Algebra 2 1.1 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

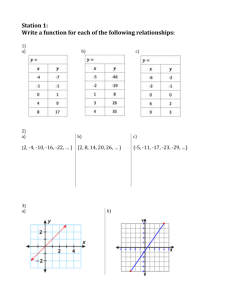
Three-Column Assessment Solve 8𝑥 − 5 4𝑥 + 1 = −1 + 2 −7𝑥 − 3 Agenda Details Test Books INB Website Accounts INB Front of 1st page – Express yourself Back of 1st page – Table of Contents (I) or (i) Front of 2nd page – Table of Contents (II) or (ii) Back of 2nd page – Table of Contents (III) of (iii) Front of 3rd page – Table of Contents (IV) or (iv) Back of 3rd page – Table of Contents (V) or (v) Front of 4th page – Algebra 2 Formula Sheet (VI) or (vi) Back of 4th page – Geometry Reference Page (VII) or (vii) Front of 5th page – Geometry Reference Page (VIII) or (viii) Back of 5th page – Frayer Model (page 1) or (pg. 1) or (1) Model Front of 6th page – Power Cornell Notes (page 2) or (pg. 2) or (2) Website accounts www.mangahigh.com first_last – password - initials www.quizlet.com www.khanacademy.com www.blendspace.com www.brainscape.com Algebra 2 1.1 Topic: Input/Output Tables Objectives: SWBAT 1) Identify and describe specific patterns in input-output tables. 2) Determine whether a linear function matches a table. Tool Kit Relations Input Output Function Domain Range Activate Prior Knowledge What is a relation? What is a function? What is an input of a function? What is an output of a function? Are all relations functions? Are all functions relations? How can you tell if a relation is a function or not? Terminology Relation: -is just a relationship between sets of numbers Example: -People (x) in this class and their heights (y) You name off someone and I can give you a height. Or you give me a height and I can give you the name of everyone that is that tall. (Hint: there can be more than one person with the same height) The set of all the inputs (x-values) is called the _________. Domain The set of all the outputs (y-values) is called the _________. Range More Terminology Function: -is a relation where each element in the domain is paired up with exactly one element in the range Yes or No? Just Remember the 3 D’s: Don’t Double the Domain Things you have done in the past. Find the value of, y = 5𝑥 − 9 , when 𝑥 = 3, 7, −5, 0. Input Process Output 3 7 -5 0 How does the value you got “out” RELATE to the value you put “in”? Function Table Game Rules: Draw all tables Find a simple rule that agrees with each table Ways to describe (or relate) each: Input to Output Output to output Examples: In Words – take away 3 from each output to get the next output In Words – the output is half of the input Algebraically – y = 3x + 1 Combination – output = input x 5 Me Table A Input, n Output, A(n) 0 0 1 2 2 4 3 6 4 8 Possible Answers: Each output is 2 more than the previous output. 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 = 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 × 2 𝑦 = 2𝑥 𝐴 𝑛 = 2𝑛 function notation We Table B Input, n Output, B(n) 0 0 1 2 2 6 3 12 4 20 Two Table C Input, n Output, C(n) 0 2 1 1 2 0 3 -1 4 -2 You Table D Input, n Output, D(n) 0 0 1 3 2 8 3 15 4 24 Upper Level Table E Input Output 0 6 1 12 2 20 3 30 4 42 What are all the possible operations that can be done to the input? Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up Input Output 0 0 1 4 2 16 3 36 4 64 Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up Input Output 0 2 1 3 2 6 3 11 4 18 Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up Input 0 1 2 3 4 Output -3 2 7 12 17 Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up Input 0 1 2 3 4 Output -16 -15 -12 -7 0 Question Why are tables important? Exit Slip Verbal: You have a job washing dishes. You are paid $7.50 an hour. Graph: Algebraic: 𝑝 = 7.5ℎ Where p is your pay and h is the number of hours you work. Table: # of hours 2 4 5 8 10 Wages Exit Slip Verbal: Your sister’s hair is 6 inches Algebraic: long and grows an inch each month. ℎ=𝑚+6 Graph: Where h is hair length and m is the number of months. Table: # of months 0 1 2 3 4 Length of hair Exit Slip Verbal: Two rabbits live in the new park. The rabbit population doubles each year. Algebraic: 𝑟 = 2𝑦 ∙ 2 𝑜𝑟 2𝑦+1 Where r is the rabbit population and y is the number of years. Graph: Table: # of years # of rabbits 0 1 2 3 4 Exit Slip Verbal: You have a $10 iTunes gift card. Each song now costs $1.50. Algebraic: 𝑏 = 10 − 1.5𝑠 Where b is the balance on your gift card and s is the number of songs you have purchased. Graph: Table: # of songs purchased Balance on Card 1 2 3 5 7 Assignment Make sure you copy all tables Pgs. 6 – 7 (3-13,16, 17-20*) Algebra 2 1.2 Topic: Domain and Range Objectives: SWBAT 1) Differentiate between a closed-form and a recursive function and write both definitions of a function. 