CP Environmental Science - Saucon Valley School District
advertisement

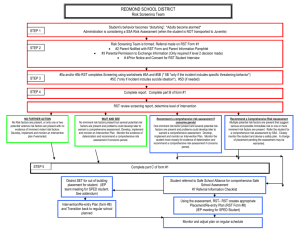
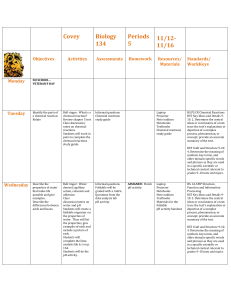
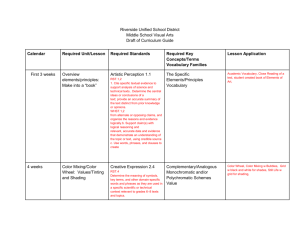
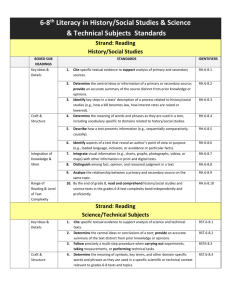
Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Course Title Grade Level Content Area Length of Course Author(s) CP Environmental Science Ninth – Tenth Grades Science Semester Tom Koch Course Description: Environmental science explains how scientists describe the workings of the environment through the study of living and nonliving factors and their interdependence. Nutrient cycles, climate, and properties of water will be examined as they relate to each other and living systems. Life will be examined from multiple system levels to grasp the interactions with each other and their environment. Evolution and its role in providing the biodiversity found on Earth will be explored as well as the state of world’s biodiversity will be examined. Finally humans’ impact upon natural ecosystems will be explored and solutions to our environmental challenges will be explored. Course Rationale: This course is meant to educate students about the environment, so that if faced with decisions that will impact their environment, they will have a thorough understanding and background to make the best decisions possible. CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 1 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Table of Contents Page 1 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 12 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21 Page 23 Page 25 Page 26 CP Environmental Science - Course Description; Course Rationale Curriculum Map Unit 1 – Introduction to Environmental Science – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; PA Science Standards; Core Literacy \ Standards for Science; Assessment Anchors; Key Unit Vocabulary Learning Objectives; Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit Unit 2 – Ecology – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; PA Science Standards; Core Literacy Standards; Assessment Anchors; Key Unit Vocabulary Learning Objectives Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit Unit 3 – Populations – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; PA Science Standards; Core Literacy Standards; Assessment Anchors; Key Unit Vocabulary Learning Objectives; Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit Unit 4 – Human Impacts – Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; PA Science Standards; Core Literacy Standards; Assessment Anchors; Key Unit Vocabulary; Learning Objectives Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit Unit 5 – Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources - Unit Description; Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings; PA Science Standards; Core Literacy Standards; Assessment Anchors; Key Unit Vocabulary; Learning Objectives Sequence of Teaching and Learning Resources for this Unit CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 2 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Curriculum Map (Semester Course) Quarter Topics covered during this time period 1 or 3 1. Introduction to Environmental Science 2. Ecology/ Evolution/ Biodiversity 2 or 4 1. Populations 2. Air, Water, and Land 3. Mineral and Energy Resources CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 3 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings PA Science Standards BIO.B.3.3.1 Applying scientific thinking BIO.B.4.1 Ecological levels of organization BIO.A.2.1 Describe the unique properties of water that support Life on Earth Key Unit Vocabulary CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Unit 1 – Introduction to Environmental Science This unit provides the foundation for the study of environmental science. It first frames environmental problems and their root causes and provides an environmental decision making process. It also goes through the scientific method to establish the process of science and the manner in which our knowledge is developed. Finally it introduces the students to the functioning of the abiotic factors in the environment How do scientists study the environment in an organized manner? What are the parts of the Earth that support life and what are their characteristics? Core Literacy Standards for Science CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-1 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-2 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-3 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-4 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-5 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-6 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-7 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-8 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-9 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1010 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1011 Assessment Anchors (if any) BIO.A.3.1 Science, ecology, hunter/ gatherer, agricultural revolution, industrial revolution, resource