Chapter 1
Introduction to Accounting
and Business
Financial and Managerial Accounting
8th Edition
Warren Reeve Fess
PowerPoint Presentation by Douglas Cloud
Professor Emeritus of Accounting
Pepperdine University
© Copyright 2004 South-Western, a division
of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved.
Task Force Image Gallery clip art included in this
electronic presentation is used with the permission of
NVTech Inc.
Some of the action has been automated,
so click the mouse when you see this
lightning bolt in the lower right-hand
corner of the screen. You can point and
Like
now.
click anywhere
onright
the screen.
Objectives
1. Describe the nature of a business.
thisin business.
2. Describe the After
role ofstudying
accounting
chapter, you should
3. Describe the importance of business ethics and
be able to:
the basic principles of proper ethical conduct.
4. Describe the profession of accounting.
5. Summarize the development of accounting
principles and relate them to practice.
6. State the accounting equation and define each
element of the equation.
Objectives
7. Explain how business transactions can be
stated in terms of the resulting change in the
basic elements of the accounting equation.
8. Describe the financial statements of a
corporation and explain how they interrelate.
9. Use the ratio of liabilities to stockholders’
equity to analyze the ability of a business to
withstand poor business conditions.
Types of Businesses
Manufacturing Business
Product
General Motors
Intel
Boeing
Nike
Coca-Cola
Sony
Cars, trucks, vans
Computer chips
Jet aircraft
Athletic shoes and apparel
Beverages
Stereos and television
Types of Businesses
Merchandising Business
Product
Wal-Mart
Toys “R” Us
Circuit City
Lands’ End
Amazon.com
General merchandise
Toys
Consumer electronics
Apparel
Internet books, music, video
retailer
Types of Businesses
Service Business
Product
Disney
Delta Air Lines
Marriott Hotels
Merrill Lynch
Sprint
Entertainment
Transportation
Hospitality and lodging
Financial advice
Telecommunication
There are three types of
business organizations
Proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
A proprietorship
is owned by one
individual.
Joe’s
Advantages
• Ease in organizing
• Low cost of
organizing
Disadvantage
• Limited source of
financial resources
• Unlimited liability
A partnership is
owned by two or
more individuals.
Joe and Marty’s
Advantages
• More financial
resources than a
proprietorship.
• Additional
management skills.
Disadvantage
• Unlimited liability.
A corporation is
organized under state
or federal statutes as a
separate legal entity.
J & M, Inc.
Advantage
• The ability to obtain
large amounts of
resources by issuing
stocks.
Disadvantage
• Double taxation.
Business Strategies
A business strategy is an integrated
set of plans and actions designed to
enable the business to gain an
advantage over its competitors, and
in doing so, to maximize its profits.
Business Strategies
Under a low-cost strategy, a business
designs and produces products or
services of acceptable quality at a cost
lower than that of its competitors.
Wal-Mart
Southwest Airlines
Business Strategies
Under a differential strategy, a business
designs and produces products or services
that possess unique attributes or
characteristics which customers are willing
to pay a premium price.
Maytag
Tommy Hilfiger
Value Chain of a Business
A value chain is the way a
business adds value for its
customers by processing inputs
into product or service.
Inputs
Business
Processes
Products or
Services
Customer
Value
Business Stakeholders
A business stakeholder is a person or
entity having an interest in the
economic performance of the business.
The Process of Providing
Information
1
Identify
stakeholders.
STAKEHOLDERS
External:
Internal:
Customers,
Owners,
creditors,
managers,
government
employees
2
Assess
stakeholders’
informational
needs.
The Process of Providing
Information
4
Record
economic
data about
business
activities
and events.
Accounting
Information
System
3
Design the
accounting
information
system to meet
stakeholders’
needs.
The Process of Providing
Information
STAKEHOLDERS
Internal:
Owners,
managers,
employees
5
Prepare
accounting
reports for
stakeholders.
External:
Customers,
creditors,
government
Accounting
Information
System
Business Ethics
Sound
Principles that
form the
foundation for
ethical
behavior
1. Avoid small ethical lapses.
2. Focus on your long-term
reputation.
3. You may expect to suffer
adverse personal
consequences for holding
to an ethical position.
Profession of Accounting
Accountants employed by a business firm or
a not-for-profit organization are said to be
engaged in private accounting.
Accountants and their staff who provide
services on a fee basis are said to be
employed in public accounting.
Generally Accepted
Accounting
Principles (GAAP)
The business entity concept
limits the economic data in
the accounting system to
data related directly to the
activities of the business.
The cost concept is the
basis for entering the
exchange price, or cost
of an acquisition in the
accounting records.
The objectivity concept
requires that the accounting
records and reports be based
upon objective evidence.
The unit-of-measure
concept requires that
economic data be
recorded in dollars.
The Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
The resources
owned by a
business
The Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
The rights of the
creditors, which
represent debts
of the business
The Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
The rights of the
owners
What is a business
transaction?
A business transaction is an economic event or
condition that directly changes an entity’s financial
condition or directly affects its results of operations.
On November 1,
2005, Chris
Clark organized
a corporation
that will be
known as
NetSolutions.
a. Chris Clark deposits $25,000 in a bank
account in the name of NetSolutions in
return for shares of stock in the
corporation.
a.
Assets
=
Cash
25,000
=
Owners’ Equity
Capital Stock
25,000 Investment by
stockholder
b. NetSolutions exchanged $20,000 for land.
Assets
Cash + Land
Bal. 25,000
b. –20,000
+20,000
Bal. 5,000
20,000
=
=
Owners’ Equity
Capital Stock
25,000
25,000
c. During the month, NetSolutions purchased
supplies for $1,350 and agreed to pay the
supplier in the near future (on account).
Assets
=
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 5,000
c.