2) State the domain and range of each function and describe the differences between the two types. Tool Kit Domain Range Function Notation Closed-form Definition Recursive Definition Card Sort Each group gets a set of cards Must sort them in groups of 4 Each group must have the corresponding table, graph, relationship (pattern) and verbal form that represents them as a whole When you are done, raise your hand and I will check to see if you got all of them right Exploring Tables Can you describe the pattern (rule) in this table in two ways? Input to Output: Input Output 0 3 1 8 2 13 3 18 4 23 Output to Output: Two Different Ways to Define a Function Closed Form is an equation (in function notation) that describes the pattern (or relationship) from input to output lets you find any output for any input by direct calculation Recursive is an equation that describes the pattern from output to output to find any value using recursive definition you must have the previous output value to find the next output value Thinking of the Real World Closed Form Recursive Exploring Tables Write the closed-form and the recursive definition of this table? Closed Form: Input Output 0 3 1 8 2 13 3 18 4 23 𝑓 𝑛 = 5𝑛 + 3 Recursive: 𝑓 𝑛 = 3 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 5 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Function Notation (ClosedForm) 𝑓 𝑛 = 5𝑛 + 3 Find: 𝑓(0) 𝑓(18) Recursive Definition 3 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 5 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Find: 𝑓(0) 𝑓(1) 𝑓(2) 𝑓(18) We Write the closed-form and recursive definitions of the table below. Closed Form: Input Output 0 3 1 5 2 7 3 9 4 11 Recursive: We Write the closed-form and recursive definitions of the table below. Closed Form: Input Output 0 5 1 9 2 13 3 17 4 21 Recursive: Group Write the closed-form and recursive definitions of the table below. Closed Form: Input Output 0 -2 1 -4 2 -6 3 -8 4 -10 Recursive: All together Write the closed-form and recursive definitions of the table below. Closed Form: Input Output 0 0 1 3 2 8 3 15 4 24 5 35 6 48 Recursive: Terminology Domain: -are the values that go “into” a function -or it is the inputs/x-values -when they ask for the domain of a function they are asking for all the possible values you could put into a function. Range: -are the values that come “out” a function -or it is the output/y-values -when they ask for the range of a function they are asking for all the possible values that could come out of the function. Closed-Form vs. Recursive Closed-Form: Input to Output Domain: All real #’s Range: All real #’s (for linear functions) Recursive: Output to Output Domain: All real #’s ≥ 0 Range: Depends on first output value We State the domain and range of each function for each definition. Closed Form: Input Output 0 3 1 5 2 7 3 9 4 11 Recursive: We State the domain and range of each function for each definition. Closed Form: Input Output 0 5 1 9 2 13 3 17 4 21 Recursive: Group State the domain and range of each function for each definition. Closed Form: Input Output 0 -2 1 -4 2 -6 3 -8 4 -10 Recursive: All together State the domain and range of each function for each definition. Closed Form: Input Output 0 0 1 3 2 8 3 15 4 24 5 35 6 48 Recursive: Fan-and-Pick Exploring Tables Can you use each function to find the output when the input is -2? Closed Form: Input Output 0 -1 1 1 2 3 3 5 4 7 Recursive: Building Tables Building Tables Building Tables Question? Why should we worry about recursive functions? Assignment Writing Functions and Building Tables WS Bell-Ringer Given the recursive definition of a function, create an input/output table for the first 5 values starting with 0. −7, 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 3𝑛, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Algebra 2 1.2 (Part 2) Objectives: SWBAT 1) Students will use recursive definitions to build tables of