depletion, pollution, biodiversity, economics, developed countries, developing countries, ecological footprint, sustainability, observation, hypothesis, prediction, experiment, variable, experimental group, control group, data, correlation, geosphere, hydrosphere, crust, mantle core, , tectonic plates, chemical weathering, atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, ozone, radiation, conduction, convection, greenhouse effect, water cycle, evaporation, condensation, precipitation, salinity, fresh water, biosphere, cohesion, adhesion, boiling point, specific heat, density, freezing point Page 4 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Learning Objectives – The student will… ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Explore the tensions between societal needs and environmental protection. Read for understanding reliable and valid scientific investigation Analyze the necessity of science to further our understanding of natural phenomena Read for understanding an environmental decision making model Apply the decision making model to a hypothetical situation Read for understanding a general overview of the atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere Describe how the geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere are dynamic Explain how the dynamic Earth enables a diverse biosphere Describe the properties of water that enable it to support life on Earth Explain why carbon is an ideal element to build large organic molecules Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks 2 (chapter 1) 2 (chapter 1) Lesson Topic Understanding Environmental Science Environment and society CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Lesson Activities ● Chapter 1 and 2 pretest ● Define environmental science and list the perceived biggest environmental problems (think pair share) ● Present the transition of our society as it relates to our environmental challenges ● Students read pages 14-15 ● Post assessment pg 15 Questions 1-6 ● Read and explain “tragedy of the commons” pg 1617 ● Determine, using a real life example, how the law of supply and demand, cost/ benefit analysis and risk assessment lead to the use/nonuse of natual resources. ● Compare using a Venn diagram how developed and developing countries use natural resources ● Environmental problems in neighborhood activity pg 20 text ● Post assessment page 21 Page 5 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study 3 (chapter 1) Culminating activies 2 scientific method 1 Using an Environmental decision making model Culminating Activity The changing Earth: Geosphere 1 2-3 1 1 1 1 The changing Earth: Atmosphere The changing Earth: Hydrosphere Properties of water Culminating activity 1 Unit #1 Test CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 ● Research and write a persuasive essay explaining the importance of science in the debate about pesticide use such as DDT and environmental issues. ● Field Exploration lab pages 28-29 ● Quiz ● Read pages 31-34 describe the steps of environmental science and explain their importance. ● Present scientific habits of mind ● Compare the strengths and weaknesses of the scientific method with the correlation method of scientific inquiry ● formative assessment page 37 ● Present on statistics and models pages 38- 44 ● Formative assessment page 44 ● Read pages 45-49 ● Use the decision-making model on two different environmental issues. (show your work!) ● Formative assessment page 49 ● Inquiry Lab page 56-57 ● Make a poster (detailed on page 54 / #33) ● Present on the processes that changes the geosphere over time. ● Plate tectonic lab ● Formative assessment page 66 ● Quick lab page 70 ● Field study (see appendix B) ● Formative assessment page 72 ● Students should make simple model of the water cycle ● Explain how ocean currents help to determine climate. ● Quick LAB page 78 ● Differentiate the availability and distribution of fresh and salt water ● Properties of water Lab ● Quiz properties of water ● ● Exploration Lab: Beaches page 88-89 ● Summative Assessment Page 6 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Resources for this Unit ● Text ● Teacher CD ● Poster paper ● Markers ● Local Field guides ● Hand Lens ● Stakes ● String ● Meter stick ● Computer/ IPad ● Newspapers magazines ● World Map CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 7 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings PA Science Standards BIO.A.2. – Describe how the properties of water support life on Earth Key Unit Vocabulary CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Unit 2 – Ecology This unit explains the basic parts of the environment. It helps to describe the relationship between the living and the nonliving portion of the environment and how they affect each other. The unit also describes the process through which the great diversity of life on Earth is established. Finally it discusses the importance of biodiversity. How every species plays of role in the functioning of the environment. How do ecosystems function. Describe the major differences of different ecosystems in terms of biotic and abiotic factors Explains the process of evolution