File
advertisement
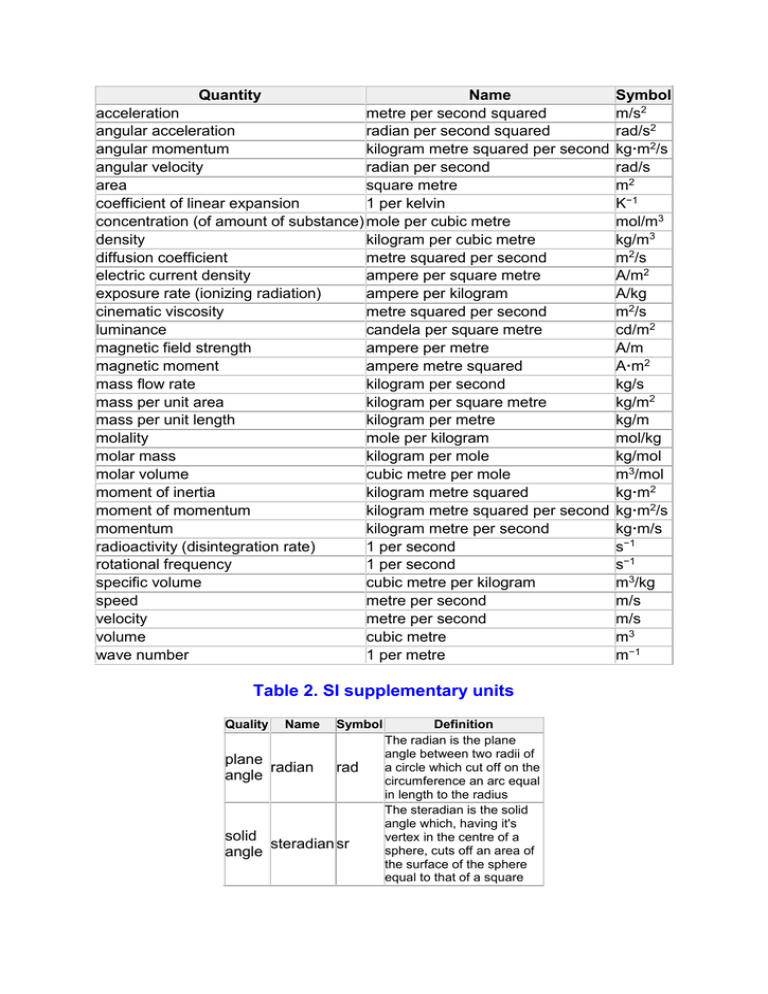
Quantity Name acceleration metre per second squared angular acceleration radian per second squared angular momentum kilogram metre squared per second angular velocity radian per second area square metre coefficient of linear expansion 1 per kelvin concentration (of amount of substance) mole per cubic metre density kilogram per cubic metre diffusion coefficient metre squared per second electric current density ampere per square metre exposure rate (ionizing radiation) ampere per kilogram cinematic viscosity metre squared per second luminance candela per square metre magnetic field strength ampere per metre magnetic moment ampere metre squared mass flow rate kilogram per second mass per unit area kilogram per square metre mass per unit length kilogram per metre molality mole per kilogram molar mass kilogram per mole molar volume cubic metre per mole moment of inertia kilogram metre squared moment of momentum kilogram metre squared per second momentum kilogram metre per second radioactivity (disintegration rate) 1 per second rotational frequency 1 per second specific volume cubic metre per kilogram speed metre per second velocity metre per second volume cubic metre wave number 1 per metre Table 2. SI supplementary units Quality Name plane radian angle Symbol rad solid steradian sr angle Definition The radian is the plane angle between two radii of a circle which cut off on the circumference an arc equal in length to the radius The steradian is the solid angle which, having it's vertex in the centre of a sphere, cuts off an area of the surface of the sphere equal to that of a square Symbol m/s2 rad/s2 kg·m2/s rad/s m2 K−1 mol/m3 kg/m3 m2/s A/m2 A/kg m2/s cd/m2 A/m A·m2 kg/s kg/m2 kg/m mol/kg kg/mol m3/mol kg·m2 kg·m2/s kg·m/s s−1 s−1 m3/kg m/s m/s m3 m−1 with sides of length equal to the radius of the sphere. Table 3. Derived units with special names Quantity Name Expression in terms Expression in of other SI Symbol terms units and of SI Base units definition of unit. admittance siemens S capacitance farad F conductance siemens S electrical ohm resistance electric coulomb C charge electric flux coulomb C electric volt V potential electromotive volt V force energy joule J energy flux watt W flux of coulomb C displacement force newton N frequency hertz Hz illuminance lux lx impedance ohm −1 C/V −1 m−2·kg−1·s3·A2 m−2·kg−1·s4·A2 m−2·kg−1·s3·A2 V/A m2·kg·s−3·A−2 A·s s·A A·s s·A W/A m2·kg·s−3·A−1 W/A m2·kg·s−3·A−1 N·m J/s m2·kg·s−2 m2·kg·s−3 A·s s·A m·kg·s−2 s−1 m−2·cd·sr m2·kg·s−3·A−2 luminous flux lumen magnetic flux weber magnetic flux tesla density magnetic tesla induction magnetic tesla polarization lm Wb kg·m/s2 s−1 lm/m2 V/A Wb/A (V·s/A) cd·sr V·s T Wb/m2 kg·s−2·A−1 T Wb/m2 kg·s−2·A−1 T Wb/m2 kg·s−2·A−1 permeance henry H Wb/A (V·s/A) m2·kg·s-2·A−2 volt V W/A m2·kg·s−3·A−1 watt W J/s m2·kg·s-3 pascal Pa N/m2 m−1·kg·s−2 inductance potential difference power pressure, stress henry H m2·kg·s−2·A−2 cd·sr m2·kg·s-2·A−1 quantity of electricity quantity of heat reactance stress susceptance weight work coulomb C A·s s·A joule N·m m2·kg·s−2 V/A N/m2 −1 kg·m/s2 N·m m2·kg·s−3·A−2 m−1·kg·s−2 m−2·kg−1·s 