8-4 Weather maps digital lesson - cms15-16
advertisement
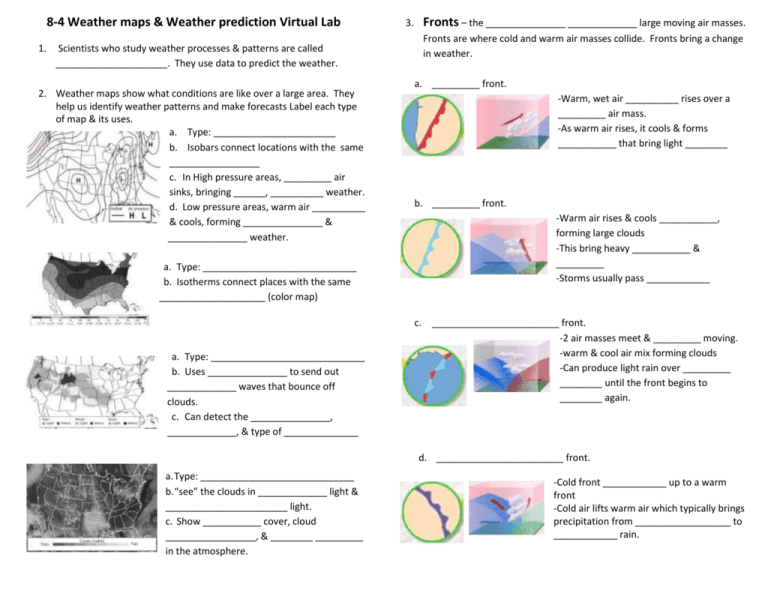
8-4 Weather maps & Weather prediction Virtual Lab 1. Scientists who study weather processes & patterns are called _____________________. They use data to predict the weather. 2. Weather maps show what conditions are like over a large area. They help us identify weather patterns and make forecasts Label each type of map & its uses. a. Type: _______________________ b. Isobars connect locations with the same _________________ c. In High pressure areas, _________ air sinks, bringing ______, __________ weather. d. Low pressure areas, warm air __________ & cools, forming _______________ & _______________ weather. a. Type: _____________________________ b. Isotherms connect places with the same ____________________ (color map) a. Type: _____________________________ b. Uses _______________ to send out _____________ waves that bounce off clouds. c. Can detect the _______________, _____________, & type of ______________ 3. Fronts – the _______________ _____________ large moving air masses. Fronts are where cold and warm air masses collide. Fronts bring a change in weather. a. _________ front. -Warm, wet air __________ rises over a _________ air mass. -As warm air rises, it cools & forms ___________ that bring light ________ b. _________ front. -Warm air rises & cools ___________, forming large clouds -This bring heavy ___________ & _________ -Storms usually pass ____________ c. ________________________ front. -2 air masses meet & _________ moving. -warm & cool air mix forming clouds -Can produce light rain over _________ ________ until the front begins to ________ again. d. ________________________ front. a. Type: _____________________________ b. “see” the clouds in _____________ light & _______________________ light. c. Show ___________ cover, cloud _________________, & ________ _________ in the atmosphere. -Cold front ____________ up to a warm front -Cold air lifts warm air which typically brings precipitation from __________________ to ____________ rain. 4. Use the following weather map to predict the weather in one of the cities. Today’s conditions Tomorrow’s conditions City Near or approaching fronts 5. Draw in the correct icons for each box to represent the weather there. 6. Match the following weather (8-4 Digital lesson Slide 5) 1. instruments to their use. Measures temperature Temperature Anemometer Precipitation Today’s conditions Tomorrow’s conditions 2. Measures Precipitation amount. Has a cup that fills up, allowing you to measure how much rain has fallen in a given amount of time. Barometer City #2 Near or approaching fronts 3. Measures wind speed. The faster the wind blows, the faster it spins. Thermometer Temperature Precipitation 4. Measures Wind Direction. As wind blows, the vane turns so that it points in the direction that the wind is blowing from. a. Weather maps help you make forecasts by tracking weather patterns b. Fronts bring _____________________, such as rain or snow c. If a front is ___________________ you know that precipitation is _____________ 5. Measures Air Pressure When atmosphere contains more air molecules in a given amount of space the air pressure increases. Rain Gauge Wind Vane