and how changes to species occur. Defines biodiversity and explains the importance of the maintenance of species over time. Core Literacy Standards for Science CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-1 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-2 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-3 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-4 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-5 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-6 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-7 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-8 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-9 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1010 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1011 Assessment Anchors (if any) BIO.A.2.1.1 Describe levels of organization in ecosystem BIO.B.4.1.2 Describe characteristic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems BIO.B.4.2.1 Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem Bio.B.4.2.2 Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem BIO.B.4.2.3 Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances BIO.4.2.4 Describe the effects of limiting factors on population dynamics and potential species extinction ecosystem, biotic, abiotic, organism, species, population, Page 8 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study community, habitat, archaea, bacteria, fungus, protist, , invertebrate, vertebrate, photosynthesis, producer, consumer, decomposer, cellular respiration, food chain, food web, trophic level, carbon cycle, nitrogen fixing bacteria, nitrogen cycle, , ecological succession, primary succession, secondary succession, pioneer species, climax community, biome, climate, latitude, altitude, tropical rain forest, temperate rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, taiga, savanna, temperate grassland, chaparral, desert, tundra, permafrost, wetland, plankton, eutrophication, estuary, salt marsh, mangrove swamp, barrier island, coral reef, Learning Objectives – The student will… ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Classify things as being biotic and abiotic factors Explain the difference between species, populations and communities Define habitat and describe how habitats are important for organisms Explain the concept of adaptation Explain the process of evolution by natural selection Describe modern day examples of evolution by natural selection such as pesticide resistance or antibiotic resistance of organisms Design a dichotomous key using common objects to explore how scientists classify organisms into the different kingdoms Explain the common characteristics of living things in the different kingdoms Observe the behavior of brine shrimp Explain how energy and matter move through an ecosystem using food chains, webs, trophic pyramids and models of the various nutrient cycles (i.e. nitrogen, carbon, water, phosphorous etc.) Describe how plants obtain and use energy from the Sun through photosynthesis Describe how living things utilize energy trapped in biological molecules through cellular respiration. Compare the processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis Explain why the amount of energy available to organisms decreases as energy flows through the food chain Explain the factors that create different biomes throughout the world Compare the different forested biomes in terms of abiotic and biotic factors Compare grassland, tundra, and deserts. List the similarities and differences Explain the factors that effect aquatic ecosystems Explore and explain the importance of wetlands for critical environmental functions Describe the importance of the most productive marine ecosystems and explain why they are the most productive areas of the oceans (ie mangroves, salt marshes CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 9 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study and coral reefs) Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks 2 Lesson Topic 4 Evolution (chapter 4) Ecosystems (chapter 4) Lesson Activities ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 2 2-3 Biodiversity (chapter 4) Energy flow in an ecosystem (chapter 5.1) CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Pretest unit #2 Read pages 93 - 96 Classroom catalyst 4.1 PowerPoint presentation 4.1 Quicklab Studying ecosystem Field Study Make a miniature desert ecosystem Formative assessment page 96 Read pages 97-101 Classroom catalyst 4.2 Teaching visuals: the evolution of thicker fur in a deer population, The evolution of pesticide resistance Presentation 4.2 Lab modeling alleles Lab Plants and pollinators Lab Relating Natural selection and frequency of Traits Field Study: Coevolution Formative assessment age 101 Read 102- 107 Classroom catalyst 4.3 Presentation 4.3 Quicklab Pollen and flower diversity Lab: Observing organisms through the seasons (exploration and observation) Lab: Making a Local field guide Formative assessment 4.3 page 107 Inquiry Lab : How do Brine Shrimp Select a Habitat Formative Assessment page 107 Read pages 117- 123 Classroom catalyst 5.1 