Air Pressure & Wind
advertisement

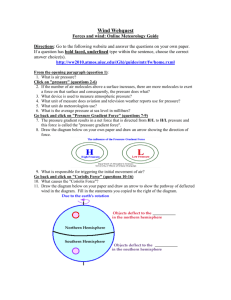
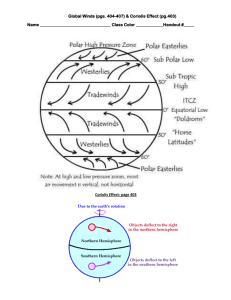
Air Pressure & Wind Air Pressure • • • • • • • Pressure exerted by weight of air above At sea level it as on average 1kg of air per square centimeter Air pressure is exerted in all directions Use barometer to measure air pressure Invented by Torricelli in 1643 Air pressure increases Hg rises Air pressure decreases Hg lowers What causes wind? • • • • Horizontal differences in air pressure Flows from high pressure to low pressure Think about opening a container of tennis balls or coffee The noise you hear is caused by air rushing from high pressure of container to lower outside pressure • Unequal heating of Earth’s surface generates pressure differences 3 Factors affect wind Pressure Difference • • • • • • Variations in air pressure are determined by barometric readings Isobars lines on a map that connect places of equal air pressure Closely spaced isobars indicate steep pressure gradient & high winds Widely spaced isobars indicate weak pressure gradient & low winds Low pressure pressure lower than area surrounding it High pressure pressure is higher than area surrounding it Pressure Difference Isobar Activity Now it is your turn to draw isobars & analyze the wind patterns. 3 factors affecting wind Coriolis Effect • • • • • • Describes how Earth’s rotation affects moving objects Deflected to the right in the North Deflected to the left in the South Affects only direction, not speed Strong the wind, strong the deflection Strongest at poles, weakest at equator 3 factors affecting wind Friction • Only important within a few km of Earth’s surface • Slow air movement, changes wind direction Highs & Lows Low system air rises and cools, forming clouds, results in precipitation High systems air sinks and warms, results in warm dry weather In Northern Hemisphere low system is counterclockwise & high system is clockwise Wind is deflected to the right because of Coriolis Effect Global Winds Warm air rises Cool air falls Creates cells of wind Westerlies blow from west to east Polar Easterlies polar high towards polar low Trade Winds winds from easterly direction between 030° https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uBqohRu2RRk Influence of Continents • Land becomes cold in winter & hot in summer • Monsoon seasonal changes in wind direction • India has large monsoons that result in rainy summers Local Winds • Land & Sea Breezes Local Winds • Valley & Mountain Breezes El Niño • • • • Normal Conditions Peruvian current flows toward equator Upwelling off the coast of Peru At the end of the year warmer currents El Niño https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FVZrw7bk1w • http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoanimations/animations/26_Nino Nina.html Assessment Questions • In the winter, large land masses often develop a seasonal • High-pressure system • Low-pressure system • Typhoon • Trade winds • Variations in air pressure from place to place are the principal cause of • Clouds • Hail • Lows • Wind • High pressure systems are characterized by • Air sinking • Air rising • Air sinking and rising at the same time • None of the above • Where is deflection of wind due to the Coriolis Effect the strongest? • Near the equator • In the mid-latitudes • Near the poles • Near the westerlies • Write a general statement relating the spacing of isobars to wind speed • How does the Coriolis Effect modify wind movement in the Northern Hemisphere? • The force exerted by the air above is called • Air pressure • Convergence • Divergence • The Coriolis effect • Explain how you would determine if an area is high or low pressure based on the isobars • Explain how a mercury barometer works. • Describe the difference between valley and mountain breezes. • Valley breezes result from the land warming during the day. This warms the air and it rises. Mountain breezes result from land cooling at night and the surrounding air cools. It sinks from the mountains down into the valley. • Explain the difference between normal and El Niño conditions. • Describe why low pressure systems typically result in clouds and precipitation. • Tip high pressure systems are high pressure because air is sinking, creating more pressure on the surface of earth. Low pressure systems are lower pressure because air is rising and relieving pressure from the surface of earth. • What are the three factors that affect wind? • Does Coriolis effect change direction, speed, or both? What about friction? • Describe which direction the following winds are moving from and where they are moving to: • Polar Easterlies • Westerlies • NE Trade Winds • SE Trade Winds