WPA Information Slideshow (5/4/2015)
advertisement

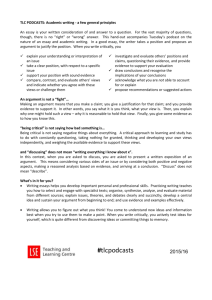
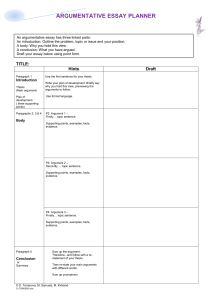
Welcome to the Writing Placement Assessment (WPA) Workshop Presented by the Department of Rhetoric and Writing Studies SDSU’s GWAR (Graduation Writing Assessment Requirement) is a Rhetorically based Writing Placement Assessment (WPA) Overall, the WPA asks students to: •Write an essay responding to a series of statements that relate directly to a reading selection in an engaging and informed way. •Write an analysis of the argument presented in the reading rather than a personal response to the topic of the article. Wondering why you have to take the WPA? Here’s some perspective to take the edge off: • At least five campuses require passing an exam. • At least four require coursework only. •About four, including SDSU, require an exam, then coursework only if necessary. • Single-essay exams range from 180 to 60 minutes. **So, think of it this way: SDSU provides students the opportunity to test out of any upper division writing courses and our assessment is a whopping 2 hours long--rather than just one hour. How the WPA is scored: 2 independent readers Score from 2-5 each Split Scores (3-4, 4-5) evaluated by a third reader Evaluated by WPA Coordinator/Chief Readers Total score of 10: Requirement fulfilled (about 15% of students taking the test, based on 2012 figures) Total score of 8: Demonstrates competency for an upper division writing course (around 55%) Total score of 6 or below: Need to take RWS 280 or 281 AND an upper division writing course (about 30%) What to do before the exam: Explore the internet for information on rhetorical strategies and rhetorical vocabulary. Some suggestions: • http://www-rohan.sdsu.edu/~gwar/understand.html •http://rhetoric.sdsu.edu/ http://rhetoric.byu.edu/ (the magical forest of rhetoric) •Google “Rhetorical Strategies” (seriously, it’s pretty informative) Write a practice essay while you time yourself! Many students say the time limit is the most challenging aspect of the assessment. While taking the WPA: Read the prompt. Identify “writing tasks” (what is the prompt actually asking you to do?) Carefully read the selection. *Underline and annotate as you read. Draft a thesis, controlling idea statement, etc. (consider creating a statement in which you articulate the overall effectiveness of the article) Plan the structure of your essay. *It need not follow the order of the tasks in the prompt. Be sure to address every component of the prompt. 6 Be aware of the time 6 These times are approximates: 15-20 minutes to read the prompt and the article Read the prompt first and underline and annotate Prewriting: List, map, or outline, thesis statement 80-90 minutes to write Don’t worry about spelling and conventions of correctness as you write 15-20 minutes to edit and proofread Make minor edits and correct any errors you find Check the time periodically; don’t count on the proctor to keep you informed What the readers are looking for: Analysis: Is your analysis of the author’s argument reasonable, credible, thorough, and well-thought out? Focus: Does the essay accurately and thoroughly address all aspects of the prompt? Organization: Do the ideas flow from one paragraph and from one sentence to another? *Make sure your essay doesn’t read like a list.* Development: Are details and specific examples used to further prove or illustrate the thesis? Grammar—Punctuation—Spelling: This is something you can do little about in the days before the test. The focus, organization, and development strategies are in your control. The WPA prompt: Craft a coherent essay (i.e. one that is not just a series of paragraph responses to the prompt) in which you respond (in an appropriate order) to all of the following components: identify and provide a brief summary of the author’s argument; describe and discuss two strategies that the author uses to support his or her argument; describe the overall structure of the reading selection and explain whether it furthers the aims of the author’s argument; discuss the premise(s) and/or assumption(s) on which the argument is based: evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing. This essay is not an “agree or disagree” exercise, nor is it intended to generate an extensive summary of the article. Responses that emphasize personal opinion or summary will not earn a passing score. To be more specific, you are being asked to: • explain the point of the author’s argument •explain how the author is using rhetorical strategies to persuade an audience • identify and explain the type of structure used • identify and explain the core premise/assumption of the article • most importantly: you must analyze and evaluate the effectiveness of each