Present 5.1 Quicklab: Modeling Biomagnification Lab: Pyramid Building (exploration / simulation STEM) Page 10 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study 2-3 Cycling of matter (chapter 5.2) 1 How Ecosystems Change (Chapter 5.3) .5 What is a biome (chapter 6.1) .5 Forest Biomes (chapter 6.2) 1 1 Grasslands, Tundra, and Deserts (Chapter 6.3) Culminating activity (chapter 6) 3 Aquatic CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Lab: Best food for yeast (exploration probeware) Demonstration: Cellular respiration Formative assessment page 123 Read Pages 124-128 Presentation 5.2 Classroom catalyst 5.2 Quicklab: Make every breath count Lab: Modeling the water cycle Lab: BEST composting (Inquiry/ Investigation) Lab: Explaining the Carbon Cycle in Fermentation (Exploration/ Observation) Formative Assessment page 128 Read Pages 129-133 Catalyst 5.3 Presentation 5.3 Field Study: Investigating Succession Formative assessment 133 Quiz Chapter 5 Read pages 143- 145 Classroom catalyst 6.1 Presentation 6.1 Quicklab: Microclimates Lab: Modeling Biomes (Inquiry/Simulation) Lab: Microclimates (Exploration/ Field Activity) Formative assessment page 145 Read pages 146- 154 Class Catalyst 6.2 Present 6.2 Lab: Identifying Sustainable Rainforest Products (Exploration/ Research) Demonstration: Exotic Fruit Formative Assessment page 154 Read pages 155- 163 Classroom Catalyst 6.3 Presentation 6.3 Quicklab: Plant Adaptations Field Study: Xeriscaping Formative Assessment page 163 Chapter Lab: Identifying Your Local Biome (Exploration/ Field Study) Chapter Quiz Read pages 173 - 178 Page 11 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Ecosystems (chapter 7.1) ● ● ● ● ● ● 3 Marine Ecosystems (chapter 7.2) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 1 1 Culminating Activity Unit Test Resources for this Unit ● Textbook ● Art Supplies ● Dissolved oxygen test kit ● Methylene Blue ● Test tubes ● Thermometer ● Plant samples ● Microscope slides ● microscope ● Hand Lens ● Fossil samples ● Various colored beans ● Paint brush ● chisels (screw drivers) CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 ● ● ● ● ● Catalyst 7.1 Presentation 7.1 Quicklab: Diatoms Lab: Stream Quality Monitoring (Exploration/ Field Activity) Lab: Limiting Nutrients for Algae (Exploration/Observation) Lab: Aquatic Primary Productivity (Inquiry/ Environmental Engineering) Formative Assessment page 178 Read Pages 179- 185 Catalyst 7.2 Present 7.2 Quicklab: Estuaries Field Study: Once Upon a Time Lab: Relating Ocean Currents and Climate (Exploration/ Observation) Lab: The Blue Green Ocean (Exploration/ Observation) Demonstration: Barrier Islands Formative Assessment page 185 Chapter Lab: Eutrophication Too Much of a Good Thing (Exploration/ Observation) Case Study: Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay Summative Assessment Page 12 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● plaster of Paris hammer dissection tray Container for mixing plaster wooden dinosaur models vegetable oil dissection picks 2L Bottles Charcoal pencil Black light flowering plant UV sensitive photo equipment Graph paper petri dishes Nails 2 inch Owl Pellets Removable sticker circles in three colors Baker’s yeast balance Salt and sugar Beakers graduated cylinders binoculars globes wind vane rain meter light meter pond water distilled water droppers pond life identification guide Stirring rod soda stopwatch Sand silt juice containers Aquarium Plant fertilizer pH paper or meter stream invertebrates field guide ice cube trays CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 13 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● buckets trisodium phosphate solution ammonium sulfate solution geographic map of US sieve kick nets soil/ coarse modeling clay grass leaves or hay grow lights automatic timer red and blue food coloring heat resistant gloves CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 14 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings PA Science Standards BIO.B.3 Theory of Evolution BIO.B.4 Ecology Key Unit Vocabulary CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Unit 3 - Populations Populations of species on the planet rely on limited resources in order to survive. When these resources are in abundance the population grows and when they are in scarcity the population declines. Other factors such as disease, predation etc. can also influence population size. The maintenance of populations is necessary to ensure environmentally productive ecosystems on planet Earth. Why do populations increase and or decrease in size? What are the factors that limit population growth? What determines the magnitude of population growth What is the value of maintaining our diversity of life on the planet and how might we preserve our Earth for future generations? Core Literacy Standards for Science CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-1 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-2 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-3 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-4 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-5 