Bal. 5,000
20,000
+ 1,350
1,350
20,000
Owners’
Liabilities + Equity
Accounts
Capital
Payable
Stock
=
25,000
+ 1,350
1,350
25,000
d. NetSolutions provided services to
customers, earning fees of $7,500 and
received the amount in cash.
Assets
=
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 5,000
1,350
20,000
d. + 7,500
Bal. 12,500
1,350
20,000
=
Owners’
Liab . + Equity
Accounts Capital Retained
Payable + Stock + Earnings
1,350 25,000
+ 7,500
1,350
25,000
7,500
Fees
earned
e. NetSolutions paid the following
expenses: wages, $2,125; rent, $800;
utilities, $450; and miscellaneous, $275.
Assets
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 12,500
1,350
20,000
e. – 3,650
Bal. 8,850
1,350
20,000
Owners’
=
Liab . + Equity
Accounts Capital Retained
Payable + Stock + Earnings
1,350 25,000
7,500
–2,125
=
– 800
Expenses
– 450
– 275
1,350 25,000
3,850
f. NetSolutions paid $950 to
creditors during the month.
Assets
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 8,850
1,350
20,000
f.
– 950
Bal. 7,900
1,350
20,000
=
=
Owners’
Liab . + Equity
Accounts Capital Retained
Payable + Stock + Earnings
1,350 25,000
3,850
– 950
400 25,000
3,850
g. At the end of the month, the cost
of supplies on hand is $550, so
$800 of supplies were used.
Assets
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 7,900
1,350
20,000
g.
– 800
Bal. 7,900
550
20,000
=
=
Owners’
Liab . + Equity
Accounts Capital Retained
Payable + Stock + Earnings
400 25,000
3,850
Supplies
– 800
Expense
400 25,000
3,050
h. At the end of the month, NetSolutions
pays $2,000 to stockholders.
Assets
Cash + Supplies + Land
Bal. 7,900
550
20,000
h. –2,000
Bal. 5,900
550
20,000
=
=
Owners’
Liab . + Equity
Accounts Capital Retained
Payable + Stock + Earnings
400 25,000
3,050
–2,000
Dividends
400 25,000
1,050
Effects of Transactions on Owners’ Equity
Capital Stock
Increased by
Stockholders’
investments
+
Effects of Transactions on Owners’ Equity
Retained Earnings
Decreased by
Decreased by
Revenues
Expenses
Dividends
+
–
–
Increased by
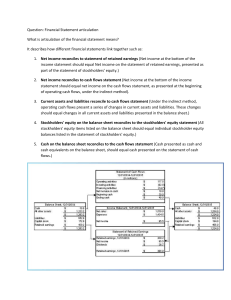
Accounting reports, called
financial statements,
provide summarized
information to the users.
Financial Statements
• Income statement—A summary of the
revenue and expenses for a specific
period of time.
• Retained earnings statement—A
summary of the earnings retained in the
corporation for a specific period of time.
• Balance sheet—A list of the assets,
liabilities, and stockholders’ equity as of a
specific date.
• Statement of cash flows—A summary of
the cash receipts and disbursements for a
specific period of time.
NetSolutions
Income Statement
For the Month Ended November 30, 2005
Fees earned
Operating expenses:
Wages expense
Rent expense
Supplies expense
Utilities expense
$7 500 00
$2 125 00
800 00
800 00
450 00
Miscellaneous expense
275 00
Total operating expenses Transfer this
Net income
amount to the
retained earnings
statement.
4 450 00
$3 050 00
NetSolutions
Retained Earnings Statement
For the Month Ended November 30, 2005
From the income
Net income for November
statement
Less dividends
Transferred to the
Retained earnings, November 30, 2005
balance sheet
$3 050 00
2 000 00
$1 050 00
NetSolutions
Balance Sheet
November 30, 2005
Assets
Cash
Supplies
Land
Total assets
From the
Liabilities
retained earnings
$ 5 900 00 Accounts Payable
statement$ 400 00
550 00 Stockholders’ Equity
20 000 00 Capital Stock $25,000
Ret. Earnings
l,050
Total liabilities and
$26 450 00 stockholder’s equity
This balance sheet presented
using the account form
26 050 00
$26 450 00
When the balance sheet displays
the liabilities and stockholders’
equity below the assets, the report
form is being used.
NetSolutions
Statement of Cash Flows
For the Month Ended November 30, 2005
Cash flows from operating activities:
Cash received from customers
$ 7 500 00
Deduct cash payments for expenses
and payments to creditors
4 600 00
Net cash flow from operating activities
2 900 00
Cash flows from investing activities:
Cash payment for acquisition of land
(20 000 00 )
Cash flows from financing activities:
Cash received as owner’s investment
$25 000 00
Deduct cash withdrawal by owner
2 000 00
Net cash flow from financing activities
23 000 00
Net cashShould
flow and
Nov.
30, 2005
bal. sheet
$ 5 900 00
match
Cash
on thecash
balance
Statement of Cash Flows
Cash Flows from Operating Activities—This
section reports a summary of cash receipts and
cash payments from operations.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities—This section
reports the cash transactions for the acquisition and
sale of relatively permanent assets.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities—This
section reports the cash transactions related to cash
investments by the owner, borrowings, and cash
withdrawals by the owner.
Financial Analysis and
Interpretation
The ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity
allows bankers, creditors, and other stakeholders
a means of analyzing the corporation’s ability to
withstand poor business conditions.
Ratio of liabilities
Total Liabilities
to stockholders’ =
Total stockholders’ equity
equity
Financial Analysis and
Interpretation
Ratio of liabilities
to stockholders’ =
equity
$400
$26,050
Ratio of liabilities
to stockholders’ = 0.015
equity
Chapter 1
The End