data and integrate that knowledge with spreadsheets. Closed-Form Vs. Recursive Without looking think of ways that closed-form and recursive definition differ: Direct Calculation vs. Building from previous Inputs to Outputs vs. Outputs to outputs 2 or more processes vs. 1 process Domains are different Ranges are different What’s the purpose of recursive functions? Buying a Car Buying a Car Suppose you buy a new car for $15,000. You put no money down and have no interest. The bank says that you will need to make a minimum payment of $300/month. Table Function Months Balance 0 1 2 3 4 Graph Buying a Car Suppose you buy a new car for $15,000. You put no money down and sign up for a 7% interest rate. The bank says that you will need to make a minimum payment of $300/month. Table Months 0 1 2 3 4 Process Balance Months Process Balance 0 $15,000 $15, 000 1 $15,000 + 0.07 × 15,000 − 300 12 $14,787.50 2 0.07 $14,787.50 + × $14,787.50 12 − 300 3 0.07 $14,573.76 + × $14,573.76 12 − 300 4 $14,573.76 $14,358.77 Programming Functions Grab a Computer Assignment Finish the Programming Assignment page 12 (1-6, 8, 12-14) – make sure you read about difference tables before you start on page 12 Fan-and-Pick -Partner up (Partner A and Partner B)-need boards -fan out the cards with the tables facing Partner A -Partner B will pick out a card without looking at it -Partner A will cover up the bottom (answer) with another card -Partner B will write down the closed-form and recursive definition of the table -When they get it……put the card off to the side -Switch roles(you get 6 minutes) Before Cornell Notes Leave a page blank for a foldable that we will create together. Don’t copy the things in red into notes Algebra 2 1.3 Topic: Constant Difference Objectives: SWBAT 1) Make a connection with the constant difference in recursive definition and the closed form coefficient. Tool Kit Constant Difference Slope y-intercept Closed-Form and Recursive Connection Create the recursive definition of the table below. In (n) Out, f(n) 0 3 1 8 2 13 3 18 4 23 Recursive: 3, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 5 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Today we are going to look at an extra column of the Input/Output tables……this will help guide us to a connection between recursive and closed-form Input, n Output, f(n) ∆ 0 3 5 1 8 5 2 13 5 3 18 5 4 23 Warning! This only works when the input goes by 1 unit. This is called the constant difference (or delta) because the difference from one output to the next is constant Exploring-the table and recursive definition Say your looking for 𝑓(4) and all you know is the recursive definition. 𝑓 4 =𝑓 3 +5 But to know 𝑓(3) you need to know 𝑓(2). So, that means you need the recursive definition again. 𝑓 3 =𝑓 2 +5 Now if I combine those two steps together: 𝑓 4 = 𝑓 2 + 5 + 5. Two steps, adding two fives. Let’s keep going…..if you want 𝑓(2), you need 𝑓(1). 𝑓 2 =𝑓 1 +5 But to know 𝑓(1) you need to know 𝑓(0). So, that means you need the recursive definition again. 𝑓 1 =𝑓 0 +5 Now if I combine all those 4 steps: 𝑓 4 = 𝑓 0 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5. Four steps of adding 5 to the beginning. To simplify that instead of adding 5 four times…..do it this way 𝑓 4 =𝑓 0 +4∙5 The definition tells me that 𝑓 0 = 3, so 𝑓(4) is 3 plus 4 times 5. Does it work? Making the connection Using the last exploration Find 𝑓(17) That means 3 (𝑓(0)) plus 17 fives or just 3 + 17 ∙ 5. Now lets make that into a Closed-Form Definition of the Function 𝑓 𝑛 = 5𝑛 + 3 Does it Work? Find: 𝑓 15 𝑓 15 = 78 Closed-Form and Recursive Connection Create the recursive definition of the table below. Input, n Output, f(n) ∆ 0 -23 9 1 -14 9 2 -5 9 3 4 9 4 13 9 5 22 9 6 31 Recursive: −23, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 9, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Now fill out the difference column. Closed-Form-previous table To get 𝑓(6) I would need to add 9 to 𝑓(0) 6 times….looks like this: 𝑓 6 = −23 + 6 ∙ 9 Because I need to add 6 steps of 9 to the 𝑓(0), the beginning. Well I don’t like it that way: 𝑓 6 = 6 ∙ 9 − 23 And to find 𝑓 And to find 𝑓 And to find 𝑓 And to find 𝑓 And to find 𝑓 5 4 3 2 1 = 5 ∙ 9 − 23 = 4 ∙ 9 − 23 = 3 ∙ 9 − 23 = 2 ∙ 9 − 23 = 1 ∙ 9 − 23 So, the closed-form would be 𝑓 𝑛 = 9𝑛 − 23 