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-6 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-7 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-8 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-9 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1010 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1011 Assessment Anchors (if any) BIO.B.3.1 Explain how natural selection can impact allelic frequencies in a population BIO.B.4.1 Describe the levels of ecological organization BIO.B.4.2.2 Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem population, density, dispersion, growth rate, reproductive potential, exponential growth, carrying capacity, niche, competition, predation, parasitism, mutualism, commensalism, symbiosis, demography, age structure, survivorship, fertility rate, migration, life expectancy, demographic transition, infrastructure, arable land, urbanization, least developed countries, biodiversity, gene, keystone species, ecotourism, endangered species, threatened species, exotic species, poaching, endemic species Page 15 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Learning Objectives – The student will… ● Describe the three main properties of a population ● Describe Exponential Population growth ● Describe how reproductive behavior of individuals can affect the growth rate of their population ● Explain how population sizes in nature are regulated ● Explain the differences between niche and habitat ● Give examples of parts of a niche ● Describe the five major types of interactions between species ● Explain the difference between parasitism and predation ● Explain how symbiotic relationships may evolve ● Describe the diversity of species on Earth and relate the difference between known numbers and estimated numbers of species ● List and describe three levels of Biodiversity ● Explain four ways biodiversity is important to ecosystems and humans ● Analyze the value of a single species ● Define and give examples of endangered and threatened species ● Describe several ways that species are threatened with extinction globally ● Explain which types of threats are having the largest impact on biodiversity ● List areas of the world that have high levels of biodiversity and many threats to species ● Compare the amount of biodiversity in the US to that of the rest of the world ● List and describe four types of efforts to save individual species ● Explain the advantages of protecting entire ecosystems rather than individual species ● Describe the main provisions of the Endangered Species Act ● Discuss ways in which efforts to protect endangered species can lead to controversy ● Describe three examples of worldwide cooperative efforts to prevent extinctions. Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks 3 Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Nature of populations (Chapter 8-1) Pretest unit #3 Read pages 197- 202 Catalyst 8.1 Presentation 8-1 Formative assessment 8-1 (page 202) QuickLab Population Growth page 198 LAB: 8.1 Calculating Generation Rate CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 16 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study 3 Interactions of species (Chapter 8-2) 2 Culminating Activity (chapter 8) Intro to Biodiversity (chapter 10-1) 3 4 Biodiversity at Risk and Protecting Biodiversity Read pages 203- 210 Catalyst 8.2 Presentation 8.2 Lab 8.2 Case Study page 206-207 Formative Assessment 8-2 page 209 Society and Environment: Conserving Top Predators 210211 Chapter review Exploration Lab: Calculating Generation Rate pages 216217 Read Pages 240- 244 Catalyst 10-1 Presentation 10-1 Lab 10.1 Lab 10.2 Formative Assessment: page 244 Read Pages 245- 251 Catalyst 10-2 Presentation 10-2 Lab 10.3 Lab 10.4 Formative Assessment page 251 Read pages 252- 257 Quicklab: Habitat Degradation page 254 Catalyst 10-3 Presentation 10-3 Lab 10.5 Formative Assessment pages 257 Resources for this Unit ● Microorganisms Blaspherisma ● Microorganisms Euplotes ● Wheat germ ● Plastic well plate ● distilled water ● microscope ● graph paper ● micropipette ● uncooked rice grains ● toothpicks CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 17 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● calculator scissors Hand lens meter stick chalk line Map of US Pictures and names of species from around the world Tap water Construction paper CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 18 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings PA Science Standards BIO.B.4 Ecology Key Unit Vocabulary Unit 4 – Human Impacts This unit explores the consequences of current methods of resource use. Students will explore how we are altering the Earth’s ecosystems as a result of our daily activities. Decision making models will be used to explore pros and cons of altering current practices. Human interactions with the environment result in environmental changes. These changes can be described in a qualitative and quantitative way. A problem solving approach can then be utilized to develop possible solutions. Core Literacy Standards for Science CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-1 