of these components. (Did this strategy/structure/premise work to convince the audience? Why/why not?) Breaking down the components of the prompt: Look at the verbs in the Prompt: Identify: Clearly label and provide examples of the strategies, structure, and assumptions used by the author. Describe, Explain, Discuss: Thoroughly explain how the author is using this information to support his/her argument. Consider the author’s motivation for utilizing this particular piece of evidence; how did he/she think it would help to further convince the readers? Evaluate: Consider the effectiveness of the devices used by the author: do these devices strengthen or weaken the argument? Why? Why not? Did this particular device help to convince the audience? Why? Why not? The introductory paragraph should (at the very least): • Identify: • the rhetorical context • the title of the article • the name of the author • the name of the publication • the author’s main claim • the intended audience • Briefly summarize: • how the author presents the argument • how the author supports the argument (a brief summary of the strategies used) • Include a thesis statement articulating why the article was/was not effective The WPA prompt: Craft a coherent essay (i.e. one that is not just a series of paragraph responses to the prompt) in which you respond (in an appropriate order) to all of the following components: identify and provide a brief summary of the author’s argument; describe and discuss two strategies that the author uses to support his or her argument; describe the overall structure of the reading selection and explain whether it furthers the aims of the author’s argument; discuss the premise(s) and/or assumption(s) on which the argument is based: evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing. This essay is not an “agree or disagree” exercise, nor is it intended to generate an extensive summary of the article. Responses that emphasize personal opinion or summary will not earn a passing score. The strategy paragraphs should (at the very least): • Identify: • at least two strategies used to support the argument • Cite: • textual evidence of the strategies • Briefly discuss: • how/why the author uses the strategies • how the strategies support the argument • Analyze: • the effectiveness of the strategies-• do they help to convince the readers? • why/why not? ?? Describe two strategies?? Strategies are moves or devices which help build and support arguments. Find two the author uses in making his or her argument: Are statistics/examples provided? Are scenarios/situations presented? Are opposing arguments refuted? Are appeals made: -To emotions (pathos)? -To logic (logos)? Are narrations, descriptions, or settings provided? Does the author use stylistic devices: repetition, alliteration, or metaphor? ?? Strategies ?? continued Does the writer of the selection: – Use descriptions? – Provide definitions? – Share personal experiences/anecdotes to appeal to emotions? – Use a concept or idea to interpret another idea? Use analogies? – This is only a partial list. Do some research on the internet to learn more terms! **In addition to identifying and describing these strategies, you must also evaluate their effectiveness (Do they “work?” Why/why not?)** The WPA prompt: Craft a coherent essay (i.e. one that is not just a series of paragraph responses to the prompt) in which you respond (in an appropriate order) to all of the following components: identify and provide a brief summary of the author’s argument; describe and discuss two strategies that the author uses to support his or her argument; describe the overall structure of the reading selection and explain whether it furthers the aims of the author’s argument; discuss the premise(s) and/or assumption(s) on which the argument is based: evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing. This essay is not an “agree or disagree” exercise, nor is it intended to generate an extensive summary of the article. Responses that emphasize personal opinion or summary will not earn a passing score. The structure paragraph should (at the very least): • Identify: • the structure used by the author • Cite: • textual evidence of the structure • Briefly discuss: • how/why the author uses this structure • how the structure moves the readers from “Point A” to “Point B” of the argument • Analyze: • the effectiveness of the structure-• was it accessible for readers? • was it appropriate for the topic? • why/why not? ?? Describe the overall structure ?? How are strategies organized in the text? How are claims in the text organized? How are examples or evidence arranged in the reading? How do the parts of the reading function? How is information “chunked” together? **In addition to identifying and describing the structure, you must also evaluate its effectiveness (Does it “work?” Why/why not?)