart to compare your city to TX.
1. Humid, Sub-humid, Semiarid, or Arid?
2. Average annual temperature
3. Average low temperature
4. Average temperature in July
5. Average annual precipitation in inches
6. Percent of years with precipitation less than 20 inches
7. Average number of sunshine per day December-February
8. Average number of clear days
9. Average relative humidity in July
10. Number of days with snow on the ground
Isotherms
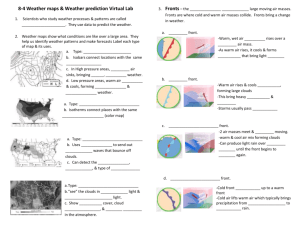
Today you will learn how to read and create Isotherms using this interactive website (link)
Record your answers on your worksheet (pdf)
Task 8 – Air masses
1. Record today’s Weather & Astronomy Data (link) (excel).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the WSM and add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
What is an air mass?
1. Use the websites below to learn about air masses:
Study Jams Video – Air Masses and Fronts (link)
take the quiz to review the material
Interactive Demo – Air Masses (link)
BrainPOP – Weather Video (link)
NOAA Air Masses (link)
USA Today (link)
2. Air Masses (pdf) {or old 2002 worksheet (pdf)} – hand in when done, will be graded for accuracy
Task 9 – Fronts & Interactive Weather Maker
Fronts – Where air masses meet
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf)
record the WSM and add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
color in the precipitation
draw the fronts (using blue and red dotted lines), along with H and L, for today (link)
go to the WunderMap, click “U.S. Fronts” and “Weather Stations” (link)
What do you notice about the temperatures on either side of the fronts?
show me your work when done
Resources
1. Fronts – symbols (link)
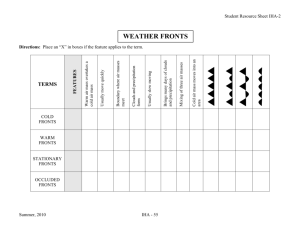
2. Handout for types of weather fronts (pdf)
3. Interactive site on weather fronts (link)
4. Interactive site on air masses (link)
What happens when air masses meet? How do air masses create weather?
Study Jams Video – Air Masses and Fronts (link)
Using this interactive website (link), find out how air masses interact to create different types of weather
Record your results on the handout and answer questions completely (pdf)
this will be graded for accuracy and completeness
Task 10 – Wind & Air Pressure
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link)
2. On your mini-map (pdf)
record the WSM and add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
color in the precipitation
draw the fronts (using blue and red dotted lines), along with H and L, for today (link) or WunderMap (link)
go to the WunderMap, click “U.S. Fronts” and “Weather Stations” (link)
What do you notice about the temperatures on either side of the fronts and the location of the
precipitation?
A) Wind & Air Pressure
1. Use the following resources to learn about wind and air pressure to complete your worksheet (pdf)
1. BrainPOP – Wind (link)
2. Study Jams -Air Pressure & Wind (link)
B) Bernoulli’s Principle – try it out!
1. Bernoulli’s Principle (link): complete 3 of the activities posted (I will supply the materials) and write 3-5
sentences for each activity using lined paper describing what you did and what you learned by doing each
activity.
2. How does wind and air pressure allow us to fly? BrainPOP Flight Movie (link)
Task 11 – Layers of the Atmosphere
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
1. WSM – add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
2. Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
3. H/L/Fronts (link)
Use the resources below to learn about the layers of the atmosphere and complete your notes (pdf).
Study Jams – Atmosphere (link)
BrainPOP – Atmosphere video (link)
Interactive – where does it go? (link)
Layers of the Atmosphere NOAA (link)
Once you have completed your notes:
Complete the illustration by adding an object to each layer and color each layer lightly.
Add the miles to each layer.
Can you add the Ozone Layer and the Ionosphere to your diagram?
Task 12 – Clouds
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
1. WSM – add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
2. Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
3. H/L/Fronts (link) or WunderMap (link)
4. NEW: Click on Satellite (link) to view cloud cover for the US
Find your adopted state – describe the cloud cover
5. NEW: Zoom the map into your state then click on Webcam (link) to view the sky in a city closest to your
adopted city
click on Video Loop to see the weather conditions for the past 24 hrs
what did you notice about the cloud cover? precipitation?
