Unit 3 PRAC SAC 2a 2014
advertisement
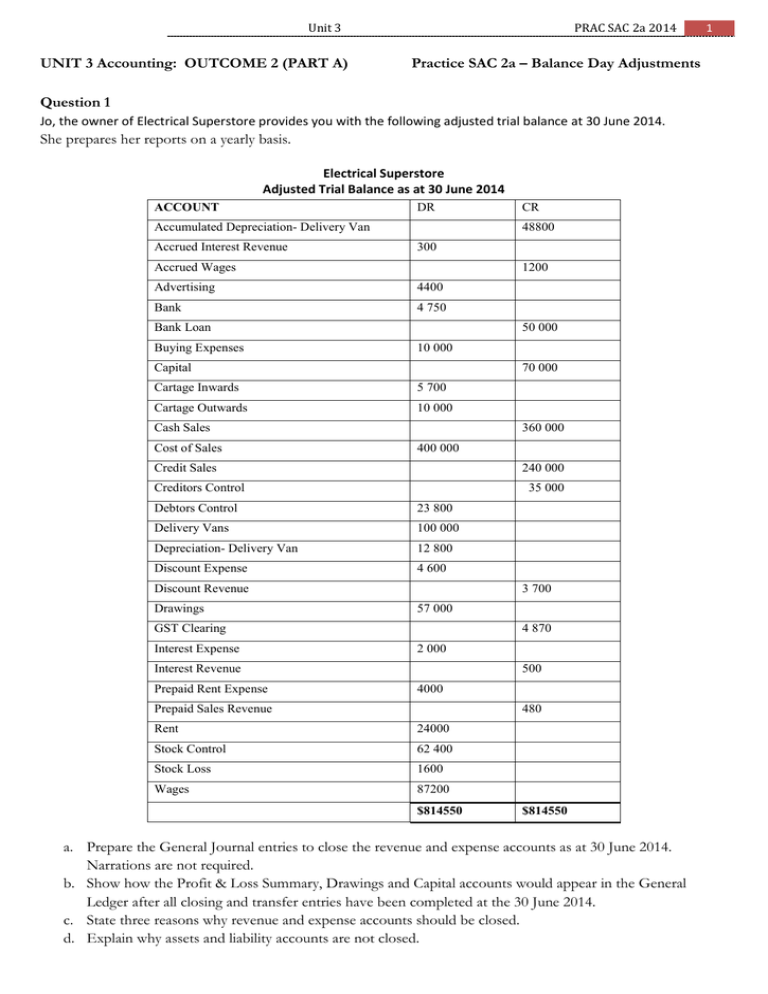
Unit 3 UNIT 3 Accounting: OUTCOME 2 (PART A) PRAC SAC 2a 2014 Practice SAC 2a – Balance Day Adjustments Question 1 Jo, the owner of Electrical Superstore provides you with the following adjusted trial balance at 30 June 2014. She prepares her reports on a yearly basis. Electrical Superstore Adjusted Trial Balance as at 30 June 2014 ACCOUNT DR Accumulated Depreciation- Delivery Van Accrued Interest Revenue 48800 300 Accrued Wages 1200 Advertising 4400 Bank 4 750 Bank Loan Buying Expenses 50 000 10 000 Capital 70 000 Cartage Inwards 5 700 Cartage Outwards 10 000 Cash Sales Cost of Sales 360 000 400 000 Credit Sales 240 000 Creditors Control 35 000 Debtors Control 23 800 Delivery Vans 100 000 Depreciation- Delivery Van 12 800 Discount Expense 4 600 Discount Revenue Drawings 3 700 57 000 GST Clearing Interest Expense 4 870 2 000 Interest Revenue Prepaid Rent Expense CR 500 4000 Prepaid Sales Revenue 480 Rent 24000 Stock Control 62 400 Stock Loss 1600 Wages 87200 $814550 $814550 a. Prepare the General Journal entries to close the revenue and expense accounts as at 30 June 2014. Narrations are not required. b. Show how the Profit & Loss Summary, Drawings and Capital accounts would appear in the General Ledger after all closing and transfer entries have been completed at the 30 June 2014. c. State three reasons why revenue and expense accounts should be closed. d. Explain why assets and liability accounts are not closed. 1 Unit 3 PRAC SAC 2a 2014 2 Question 2 Rita owns and operates Glamour Bags, a small business selling designer bags. The accountant provided the following Pre-Adjustment Trial Balance (extract) as at 30 September 2014. Glamour Bags Pre-Adjustment Trial Balance (extract) as at 30 September 2014 Account Accumulated Depreciation – Shelving Prepaid Rent Expense Shelving Stock Control Debit Credit 4 290 11200 10 800 35 000 The accountant also noted the following. Reports are prepared on a quarterly basis. Shelving costing $3 300 including GST was purchased using cash on 1 September 2014. Shelving is depreciated at a rate of 10% per annum using the straight line method. Rent is paid six months in advance on 1 August and 1 February each year. The payment made on 1 August 2014 was $9 600 plus GST. On 16 September 2014, Rita took 1 bag from the store as a gift for her sister but this was not recorded. The bags cost the business $500 plus GST each and sell for $1000 plus GST each. Electricity of $400 plus GST for September from Origin Energy will not be paid until the end of October 2014. The stocktake determined $35 200 worth of stock on hand as at 30 September 2014. a. Calculate the depreciation expense of Shelving for the quarter ended 30 September 2014. b. Prepare the General Journal entries required on 30 September 2014. Narrations are not required. c. Explain the effect on the Income Statement and the Balance Sheet if the entry for the electricity was not recorded. d. Show how rent expense and prepaid rent accounts would appear in the General Ledger of Glamour Bags as at the 30 September 2014 after all closing and balancing entries have been made. e. Show how depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation accounts would appear in the General Ledger of Glamour Bags as at the 30 September 2014 after all closing and balancing entries have been made. f. With reference to one accounting principle justify why balance day adjustments are made. Provide two examples to support your answer. g. With reference to one qualitative characteristic justify why balance day adjustments are made. Provide two examples to support your answer. On 31 October 2014 cheque 568 was used to pay Origin Energy $990 including GST. h. Record this cheque in the Cash Payments Journal. Unit 3 PRAC SAC 2a 2014 3 Question 3 Noah owns a business selling solutions to accounting problems. His journals have been prepared, however, the