** ?? Structure Continued ?? How does the structure affect the persuasiveness of the reading as a whole? Consider these structural relationships: •Problem/solution •Cause/effect •Compare/contrast •Action/consequence The WPA prompt: Craft a coherent essay (i.e. one that is not just a series of paragraph responses to the prompt) in which you respond (in an appropriate order) to all of the following components: identify and provide a brief summary of the author’s argument; describe and discuss two strategies that the author uses to support his or her argument; describe the overall structure of the reading selection and explain whether it furthers the aims of the author’s argument; discuss the premise(s) and/or assumption(s) on which the argument is based: evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing. This essay is not an “agree or disagree” exercise, nor is it intended to generate an extensive summary of the article. Responses that emphasize personal opinion or summary will not earn a passing score. The premise/assumption paragraph should (at the very least): • Identify: • the premise on which the argument is based • where in the text this premise is evident • Briefly discuss: • how/why the author bases the argument on this premise • how the premise strengthens/does not strengthen the argument • Analyze: • the effectiveness of the premise/assumption • would most audiences find this premise valid/reasonable? • was it appropriate for the intended audience? • why/why not? ?? Discuss the premises and/or assumptions ?? Assumptions and premises are the components of the argument that are accepted as true by both the writer and the audience. An Assumption is defined as a fact or statement taken for granted while a Premise is defined as proposition proved by argument or inference. Assumptions and premises constitute the principles, beliefs and core values the author assumes the audience holds true. Look for “obvious” things that “need no explanation,” yet are vital to the writer’s argument. **In addition to identifying and describing the assumption/premise, you must also evaluate its effectiveness (Does it “work?” Why/why not?)** The WPA prompt: Craft a coherent essay (i.e. one that is not just a series of paragraph responses to the prompt) in which you respond (in an appropriate order) to all of the following components: identify and provide a brief summary of the author’s argument; describe and discuss two strategies that the author uses to support his or her argument; describe the overall structure of the reading selection and explain whether it furthers the aims of the author’s argument; discuss the premise(s) and/or assumption(s) on which the argument is based: evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing. This essay is not an “agree or disagree” exercise, nor is it intended to generate an extensive summary of the article. Responses that emphasize personal opinion or summary will not earn a passing score. ?? Evaluate the extent to which you find the argument convincing ?? Make your own argument regarding the effectiveness of the author’s argument; NOT your stance on the topic. Use examples from the reading. Use quotations to support your analysis. *If you quote from the article, use no more than a short phrase. *Provide an analysis of the quotation, explaining how it supports your argument. Do not just summarize; respond to all parts of the questions. Address the credibility of the author. 66 Time is almost out 66 Spend 15-20 minutes proofreading. Do not proofread while writing. Do not sabotage yourself by trying to squeeze in too many re-writes. If you need to shift chunks of your writing, simply give clear directions for the readers. Look for errors you typically make. Be careful of very basic errors, such as confusion of their/they’re/there or its/it’s. 2010 Pass Rate Summary Continued General Academic Writing Tips: • Avoid referring to the author by his/her first name. • Be careful of using “you” and “like.” • Avoid using “talks about” and “says” • If you “know” something, be sure to explain how and why you know it. • Create topic sentences for your paragraphs that are attention-grabbing and informative. Avoid: “The author’s first strategy is . . .” • Don’t assume the readers will automatically know what you are trying to say. WARNING: There is no automatic formula for earning a “10” on the WPA. These essays are written by humans (you) and read by humans (university faculty). It is important to engage and interest the readers while creating a clear, concise, and effective analysis of the author’s argument. You are ultimately making an argument about the effectiveness of another author’s argument.