Animal Respiration
advertisement

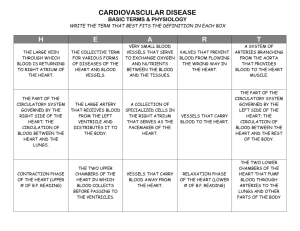
Taking in oxygen, expelling CO2 Breathe through moist skin Gases move through by diffusion Oxygen diffuses into the muscle cells Gills are surrounded by blood vessels and have a lot of surface area for removing oxygen dissolved in water Water passes over gills and oxygen diffuses into vessels Oxygen is carried to muscles through vessels Juveniles have gills Adults develop lungs ◦ No diaphragm ◦ Air has to be pushed in and out Adults can also breathe through moist skin by diffusion Some aquatic reptiles can breathe through skin Air is sucked in by expansion of ribcage Crocodiles have a diaphragm High need for oxygen Air sacs allow for one-way air flow Fresh air flows through lungs; stale air doesn’t http://www.smm.org/heart/lungs/breathing.htm Inhalation: diaphragm lowers, chest volume increases, chest pressure decreases, air rushes in Exhalation: opposite happens Transports materials throughout body (gases, nutrients, wastes, etc.) Has blood vessels (closed circulation) Has 5 pumping vessels that act as hearts Heart No loop of blood vessels (open circulatory system) Hemolymph (no blood) 2-chambered heart One loop of blood vessels Good enough for life in water Juvenile: 2-chambered heart Adult: 3-chambered heart 3-chambered heart (except for crocs) 4-chambered heart (most efficient) 2 loops of blood vessels Keeps oxygen-rich blood separate from oxygen-poor blood Oxygen is taken in by respiratory system, diffuses into blood vessels, gets taken to rest of body.