following adjustments are yet to be recorded at 31 March 2014. A debtor Amy was declared bankrupt. Of the $3000 debt owed to Noah, only 10 cents in every dollar will be received. Discount Revenue of $100 was incorrectly credited to the Discount Expense account. A payment of $550 for wages was incorrectly entered as $505 A physical stock take revealed a stock loss of $250 The payment of $200 to Creditor -Hussein was incorrectly recorded in the Creditor-Hairy account. The payment of a water bill , $400 plus $40 GST was incorrectly recorded as wages of $440 A payment of $700 for Delivery Inwards was incorrectly debited to Delivery Outwards. The $70 GST was correctly posted. a. Prepare the General journal entries to record the necessary corrections or adjustments. Narrations are not required. Question 4 A business purchased equipment on 1 January 2011 for $24 000 plus GST. The equipment had an estimated useful life of four years and a residual value of $3 000. The business prepares reports annually on 30 June. a. Assuming the business used the reducing balance method at 30% per annum, calculate the depreciation expense for the year ended 30 June 2012. b. On 30 June 2013, the Balance Sheet reported the equipment as follows. Non-Current Assets (extract) $ $ Equipment 24 000 Less Accumulated Depreciation of Equipment 14 004 9 996 Explain what the carrying value of $9 996 in the Balance Sheet represents. c. Calculate what the carrying value of the equipment would have been at 30 June 2013 if the straight line method of depreciation had been used each year. d. Discuss the appropriate method of depreciation to use for the equipment. Unit 3 PRAC SAC 2a 2014 Question 5 The transactions provided below for Best Timber Supplies relate to an order for timber placed by a customer, James Hay, to the value of $3500 plus GST (cost $1500 plus GST). • 28 June 2014: A deposit of $500 was received from James Hay (Receipt 235). • 2 July 2014: The goods were delivered to James Hay (Invoice 121) The business prepares reports monthly. a. Record the deposit into the appropriate journal. b. Explain how the deposit received would be classified in the Balance Sheet as at 30 June 2014. c. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale of the timber on the 2 July 2014. Question 6 On 30 June 2014 the following ledger account was prepared by the accountant. Accrued Interest Date 2014 June 30 Cross-reference Bank (2) $ 400 Date 2014 Cross-reference $ June 1 Balance (1) June 30 Interest (3) 400 800 a. Explain how the Accrued Interest would be reported in the Balance Sheet on the 1 June 2014. b. Explain what each entry in the Accrued Interest account represents. c. Explain the impact of transaction (3) on the Income Statement. Question 7 On 30 June 2014 the following ledger account was prepared by the accountant. Accrued Interest Date 2014 June 1 June 30 Cross-reference Balance (1) Interest (3) $ 400 800 Date 2014 June 30 Cross-reference Bank (2) $ 400 a. Explain how the Accrued Interest would be reported in the Balance Sheet on the 1 June 2014. b. Explain what each entry in the Accrued Interest account represents. c. Explain the impact of transaction (3) on the Income Statement. 4 Unit 3 PRAC SAC 2a 2014 5 Question 8 On 1 January 2013 Matt set up a business by contributing the following assets and liabilities. Matt commenced Matt’s Plant Supplies by obtaining a business loan from Bank Easy for $20000. The loan is to be repaid at $4000 per year. The bank also provided an overdraft facility of $10 000 to the business. Matt contributed $3000 cash and organised payment of the advertising for the next 6 months paying $5280 (including GST) from his personal account. He also brought into the business Equipment $18 000 and Fittings $3000 and a Motor Vehicle with an original cost of $15 000, but Matt and the accountant have settled on an agreed value of $9 000 at 1 January 2014. a. Prepare the necessary journal entries.