Notice the 9 comes from the constant difference and the -23 comes from the value at 𝑓 0 . Making the Connection Input, n Output, f(n) ∆ 0 -23 9 1 -14 9 2 -5 9 3 4 9 4 13 9 5 22 9 6 31 The recursive is adding 9 to previous output (constant different. −23, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 9, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 Notice: -23 is the value of the function (output) when n = 0 (or x(input), we could say) The closed-form is 𝑓 𝑛 = 9𝑛 − 23 -the 9 comes from the constant difference -and the -23 came from when the input is 0 Can you see the connection????? Something you have seen before 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 What is this? Yes, slope-intercept form. What is the m? Yes, the slope. What is the b. Yes, the y-intercept. What is the x-coordinate at the y-intercept? Yes, 0. Going back to Definition of a Function Input, n Output, f(n) ∆ 0 -7 -3 Lets Graph these points and see what it creates: (0, -7) (1, -10) 1 -10 -3 2 -13 -3 3 -16 -3 4 -19 (2, -13) (3, -16) (4, -19) Graphing Grab a computer and go to www.desmos.com. Go to tables of data Go to add item and put information into table Fill out table You may have to zoom out to see what it creates -Go to next slide after everyone has computer and information put in Look at this table in recursive definition: −7, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 − 3, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 The n’s are our inputs (x-values) so when n (or x) = 0 the output (y-value) is -7…….so would that be the y-intercept? What is the slope of your graph? −3 Every time it runs 1 it falls 3 or 1 𝑜𝑟 − 3. How does the delta column relate to this? Does this stay CONSTANT throughout the whole graph? Now write the slope-intercept form of this graph: 𝑦 = −3𝑥 − 7 Could this be our closed-form of it? 𝑓 𝑛 = −3𝑛 − 7 Does it work? When the input is 0, then the output will be the y-intercept. Input, n Output, f(n) ∆ 0 -7 -3 1 -10 -3 2 -13 -3 3 -16 -3 4 -19 So the constant difference is the slope Fill out the missing pieces and then graph information Input Output ∆ -3 -3 2 -2 -1 2 -1 1 2 0 3 2 1 5 After graphing, answer these questions with your group: (don’t need to write answer just discuss except for the #4) 1. What does it create? 2. What is the slope? 3. What is the y-intercept? 4. Write the recursive and closed-form of this function. Does the closed-form have any relationship with slopeintercept form? Fill out the missing pieces and then graph information Input Output ∆ 0 -3 6 1 3 6 2 9 6 3 4 15 21 6 After graphing, answer these questions with your group: (don’t need to write answer just discuss except for the #4) 1. What does it create? 2. What is the slope? 3. What is the y-intercept? 4. Write the recursive and closed-form of this function. Does the closed-form have any relationship with slopeintercept form? Fill out the missing pieces and then graph information Input Output ∆ 2 0 -4 3 -4 -4 4 -8 -4 5 -12 -4 6 -16 After graphing, answer these questions with your group: (don’t need to write answer just discuss except for the #4) 1. What does it create? 2. What is the slope? 3. What is the y-intercept? 4. Write the recursive and closed-form of this function. Does the closed-form have any relationship with slopeintercept form? Fill out the missing pieces and then graph informationwarning the inputs don’t go by 1 unit and the table doesn’t’ start at 0. Input Output ∆ -5 8 4 -3 12 4 -1 16 4 1 20 4 3 24 After graphing, answer these questions with your group: (don’t need to write answer just discuss except for the #4) 1. What does it create? 2. What is the slope? 3. What is the y-intercept? 4. Write the recursive and closed-form of this function. Does the closed-form have any relationship with slopeintercept form? Fill out the missing pieces and then graph informationwarning the input doesn’t start at 0. Input Output ∆ -1 6.5 1 2 0 7 1 2 1 7.5 1 2 2 8 1 2 3 8.5 After graphing, answer these questions with your group: (don’t need to write answer just discuss except for the #4) 1. What does it create? 2. What is the slope? 3. What is the y-intercept? 