3·A2 m·kg·s−2 m2·kg·s−2 J ohm pascal Pa siemens S newton N joule J Notes to the above table The expressions in the fourth column represent the definitions of the respective units in symbolic form. For instance, the quantity force is defined as the product of mass and acceleration (F = m·a) so the definition of the unit of force, the newton (N) is given by 1 N = 1 kg·m/s2. Mechanical energy must not be expressed in newton metres (N·m) but only in joules (J). The former unit is used only for torque or moment of force. In the expressions for the lumen (lm) and lux (lx) in the fifth column, the steradian (sr) is treated as a base unit. Table 4. SI derived units expressed in terms of SI derived units with special names as well as SI based units and SI supplementary units: Quality absorbed dose Name joul per kilogram watt per metre squared coefficient of heat transfer kelvin conductivity siemens per metre dialectric polarization coulomb per square metre displacement coulomb per square metre dynamic viscosity pascal second electric charge density coulomb per cubic metre electric dipole moment coulomb metre electric field strength volt per metre energy density joul per cubic metre entropy joule per kelvin exposure (ionizing coulomb per kilogram radiation) heat capacity joule per kelvin heat flux density watt per square metre magnetic dipole moment weber metre molar energy joule per mole molar entropy joule per mole kelvin Expression in terms of Symbol SI Base units and SI Supplementary units J/kg m2·s−2 W/m2·K kg·s−3·K−1 S/m C/m2 C/m2 Pa·s C/m3 C·m V /m J/m3 J/K m−3·kg−1·s 3·A2 m−2·s·A m−2·s·A m−1·kg·s−1 m-3·s·A m·s·A m·kg·s−3·A−1 m-1·kg·s−2 m2·kg·s−2·K−1 C/kg kg−1·s·A J/K m2·kg·s−2·K−1 W /m2 kg·s-3 Wb·m m3·kg·s−2·A−1 J/mol m2·kg·s−2·mol−1 J/mol·K m2·kg·s−2·K -1·mol−1 molar heat capacity moment of force permeability permittivity radiant intensity reluctance resistivity specific energy specific entropy specific heat capacity specific latent heat surface charge density surface tension thermal conductivity torque joule per mole kelvin newton metre henry per metre farad per metre watt per steradian 1 per henry ohm metre joule per kilogram joule per kilogram kelvin joule per kilogram kelvin joule per kilogram coulomb per square metre newton per metre watt per metre kelvin newton metre J/mol·K m2·kg·s−2·K -1·mol−1 N·m m2·kg·s−2 H/m m·kg·s−2·A−2 F/m m−3·kg−1·A2 W /sr m2·kg·s−3·srl−1 H−1 m-2·kg−1·s 2·A2 Ω·m m3·kg·s−3·A−2 J/kg m2·s−2 J/kg·K m2·s−2·K−1 J/kg·K m2·s−2·K−1 J/kg m2·s−2 C/m2 m−2·s·A N/m kg·s−2 W /m·K m·kg·s-3·K−1 N·m m2·kg·s−2 Notes to the above table In the interests of uniformity it is preferable to define, as far as possible, the SI (Systeme Internationale) derived units in accordance with the combinations given in the above tables. This does not, however, exclude the possibility of using other equivalent combinations in special cases. In education, for example, it may be convenient to define electric field strength initially in terms of the force experienced by unit charge and to use the corresponding unit newton per coulomb (N/C) instead of volt per metre (V/m). Note that: 1 V/m = 1 W/A·m = 1 N·m/s·A·m = 1 N/C. Torque of moment of force should not be