Pearson's product moment-correlation
advertisement

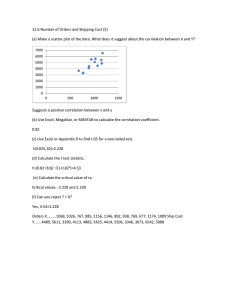
4.2 Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient Mathematical Studies for the IB Diploma Second Edition © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2012 Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient When the relationship between two variables needs to be studied, a good way of representing the data graphically is to use a scatter diagram. With a scatter diagram, a series of points is plotted. The x- and y-coordinates of each point are taken from the values of the variables. The data and scatter diagram below show the height of young children (cm) plotted against their mass (kg). 24 Mass (kg) 22 20 Height Mass Height Mass 34 3.8 86 11.1 40 7.0 87 16.4 45 9.0 95 20.9 46 4.2 96 16.2 52 10.1 96 14.0 59 6.2 101 19.5 63 9.9 108 15.9 64 16.0 109 12.0 71 15.8 117 19.4 73 9.9 121 14.3 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 Height (cm) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 Mathematical Studies for the IB Diploma Second Edition © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2012 Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient 24 From the graph it is clear that there is a relationship between the two variables. Generally, as height increases so does mass. Mass (kg) 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 Height (cm) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 This can be emphasized by plotting a line of best fit. This should pass through the point x, y which represents the mean values of the height and mass. To see how strong a correlation there is between the two variables, Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient can be calculated. Mathematical Studies for the IB Diploma Second Edition © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2012 Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient The value of Pearson’s product–moment coefficient (r ) gives an indication of the level of correlation between two variables. It has a value in the range –1 ≤ r ≤ 1. s xy r The value of r is calculated using the formula sx s y where s x is the standard deviation of x, s y is the standard deviation of y and s xy is the covariance of x and y A value of r near –1 implies a strong negative correlation between the two variables. A value of r near +1 implies a strong positive correlation between the two variables. A value of r near 0 implies there is little or no correlation between the two variables. Mathematical Studies for the IB Diploma Second Edition © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2012 Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient For the data given earlier, the results can be entered in a GDC calculator and the value of r calculated. r = 0.767 This value of r shows that there is a moderate positive correlation between a child’s height and mass. Mathematical Studies for the IB Diploma Second Edition © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2012