Engg Analysis Problems (Qazi group)
advertisement

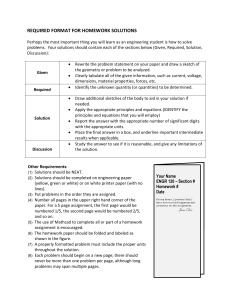
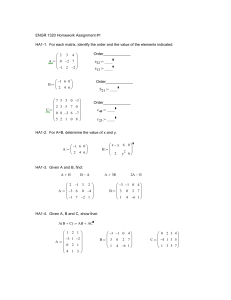
Engineering Analysis (Assignment Problems) Submitted to: Prof. Dr. HameedUllah Mughal Submitted By: Engr. Qazi Shahzad Ali: 2011-MS-MED-10 Engr.Muhammad Mohsin Masood: 2011-MS-MED-09 Engr.Maqsood Ashraf Bala: 2011-MS-MED-04 Engr. Ahmad Asad: 2011-MS-MED-17 Problem 1: In a mechanical workshop a circular part at 1200 K is allowed to cool down in air at an ambient temperature of. Assuming heat is lost only due to radiation, the differential equation for the temperature of the part is given by Where is in and in seconds. Find the temperature at t=480 seconds using Euler’s method. Assume a step size of seconds h=240 seconds. Problem 2: The following table shows the temperature of a lake at given temperature Temperature oC 19.1 19.1 19 18.8 Depth, Z (m) 0 -1 -2 -3 18.7 18.3 -4 -5 18.2 17.6 11.7 9.9 -6 -7 -8 -9 9.1 -10 Use largest change in temperature is between z = - 8 m and z = - 7 m Determine the value of the temperature at z = -7.5 m using Newton’s divided difference method of interpolation and 2nd order polynomial. Find the absolute relative approximate error for the second order polynomial approximation. Problem 3: In processing plant the concentration of salt x in a homemade soap maker is given as a function of time by 𝑑𝑥 = 37.5 − 3.5𝑥 𝑑𝑡 At the initial time, t=0 the salt concentration in the tank is 50 g/L. Using Runge-Kutta 2nd order method and a step size of min h=1.5 min, what is the salt concentration after 3 minutes? Problem 4: The final result of a research center in form of following equation 2 𝐸𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝐹(𝑥) = ∫ √𝑥𝑑𝑥 1 1. Compute the results by using Trapezoidal and Simpson’s 1/3rd rules, taking h=0.25 in each case. 2. Calculate the exact value to 4dp and compare the results obtained in above both cases with exact solution. Problem 5: The power P is supplied to wheels is function of speed v of a car. If the mass of the car is m=2000kg determine the time t for the car to accelerate from 1 m/s to 6 m/s and the power at these speeds is 4.7kW and 43.2kW respectively. Use trapezoidal method to evaluate the value of time. Following is the relation that can be employed 6 𝑡 = 𝑚∫ 1 Problem 6: Convert the following numbers: 1. 2. 3. 4. (512.5)10= (?)2 (111.1011)2= (?)10 (D2763)16= (?)10 (10011100)2= (?)16 𝑣 𝑑𝑣 𝑃 Problem 7: The output of a simple mechanical milling machine during design phase is in form of following system of equations; use the LU decomposition without pivoting method to solve the following matrix: Problem 8: A team of three parachutists is attached to a weightless cord while free falling with a velocity of 5m/s, calculate the tension in each part of cord and the acceleration of team by using Naïve Gauss Elimination method. c3v c2v m3g Parachutist 1 2 3 m2g Mass (kg) 70 60 40 70 1 0 a 636 60 - 1 1 T 518 40 0 1 R 307 c1v m1g Drag Co-efficient (kg/s) 10 14 17 Problem 9: By working as a marketing Engineer in Machine Tool Company, the equation that gives the minimum number of CNC lathe machines to be sold after considering the total costs and the total sales is Use the Newton-Raphson method of finding roots of equations to find the minimum number of CNC lathe machines that need to be sold to make a profit. a) Conduct three iterations to estimate the root of the above equations. b) Find the absolute relative approximate error at the end of each iteration and the number of significant digits at least correct at the end of each iteration. Problem 10: Water is flowing in a channel at a rate of Q = 20 m3/s. The critical depth ‘y ’ for such a channel must satisfy the equation: 0 = 1- (Q2/g*Ac3)*B Where g = 9.81 m/s2, Ac= cross sectional area of the channel (m2), B = width of the channel at the surface (m) The width and cross sectional area can be related to depth ‘y’ by: Ac= 3y + y2/2 B=3+y Use Bisection method to solve for error less than 1%. Use initial guess of xl= 0.5 and xu= 2.5 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++