4. Write the recursive and closed-form of this function. Does the closed-form have any relationship with slopeintercept form? Assignment page 19 (1-8, 10-14, 16-17) Algebra 2 1.4 Topic: Slope Objectives: SWBAT 1) Link new information of linear functions to existing knowledge of y = mx + b. Foldable Ways to say domain: Input x-values x n What goes in independent variable x-axis Ways to say range: Output y-values y f(n) What comes out dependent variable y-axis Old Information Copy the table. -2 -7 -1 -4 0 -1 1 2 2 5 3 8 Recursive: Write the slope-intercept form of this line. Snap Shot: Graph −2, −7 −1, −4 0, −1 1,2 Fill out the 2,5 ∆ column. 3,8 Closed-form: What did it create? What is the slope of this graph? Where does it cross the yaxis? Good Quiz Questions What type of function is formed when there are constant differences? What is the constant difference to the function? What is f(0)? What is its significance? What does domain mean? What does range mean? What is a closed form function? What is a recursive function? What are the 4 differences between closed and recursive functions? Exploration of the Constant Difference 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 ∆ = 𝑆𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 = Copy the table below. In Out 0 1 22 2 3 4 10 ∆ 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑦 = 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑥 Not much information but can get plenty from it (ME) In Out -5 9 -2 3 Find the slope or constant change. Could you find the closed-form from this information? 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑦 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 ∆ = 𝑆𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 = = 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑥 Not much information but can get plenty from it (WE) In Out 2 14 7 44 Find the slope or constant change. Could you find the closed-form from this information? 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑦 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 ∆ = 𝑆𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 = = 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑥 Not much information but can get plenty from it (TWO) In Out -1 8 5 11 Find the slope or constant change. Could you find the closed-form from this information? 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑦 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 ∆ = 𝑆𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 = = 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑠 Δ𝑥 Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up When the input is 4 the output is 21. When the input is 12, the output is 37. What is the slope? What is the output when the input is 0? What is the significance of this value? Can you find the closed-form? Stand Up, Board Up, Pair Up Find slope, Find f(0), Write Closed-form In Out 3 6 18 In Out -2 -6 8 4 11 Assignment Pg. 24 (1-15) QUIZ NEXT CLASS!!! 3-Column Assessment The table below represents a linear function. Find the slope ∆ , f(0), and Closed-form of the following table. In, n Out, f(n) 14 1 26 7 Algebra 2 1.5(Part 1) Topic: Second Difference Objectives: SWBAT 1) Use the difference column to decide what type of function can fit a table. 2) Discover the meaning of differences beyond the first ∆. Use that info to write rules for higher order functions. Tool Kit Linear Function Polynomial Terms Coefficient Leading Coefficient Quadratic Function Terminology Terms – are the parts that make up an expression or equation (multiplication glues things together) Coefficient – the number in front of a variable (it is the numerical factor of a term) Example: 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 9 Find the ∆, Find f(0), and Find the Closed-Form ∆: Input, n Output, A(n) 0 0 1 2 2 4 3 6 4 8 𝐴 0 : 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: How can you tell this is a linear function? Find the ∆, Find f(0), and Find the Closed-Form Input, n Output, C(n) 0 2 1 1 2 0 3 -1 4 -2 ∆: 𝐶 0 : 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: How can you tell this is a linear function? Find the ∆, Find f(0), and Find the Closed-Form Input 0 1 2 3 4 Output -3 2 7 12 17 ∆: 𝑓 0 : 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: How can you tell this is a linear function? Find the ∆, Find f(0), and Find the Closed-Form Input, n Output, B(n) 0 0 1 2 2 6 3 12 4 20 ∆: 𝐵 0 : 