Attention & Memory
advertisement

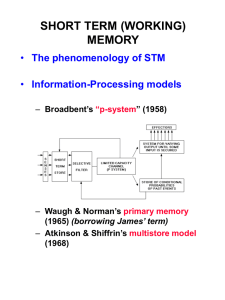
Attention • System interrupt attracted by alternative stimuli (dog in street) • Conscious reallocation device • Attention as limited resource • Attention as bottleneck – – – – – Cocktail party effect : Colin Cherry Filter theory: Donald Broadbent Attenuation theory: Anne Triesman Late selection theory: Donald MacKay (pennies) Spotlight model: Michael Posner Memory: Central to the Self • Early work of Ebbinghaus – Methodology (recall, recognition, savings) – Time course of loss – Overlearning • Serial position effect and its implications: a multi-store model of memory Conclusion: a multi-store model of memory • The serial position results suggest a separation of a short term and a long term store or component of memory • But there may be more! Sperling: Sensory Storage (iconic memory) • Whole vs partial report • Rapid decay • Backward masking H Z R B P D S C K V M W G T X Y N Q D P C M L W M B W X Q V P T N Z Y G R Y D N V B Q Z G L S K W P G D B Q T C K G N V Sperling exper. Whole vs Partial Report Delay of tone--fast decay Summary: Iconic Memory • • • • Capacity: Very large Duration: Very short Transfer: Readout to STM Loss: Phenomenon of backward masking (and its necessity!) A Multi-store model of memory • Benefits and limitations • First memory: sensory store • Next: Short term memory Short term memory • • • • • • • Current contents of memory Fundamental bottleneck in processing Multiple interpretations Capacity Duration Transfer Loss Basic Operations of STM • • • • How things enter it How things stay in it. How we search for things within it. How things leave it Peterson & Peterson: Decay Waugh & Norman: Interference Sternberg: Memory scanning STM-WM (an alternative view) • Another way of looking at it (STM vs Working Memory) (Baddeley) • The "bottleneck" issue and an example or two. • Beating the limits--the work of Chase and Ericcsson: chunks & retrieval structures. • Finally, how do things move on--elaborative rehearsal Baddeley: Model of Working Memory Chase, Ericcsson & Staszewski: Retrieval Structures