February 7, 2007 Webinar Notes
advertisement

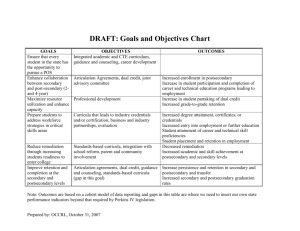
February 7, 2007 Webinar Notes • You need to phone in to the conference call number to receive audio for this program. If you experience problems, please email info@educationalpolicy.org and we’ll try and help. • Ask questions using the chat function on the right side of your screen. We will try and answer questions in order. In the chance we do not get to your question, we will provide answers online after the webinar. • The webinar will be available online for download after completion of the event. • The powerpoint file is currently online under our events page. Effective Practices Database • http://studentretention.org/epss.html EPI Retention Listserv http://www.educationalpolicy.org/retentionlistserv.html Our Objectives • Are objectives during this webinar are to provide participants with: A more comprehensive understanding of theoretical and practical reasons for student departure and success; An understanding of the barriers to student success; A framework for developing a comprehensive plan for improving student success at your institution; Data on student success and persistence at the two- and four-year levels in Canada and the U.S.; Strategies and best practices for improving student success on campus; An opportunity to create diverse networks of professionals like yourself who are committed to serving students at a high level; Motivation to improve services to all students; Learn more about our non-profit organization About the Presenter Watson Scott Swail, Ed.D. • Earned doctorate in educational policy from The George Washington University in Washington, DC. • Received his Masters in Science degree from Old Dominion University in Norfolk, VA. • Received his BA in Education from University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB. • Served as a middle school teacher for seven years in Canada and the US • Worked as policy analyst for The College Board and Senior Research Scientist at SRI International • Dissertation focused on the retention of minority students in STEM fields. Who do we serve? Number of Institutions Attended Initial Degree Goal Attendance Intensity and Continuity Delayed Enrollment Degree Goal vs. Degree Attainment Degree Attainment and Persistence Why is Retention an Important Issue? – Retention stable at 50 percent – Issues of cost and quality – Federal and state intervention Dropout and Defaults Borrowers Who Completed BA Borrowers who Dropped Out 2 In Default on Loans 22 7 Unemployed 15 0 5 10 15 20 25 When does student dropout/departure occur? After first year After second year $70,000 or greater 11 $45,000–69,999 9 12 6 16 Less than $25,000 15 5 8 16 12 5 15 Black, non-Hispanic 17 16 All four-year students 14 0 12 10 5 6 17 14 4 7 Hispanic White, non-Hispanic 7 14 7 After fourth year 2 12 $25,000–44,999 Asian/Pacific Islander After third year 9 6 10 6 7 4 13 6 20 30 5 40 50 60 The Ongoing Retention Challenge • One quarter of all students who enter postsecondary education for the first time end up at another institution before attaining a postsecondary degree. • Almost half (46 percent) of first-time students who left their initial institution by the end of the first year never came back to postsecondary education. • Students who attend full-time or whose attendance was continuous were much more likely to achieve their degree goals than other students. However, only about two-thirds of students were continuously enrolled. The Ongoing Retention Challenge • 50 percent of four-year students who did not delay entry into PSE earned their degree at their first institution, compared to only 27 percent of students who were delayed entrants. • 42 percent of students whose first-year grade point average was 2.25 or less left postsecondary education permanently. Why do Students Leave? – – – – – Academic Preparedness Campus Climate Commitment to Educational Goals and the Institution Social and Academic Integration Financial Aid Why should institutions care? – – – – Loss of revenue to the institution Poor business model Lower prestige and moral It’s the right thing to do; it’s in the mission Seven Questions for Student Retention 1. Do you understand the nature of the problem? 2. Do you know why your students leave? 3. Do you know what your institution is already doing to ameliorate these issues? 4. Do you know how effective these programs or strategies are? 5. Do you know what programs and strategies may be worth considering? 6. Do you have evidence that there exists significant support on campus to do something about this issue? 7. Do you understand the institutional change process? The Student Experience Institutional Factors The Student Experience Financial Aid Recruitment & Admissions Academic Services Student Services Curriculum & Instruction The Student Experience +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- The Student Experience Institutional Factors What is Your Triangle? The Student Experience Institutional Factors Five Components of the Student Retention Framework Top Ten Considerations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rely on proven research. Suit the particular needs of the campus. Institutionalize and become a regular part of campus service. Involve all campus departments and all campus personnel. Take into consideration the dynamics of the change process and provide extensive and appropriate retraining of staff. 6. Focus on students. 7. Ensure that the program is fiscally responsible. 8. Support institutional research in the monitoring of programs and students. 9. Be patient. 10. Be sensitive to students’ needs and target the most needy student populations.