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: How can you tell this is not a linear function? Find the ∆, Find f(0), and Find the Closed-Form Input Output 0 6 1 12 2 20 3 30 4 42 ∆: 𝑓 0 : 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: How can you tell this is not a linear function? Problem from 1.2 The table below represents the function 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏. Fill out the outputs for the corresponding inputs and then fill out the ∆ column. Input (𝒙) Output 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝒂𝒙 + 𝒃 ∆ 0 𝑏 𝑎 1 𝑎+𝑏 𝑎 2 2𝑎 + 𝑏 𝑎 3 3𝑎 + 𝑏 𝑎 4 4𝑎 + 𝑏 Ways to tell if it is a linear function: The difference from one output to another output is constant…….meaning it is the same throughout the whole table (per input) The highest degree (power) of the variable is 1 in the polynomial you created from the Closed-Form Input, n Output, C(n) 0 2 1 1 2 0 3 -1 4 -2 ∆: -1 𝐶 0 :2 𝐶𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 − 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑚: 𝑓 𝑛 = −𝑛 + 2 Extending the Differences In Out ∆ ∆𝟐 0 1 1 2 1 2 3 2 2 5 5 2 3 10 7 4 17 Terminology Leading Coefficient – is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree(power) Quadratic Function - a polynomial with a degree of 2 Example: 𝑓 𝑥 = 4𝑥 2 + 9𝑥 − 15 Second Difference Needed The table below represents the function 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐. Fill out the outputs for the corresponding inputs and then fill out the ∆ column. Does it come out constant? In Out ∆ ∆𝟐 (𝒙) 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒃𝒙 + 𝒄 0 1 2 3 4 𝑐 𝑎+𝑏 2𝑎 𝑎+𝑏+𝑐 3𝑎 + 𝑏 2𝑎 4𝑎 + 2𝑏 + 𝑐 5𝑎 + 𝑏 2𝑎 9𝑎 + 3𝑏 + 𝑐 7𝑎 + 𝑏 16𝑎 + 4𝑏 + 𝑐 Input Output 0 6 1 12 2 20 3 30 4 42 Linear or Quadratic?? In Out 0 8 1 11 2 16 3 23 4 32 ∆ ∆𝟐 Linear, Quadratic, or Something else?? In Out 0 5 1 6 2 13 3 32 4 69 ∆ ∆𝟐 ∆𝟑 Assignment page 34 (3-5, 7, 13, 17) #5 - pick an equation where the leading coefficient ≠ 1 and has more than 1 term Algebra 2 1.5(Part 2) Topic: Writing Quadratic Functions Objectives: SWBAT 1) Discover the meaning of differences beyond the first ∆. Use that info to write rules for additional functions. Taking a Look Back The table below represents the function 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐. Fill out the outputs for the corresponding inputs and then fill out the ∆ column. Does it come out constant? In Out ∆ ∆𝟐 (𝒙) 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒃𝒙 + 𝒄 This will help us with writing a Quadratic Function 0 1 2 3 4 𝑐 𝑎+𝑏 2𝑎 𝑎+𝑏+𝑐 3𝑎 + 𝑏 2𝑎 4𝑎 + 2𝑏 + 𝑐 5𝑎 + 𝑏 2𝑎 9𝑎 + 3𝑏 + 𝑐 7𝑎 + 𝑏 16𝑎 + 4𝑏 + 𝑐 What you should have noticed The 𝑓(0) is the 𝑐. The ∆2 is twice as much as the leading coefficient 𝑎 . The ∆ of 𝑓 1 and 𝑓 0 is equal to 𝑎 + 𝑏. Taking a Deeper Look The table below represents the function, 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 5. Find the outputs for the corresponding inputs. Find the ∆ and ∆2 . Then relate the things you find with the 𝑎 − 𝑙𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑐𝑜𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡, 𝑏 − 𝑚𝑖𝑑𝑑𝑙𝑒 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑐𝑜𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡, and 𝑐 − 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡. In (𝒙) Out 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝟑𝒙𝟐 + 𝟒𝒙 + 𝟓 ∆ ∆𝟐 5 7 6 1 12 13 6 2 25 19 6 3 44 25 4 69 0 Foldable Steps Step #1 -Find the 𝑓 0 value…this is your 𝑐 − 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡. Step #2 -Find the ∆ and ∆2 ….the ∆2 is twice your 𝑎 − 𝑙𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑐𝑜𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡….