old age power point
advertisement

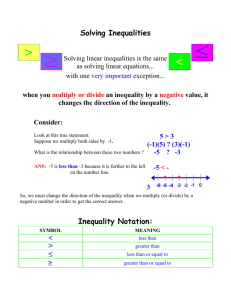
Main Menu Defining Old Age Employment Aging of Population Life Expectancy Inequality Marital Status Sources of Income Death Staying Active How do we define old age? • Chronological Age: – In the United States, 65 is considered old because people can receive Social Security benefits and Medicare; however, the eligibility age has risen for some to 67 – Does this mean old age now begins at 67? – In order to join the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), a member has to be 50. – Should 50 be considered old age? • Older Age is divided into 3 categories based on chronological age: – Young old: ages 65-74 – Middle old: ages 75-84 – Oldest old: ages 85-older Defining Old Age • Functional Age: – One is defined as being old based on how he/she looks and what he/she can do – Does this mean a women (age 75) who can swim five laps in a pool is younger than a man (age 40) who can swim only one lap? – Cosmetic surgery can alter the way people look, thus, altering their appearance – Three categories of functional age: • Well Elderly • Somewhat impaired • Frail Elderly • Subjective Age: – Is concerned with how the individual defines themselves – How one perceives themselves in age is greatly dependent on one’s functional age – The two most important factors in determining subjective age are: • One’s activity level • One’s health How has the population aged over time? Aging of the Population • 1900: – 3.1 million older adults – About 1 of every 25 people – Approximately 4% of population • 2002: – 35+ million older adults – About 1 of every 8 people – Approximately 13% of population • 2000: – – – – – 15% of whites 65+ 8.2% of blacks 65+ 7.8% of Asians and Pacific Islanders 65+ 6.0% of American Indians and Native Alaskans 65+ 4.9% of Hispanics 65+ • The United Nations Typology of Aging: – Young Country – Mature Country • Between 4%-7% of the population is 65+ • Less than 4% of the population is 65+ – Aged Country • More than 7% of the population is 65+ • Population Pyramids: – http://www.census.gov/ipc/ww w/idbpyr.html – Is the United States a young, mature, or old country? Who lives longer? • Increase in population of those 65+ is due to an increase in life expectancy • Life expectancy is defined as the average number of years people in a given population can expect to live • Who lives longer, men or women? Life Expectancy • Leading causes of death in 1900: – Pneumonia and influenza – Tuberculosis – Gastritis, enteritis, colitis • Leading causes of death in 1998: – Cardiovascular disease – All cancers – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease • Today, more older adults suffer from chronic illnesses such as cancer, diabetes, arthritis, and osteoporosis due to improvements in medicine/technology and the decline in parasitic diseases • Who do you think suffers from more chronic illnesses, men or women? Who spends more time in widowhood? • • • A larger percentage of women are widows due to the shorter life expectancy of their male partners In addition, widowed men are seven times more likely to remarry than widowed women Why are women less likely to remarry after the death of a spouse than their male counterparts? Sources of Income for Older Adults in 2000 Social Security Pensions Savings/Assets Inequality in Old Age • Theory of Cumulative Disadvantage: – • A theory that people who begin life with greater resources continue to have opportunities to accumulate more of them while those who begin with few resources fall further behind What group/s are at a an economic disadvantage in old age? 1. 2. Women Minorities • Gender Inequality: – Women have lower incomes than men, thus receiving less in Social Security Benefits – Women have unstable work histories due to child labor – Women are less likely than men to receive money from pensions: • 30% of white women • 10% black women • 13% Hispanics women – Women work in jobs that lack pension plans Inequality in Old Age • Race/Ethnic Inequality: – 2001 poverty level: • 8.9% of elderly whites • 21.9% of elderly blacks • 21.8% of Hispanics – African Americans: • due to discrimination, have experienced higher rates of unemployment and are payed less • Work in more blue-collar, service industry jobs • Hispanics: – 1995 Poverty Statistics • 31.7% of Puerto Ricans • 23.1% of Mexicans • 12.1% of Cubans – Mexicans have the lowest rates of health insurance due to migrant work – Many are unable to receive Social Security Benefits because they are illegal aliens • Native Americans: – Have this highest unemployment rates of all minorities – Most poorly educated of all minorities How do older adults stay active? • Volunteering • Exercising • Religious Participation Employment • Employment: – In 2001, 13.1% of Americans 65+ were in the labor force • 2.5 million men • 1.8 million women • Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967: – Banned discrimination against workers aged 40-65 and forbade employers to fire, demote, or reduce the salaries of older workers without good cause • Bridge Jobs: – are jobs which span the period between full-time employment and permanent retirement • Contingent Work: – An arrangement under which workers do not become a part of a firm’s permanent workforce, but are hired only to do a specific job on a parttime or temporary basis • Retirement: – Duties: • Avoid full time employment • Sometimes provide free services • Live within income • Do not become a burden to family and society – Crisis theory – views the occupational role as the major source of personal validation Stages of Dying • Elizabeth Kubler- Ross: – Stages of Dying 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Denial Anger Bargain Depression Acceptance • Hospice: – Goal is to allow the terminally ill to die easily and in peace, without pain, in their own homes, special units of hospitals, or hospice facilities • Active Euthanasia: – Occurs when a physician, close friend, or relative helps an ill or disabled person terminate his or her life • Passive Euthanasia: – Withdrawing medical treatment from the hopelessly ill