Resources
Complete your notes using the resources below. Cloud Notes (pdf) & Diagram (link)
BrainPOP Clouds video (link)
Study Jams Cloud slides (link)
Types of Clouds Identification (link)
Clouds and weather (link)
Cloud types (link)
Clouds and fronts (link)
Cloud Identification Chart (pdf)
Optional: NOAA Cloud Spotter – make your own cloud identification wheel (pdf)
Task 13 – Thunderstorms
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
1. WSM – add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
2. Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
3. H/L/Fronts (link) or WunderMap (link)
4. NEW: Click on Severe (link) and then check the box next to Lightning to view lighting activity for the US
Using orange, shade in areas of lightning activity on your mini-map
Answer these questions on your mini-map
1. What does yellow indicate on the map for precipitation?
2. What do you notice about the areas of lightning and their relationship to areas of precipitation?
3. Did all areas of precipitation have lightning activity?
4. Zoom into an area with lightning activity, what state did you pick?
What do the pink (+) symbols stand for?
What do the red (+) symbols stand for?
What do the dark blue (-) symbols stand for?
What do the light blue (-) symbols stand for?
Resources:
Complete Moving Masses and the Formation of Thunderstorms handout (pdf pages 13-19)
Storm Prediction Center (link)
NatGeo Lightning 101 Video (link)
BrainPop Video: Thunderstorms (link)
Life cycle of a Thunderstorm (link) or (link)
Interactive: NatGeo Make Lighting Strike (link)
Reading Comprehension (pdf)
Task 14 – Tornadoes
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link) (excel).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
WSM – add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
H/L/Fronts (link) or WunderMap (link)
NEW: Click on Severe (link)
1. Check the box next to Lightning to view lightning activity for the US
Using orange, shade in areas of lightning activity on your mini-map
2. Check the box next to Tornado to view tornadic activity for the US
Using purple, shade in any tornado activity on your mini-map
there may not be any today
Using purple, outline any areas that are under a Tornado Watch or Warning(link)
there may not be any today
3. Tornado Alley (link)
1. On your handout (pdf pages 20-21), color in the states that are part of “Tornado Alley”
2. Is your adopted city in tornado alley?
3. How many tornadoes per year, on average, occur in your adopted state? (link)
4. On average, how many tornadoes occur in TX?
5. Which state has the most tornadoes? least tornadoes?
4. Saffir-Simpson Scale – Rate the Tornado Damage for each image (link)
Resources:
Storm Prediction Center (link) – Issues watches, warnings, and advisories
BrainPOP Tornado Video (link)
NatGeo Tornadoes 101 Video (link)
NOAA Tornado 101 (link)
NOAA – Tornado resources (link)
NOAA – Yesterday’s Tornado Data (link)
Red Cross Tornado Packet – lots of great stuff in here, Fujita scale, mapping skills, etc, (pdf)
Task 15 – Hurricanes (updated 4/28/15)
1. Record today’s Weather, yesterday’s Hi/Lo/Precipitation, & Astronomy Data (link).
2. On your mini-map (pdf) record the following:
WSM – add it to the classroom map of the USA (pdf)
Precipitation (Rain – green, Snow – blue)
H/L/Fronts (link) or WunderMap (link)
NEW: Click on Tropical (link)
1. Check the box next to Hurricanes/Typhoons to view activity for the US
Using the color code under “Legend”, place a Hurricane symbol on your map to indicate the location
of any current Hurricanes or Typhoons
There may not be any activity today
2. Check the box next to Sea Surface Temperature
What is the approximate temperature for the water off the coast of Texas? Write the temperature
on your mini map.
Does your adopted state touch a body of water?
If so, do the same for your adopted state.
Complete the following using the resources below:
BrainPOP Hurricanes Video (link) & Activity Sheets (link)
Hurricane Notes (pdf)
Tracking Hurricanes (spreadsheets)
Choose any one Hurricane and plot it on the NOAA/NWS Atlantic Basin Hurricane Tracking Chart (pdf)
Resources
Hurricane Names (link)
NOAA/NWS Historical Hurricane Data (link) – Data for every Hurricanes, including maps
Weather Underground Hurricane Archive (link)
NOAA/NWS National Hurricane Center (link)
Interactive Activities
Create-a-Cane (link)
Aim a Hurricane (link)
Hurricane Tracker (link)
How Hurricanes Form (link)
NatGeo – Forces of Nature (link)
Saffir-Simpson Scale (link) – What happens when a hurricane hits your neighborhood?
Additional Resource:
Practice latitude and longitude: plotting hurricanes worksheet (pdf)
Hurricane Isabel 2003: tracking and analysis of Hurricane Isabel (pdf)
Modified from www.middleschoolscience.com