∆2 ÷ by 2 Step #3 -Use your ∆ between 𝑓 1 and 𝑓 0 …this is your 𝑎 + 𝑏, use this to find your 𝑏 − 𝑚𝑖𝑑𝑑𝑙𝑒 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑐𝑜𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 Step #4 -Write your function in the form, 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐, with all the missing pieces Honors Writing the Recursive Definition of a Quadratic Function Step #1 -Find your ∆ and ∆2 Step #2 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + ∆2 𝑛 − 1 + ∆(𝑓 1 − 𝑓(0)), 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 𝑜𝑟 < 𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 Together Fill out table…..figure out if it is linear or quadratic then write the function that represents the table Input Output 0 -2 1 0 2 16 3 46 4 90 ∆ ∆𝟐 Your Turn Fill out table…..figure out if it is linear or quadratic then write the function that represents the table Input Output 0 -6 1 1 2 14 3 33 4 58 ∆ ∆𝟐 One more Fill out table…..figure out if it is linear or quadratic then write the function that represents the table Input Output 0 -5 3 -4 6 -3 9 -2 12 -1 ∆ ∆𝟐 Group Activity Person #1 Person #2 Person #3 Person #4 In Out In Out In Out In Out 0 10 0 -8 0 -1 0 11 1 17 1 -13 1 7 1 9 2 32 2 -16 2 21 2 17 3 55 3 -17 3 41 3 35 4 86 4 -16 4 67 4 63 Answers-Closed-Form #1 𝑓 𝑥 = 4𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 10 #2 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 − 6𝑥 − 8 #3 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 − 1 #4 𝑓 𝑥 = 5𝑥 2 − 7𝑥 + 11 Answers-Recursive-Honors #1 −10, 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 8 𝑛 − 1 + 7, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 −8, 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 2 𝑛 − 1 − 5, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 −1, 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 6 𝑛 − 1 + 8, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 11, 𝑓 𝑛 = 𝑓 𝑛 − 1 + 10 𝑛 − 1 − 2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 = 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑛 > 0 #2 𝑓 𝑛 = #3 #4 Assignment page 34 (1-2, 10, 14-15) Algebra 2 1.6 Topic: Gathering Data Objectives: SWBAT 1) Decide whether a linear function reasonably represents a data set. Warning!! You will be having a project due for Unit 1 over gathering data and making connections with the data Tool Kit Correlation Positive Correlation Negative Correlation Line of Best Fit Balance Point Linear Regression Point-Slope Form Terminology Correlation -The word correlation is made of CO-(meaning “together”) and RELATION. Coming to the conclusion it means finding a relationship between two or more things…….(in our case inputs-outputs) Positive Correlation -a correlation is positive if values increase together Negative Correlation -a correlation is negative if one value decreases as the other increases Line of Best Fit -is a line that is drawn through the data on a scatter plot to describe the trend of the data Linear Regression -a statistical procedure in which a straight line is established through a data set that best represents a relationship between the two sets of data Outlier -a data point that is far away from the rest and looks like it doesn’t belong in the data Point-Slope Form -if given a point ℎ, 𝑘 that is on a line and given the slope 𝑚 of that line, the following equation can be used to find the equation of the line: 𝑦 − 𝑘 = 𝑚(𝑥 − ℎ) Example: A line passes through the point 5, −3 and has a slope of -5. Find the equation 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 of the line. Me, We, Two, You Given the point 4,3 and the slope 2. Find the equation of the line that contains this point and has this slope. Given the point −1,0 and the slope 2. Find the equation of the line that contains this point and has this slope. Given the point −12, −5 and the slope 4. Find the equation of the line that contains this point and has this slope. 1 Given the point 12, −5 and the slope . Find the equation of 2 the line that contains this point and has this slope. Levels of Correlation Ice Cream Sales vs Temperature Temperature °C Ice Cream Sales 14.2° $215 16.4° $325 11.9° $185 15.2° $332 18.5° $406 22.1° $522 19.4° $412 25.1° $614 23.4° $544 18.1° $421 22.6° $445 17.2° $408 Conclusion: (Making a connection)…The data above has a high positive correlation because as the temperature increases the sales in ice cream increases as well. Partner Exploration Finding the Line of Best Fit by Hand -Find a balance point….means to find the average of the inputs 𝑥 − 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠 and the average of the outputs 𝑦 − 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠 …this is called point 𝑥, 𝑦 -Find the average of the ∆′ 𝑠 (this will be your average slope) -Plug information into the point-slope form using 𝑥, 𝑦 as your point and your average of the ∆′ 𝑠 as your slope Letting the Calculator do the Work -Make sure Diagnostics are turned on 𝑆𝑇𝐴𝑇 → 𝐸𝐷𝐼𝑇 → 1: 𝐸𝐷𝐼𝑇 … → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝐿1 CLEAR L1: Push the up arrow→ 𝐶𝐿𝐸𝐴𝑅 → 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 Enter your rolls in L1 Clear L2 Enter Totals in L2 2nd Quit Continued…. 