expressed in joules (J) but only in newton metres (N·m). The values of certain so-called dimensionless quantities such as index of refraction, relative permeability and relative permittivity are expressed as pure numbers. Each of these quantities does have an SI unit but this consists of the ratio of two identical SI units and thus may be expressed by the number 1. SI Derived Units / Abgeleitete SI-Einheiten English/German Frequency / Frequenz hertz: Hz = 1/s Force / Kraft newton: N = m kg/s2 Pressure, stress / Druck, mechanische Spannung pascal: Pa = N/m2= kg/m s2 Energy, work, quantity of heat / Energie, Arbeit, Wärmemenge joule: J = N m = m2kg/s2 Power, radiant flux / Leistung watt: W = J/s = m2kg/s3 Quantity of electricity, electric charge / elektrische Ladung coulomb: C = s A Electric potential / elektrische Spannung volt: V = W/A = m2kg/s3 A Capacitance / Kapazität farad: F = C/V = s4A2/m2 kg Electric resistance / elektrischer Widerstand ohm: Omega = V/A = m2kg/s3 A2 Conductance / elektr.Leitfähigkeit siemens: S = A/V = s3A2/m2 kg Magnetic flux / magnetischer Fluss weber: Wb = V s = m2kg/s2 A Magnetic flux density, magnetic induction / Magnetische Induktion tesla: T = Wb/m2 = kg/s2 A Inductance / Induktivität henry: H = Wb/A = m2kg/s2 A2 Luminous flux / Lichtstrom lumen:lm = cd sr Illuminance / Beleuchtungsstärke lux:lx = lm/m2 = cd sr/m2 Activity (ionizing radiations) / Radioaktivität becquerel: Bq = 1/s Absorbed dose / Absorbierte Strahlendosis gray: Gy = J/kg = m2/s2 Dynamic viscosity / Dynamische Viskosität pascal second: Pa s = kg/m s Moment of force / Drehmoment meter newton: N m = m2 kg/s2 Surface tension / Oberflächenspannung newton per meter:N/m = kg/s2 Heat flux density, irradiance / Wärmeflussdichte watt per squaremeter: W/m2 = kg/s3 Heat capacity, entropy / Wärmekapazität,Entropie joule per kelvin:J/K = m2 kg/s2 K Specific heat capacity, specific entropy /Spez. Wärmekapazität, spez. Entropie joule per kilogramkelvin: J/kg K = m2/s2 K Specific energy / Spezifische Energie joule per kilogram:J/kg = m2/s2 Thermal conductivity / Thermische Leitfähigkeit watt per meterkelvin: W/m K = m kg/s3 K Energy density / Energiedichte joule per cubicmeter: J/m3 = kg/m s2 Electric field strength / Elektrische Feldstärke volt per meter: V/m = m kg/s3 A Electric charge density / Elektrische Ladungsdichte coulomb per cubicmeter: C/m3 = s A/m3 Electric displacement, electric flux density /Elektrische Flussdichte coulomb per squaremeter: C/m2 = s A/m2 Permittivity / Influenz farad per meter: F/m = s4 A2/m3 kg Permeability / Permeabilität henry per meter: H/m = m kg/s2 A2 Molar energy / Molare Energie joule per mole:J/mol = m2 kg/s2 mol Molar entropy, molar heat capacity / Molare Entropie, molare Wärmekapazität joule per molekelvin: J/mol K = m2 kg/s2 K mol Exposure (ionizing radiations) / Exposition coulomb per kilogram: C/kg = s A/kg Absorbed dose rate / Absorbierte Dosisrate gray per second: Gy/s = m2/s3 cgs Units / cgs-Einheiten erg 1erg = E-7 J dyne 1 dyn = E-5 N poise 1 P = 1 dyn s/cm2 = 0.1 Pa s stokes 1 St = 1 cm2/s = E-4 m2/s gauss 1G = E-4 T oersted 1Oe = (1000/(4∙pi)) A/m maxwell 1Mx = E-8 Wb stilb 1sb = 1 cd/cm2 = E4 cd/m2 phot 1ph = E4 lx