𝑆𝑇𝐴𝑇 → 𝐶𝐴𝐿𝐶 → 4: 𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑅𝑒𝑔 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝐿1 , 𝐿2 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑅𝑒𝑔 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑎 = Slope 𝑏 = y-intercept 𝑟 2 = Coefficient of Determination 𝑟 = Correlation Coefficient -the 𝑟 value appears only with linear functions. It tells you if the correlation is positive or negative and how strong…..closer to +1 the more stronger positive correlation….closer to -1 the more stronger negative correlation -the 𝑟 2 value tells you how closely the line matches the data – called the coefficient of determination, it is a percentage of points that are explained by the equation Graphing Investigation with Calculator(Dice Roll) Make sure Scatter Plot is on 𝑌 =→ 𝑢𝑝 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 → 𝑃𝐿𝑂𝑇 1 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 Window Xmin: Xmax: Xscal: Ymin: Ymax: Yscal: 0 20 1 0 120 5 Now Let the Computer Do the Work Assignment Point-Slope WS Fitting Lines to Data (Olympics) • Look at the table and scatter plot on page 46 • What does the table of data display? • What type of function does the scatter plot most closely represent? • What type of correlation does the data have? Positive/Negative? How can you tell? Letting the Calculator do the Work -Make sure Diagnostics are turned on 𝑆𝑇𝐴𝑇 → 𝐸𝐷𝐼𝑇 → 1: 𝐸𝐷𝐼𝑇 … → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝐿1 CLEAR L1: Push the up arrow→ 𝐶𝐿𝐸𝐴𝑅 → 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 Enter the years of the Olympics in L1 Clear L2 Enter the times into L2 2nd Quit Continued…. 𝑆𝑇𝐴𝑇 → 𝐶𝐴𝐿𝐶 → 4: 𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑅𝑒𝑔 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝐿1 , 𝐿2 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑅𝑒𝑔 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏 𝑎 = Slope (-.3939854136) 𝑏 = y-intercept (996.023809) 𝑟 2 = Coefficient of Determination (.794626912) 𝑟 = Correlation Coefficient (-.8914184831) Line of Best Fit: 𝑦 = −.3939854136𝑥 + 996.023809 -the 𝑟 value appears only with linear functions. It tells you if the correlation is positive or negative and how strong…..closer to +1 the more stronger positive correlation….closer to -1 the more stronger negative correlation -the 𝑟 2 value tells you how closely the line matches the data – called the coefficient of determination, it is a percentage of points that are explained by the equation Questions? Why are there two breaks in years for the Olympics? (19121920 & 1936-1948) Why do you think there was a huge drop from 1896 to 1900? Why do you think we keep getting faster and faster? Could we use this line of best fit (function) to predict what times would be in the future? Why? or Why Not? What would be the time in 2020 if we keep going at this trend? Graphing Investigation with Calculator (Olympics) Make sure Scatter Plot is on 𝑌 =→ 𝑢𝑝 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 → 𝑃𝐿𝑂𝑇 1 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 → 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛 𝑎𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑤 Window Xmin: Xmax: Xscal: Ymin: Ymax: Yscal: 1850 2030 1 150 300 100 Modeling Motion Questions? What is the path of ball as it travels through the air? What function does this most closely resemble? What information do we need to have to model this function? Input Output 80 0 1 70 18 33 60 36 54 50 54 68 40 67 72 30 Series1 71 73 20 76 73 10 80 73 0 93 69 -10 108 61 -20 121 48 -30 135 32 149 10 163 -16 0 50 100 150 200 Let the Calculator do the Work 𝑆𝑇𝐴𝑇 → 𝐶𝐴𝐿𝐶 → 5: 𝑄𝑢𝑎𝑑𝑅𝑒𝑔 → 𝐿1 , 𝐿2 → 𝐸𝑁𝑇𝐸𝑅 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 𝑎 = −.0120712664 𝑏 = 1.849039066 𝑐 = 2.464304234 𝑟 2 = .9993252846 QuadReg: 𝑦 = −.0120712664𝑥 2 + 1.849039066𝑥 + 2.464304234 Predict how high up the ball would be if it was 20 units away from you. What Function are You? Unit1 Project