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-2 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-3 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-4 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-5 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-6 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-7 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-8 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-9 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1010 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1011 Assessment Anchors (if any) BIO.B.4.1.2 Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems BIO.4.2.4 Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances surface water, river system, watershed, groundwater, aquifer, porosity, permeability, recharge zone, potable, pathogen, dam, reservoir, water pollution, point-source pollution, non point pollution, wastewater, artificial eutrophication, thermal pollution, biomagnification, air pollution, primary pollutant, secondary pollutant, smog, temperature inversion, acid precipitation, pH, climate, latitude, ozone layer, CFC’s, ozone hole, greenhouse gases, global warming, Learning Objectives – The student will… ● Describe the distribution of Earth’s water resources ● Explain why fresh water is one of Earth’s limited resources ● Describe the distribution of Earth’s surface water CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 19 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Describe the relationship between groundwater and surface water in a watershed Identify patterns of global water use Explain how water is treated so that it can be used for drinking Id how water is used in homes, in industry, and agriculture, Describe how dams and water diversion projects are used to manage freshwater resources Id five ways that water can be conserved Compare point source pollution and non point source pollution Classify water pollutants by five types Explain why groundwater pollution is difficult to clean up Describe the major sources of ocean pollution, and explain the effects of pollution on ecosystems Describe the six major laws designed to improve water quality in the US Explain the causes of acid precipitation Explain how acid precipitation affects plants, soils, and aquatic ecosystems Describe three ways that acid precipitation affects humans Describe ways that countries are working together to solve the problem of acid precipitation Explain the difference between weather and climate Identify four factors that determine climate Explain why different parts of Earth have different climate Explain what causes the seasons Explain how the ozone layer shields the Earth from much of the Sun’s harmful radiation Explain how CFC’s damage the ozone layer Explain the process by which the ozone hole forms Describe the damaging effects of UV radiation. Explain why the threat to the ozone layer is still continuing today Explain why Earth’s atmosphere is like the glass in a greenhouse Explain why the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere is increasing Id one possible explanation for the increase in average global temperature Describe what a warmer Earth might be like Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks 1 Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Water Resources (chapter 11) Pretest unit #4 Read pages 269- 275 Catalyst 11-1 Presentation 11-1 CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 20 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study 1 Water Use and Management (chapter 11) 1 Water Pollution (chapter 11) 1 Acid Precipitation (chapter 12-3) 2 Climate (chapter 13-1) 1 Ozone Shield (chapter 13-2) 1 Climate Change (chapter 13-3) 1 Summative Assessment Case Study: Ogallala Aquifer Formative Assessment page 275 Read pages 276- 283 Catalyst 11-2 Presentation 11-2 Formative Assessment page 283 Lab 11-1 Read pages 284- 293 Catalyst 11-3 Presentation 11-3 Formative Assessment page 293 Classroom catalyst 12-1 Read pages 314 - 317 Quicklab: Effects of Acid Precipitation page 316 Killer Smog: Page 319 Catalyst 13-1 Present 13-1 Read Pages 327-334 Formative Assessment 334 Lab 13.1 Catalyst 13-2 Present 13-2 Read pages 335- 338 Lab 13.2 Formative Assessment 338 Catalyst 13-3 Present 13-3 Read Pages 339- 345 Lab 13.3,13.4,13.5 Formative Assessment 345 Unit #4 Test Resources for this Unit ● Calculator ● Pen/ Pencil ● Data table ● kick nets ● plastic foam egg cartons ● macro invertebrate field identification guides CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 21 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Hand lens Almanac atlas rain gauge thermometer weather reports graph paper heat lamp meter stick soil water acrylic sheets baking sheets construction paper lotion sunscreen sun sensitive paper cotton swabs wax pencil filter paper permanent marker incubator refrigerator seeds zip loc bags CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 22 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study Unit Title Unit Description Essential Questions & Enduring Understandings Unit 5 – Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Resources will be categorized according to renewable and nonrenewable resources. Mineral and energy resource use/ availability will be explored. The management of these resources as well as the management of wastes derived from these resources will also be explained. Finally a discussion of sustainability and minimal impacts of resource use will be covered. Humans require natural resources to meet society’s needs. A decision making model will be used to examine the kinds of resources necessary to develop an understanding of sustainability. PA Science Standards Core Literacy Standards for Science CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-1 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-2 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-3 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-4 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-5 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-6 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-7 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-8 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.10-9 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1010 CSSELA-Literacy.RST.9.1011 BIO.B.4 Ecology Key Unit Vocabulary Assessment Anchors (if any) BIO.B.4.2.4 Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances BIO.B.4.2.5 Describe the effects of limiting factors on population dynamics and potential species extinction Mineral, ore mineral, subsurface mining, surface mining, placer deposit, smelting, fossil fuels, electric generator, petroleum, oil reserves, nuclear energy, nuclear fission, renewable energy, passive solar heating, active solar heating, biomass fuels, hydroelectric energy, geothermal energy, alternative energy, ocean thermal energy conversion, fuel cell, energy efficiency, energy conservation, solid waste, biodegradable, municipal solid waste, landfill, source reduction, recycling, compost, hazardous waste, deep-well injection, surface impoundment, Learning Objectives – The student will… ● Define the term mineral CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 23 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● Explain the difference between a metal and a nonmetal and give two examples of each ● Describe the processes by which ores form ● Describe the manner in which mining companies explore for new mineral deposits ● Describe three methods of subsurface mining ● Describe two methods of surface mining ● Define placer deposit, and explain how placer deposits form ● Describe the steps that take place in smelting an ore ● List five factors that influence the value of a fuel ● Explain how fuels are used to generate electricity in an electric power plant ● Id patterns of energy consumption and production in the world and in the US ● Explain how fossil fuels form and how they are used ● Compare the advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuel use ● List three factors that influence predictions of fossil fuel production ● Describe nuclear fission ● Describe how a nuclear power plant works ● List three advantages and three disadvantages of nuclear energy ● List six forms of renewable energy, and compare their advantages and disadvantages ● Describe the differences between passive solar heating , active solar heating, and photovoltaic energy ● Describe the current state of wind energy technology ● Explain the differences in biomass fuel use between developed and developing nations ● Describe how hydroelectric energy, geothermal energy, and geothermal heat pumps works. ● Describe three alternative energy technologies ● Identify two ways that hydrogen could be used as a fuel source in the future ● Explain the difference between energy efficiency and energy conservation ● Describe two forms energy efficient transportation ● Id three ways that you can conserve energy in your daily life ● Name on characteristic that makes a material biodegradable ● Id two types of solid waste ● Describe how a modern landfill works ● Name two environmental problems caused by landfills ● Id three ways you can produce less waste ● Describe how you can use your consumer buying power to reduce solid waste ● List the steps that an item must go through to be recycled ● List two benefits of composting ● Name one advantage and one disadvantage to producing degradable plastic ● Name two characteristics of hazardous waste ● Describe one law that governs hazardous waste CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 24 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● Describe two ways to treat hazardous waste safety Sequence of Teaching and Learning Number of Lessons / Blocks 1 Lesson Topic Lesson Activities Mineral and Mineral Resources 1 Mineral exploration and mining 1 Energy Resources and fossil fuels 1 Nuclear Energy 1 Renewable Energy Today Pretest unit #5 Catalyst 16-1 Read pages 411- 414 Maps in Action page 426 Presentation 16-1 Lab 16-1 Formative Assessment page 414 Catalyst 10-2 Read pages 415- 420 Case Study page 419 Quicklab page 420 Presentation 16-2 Formativ Assessment page 420 Catalyst 17-1 Read pages 435- 443 Present 17-1 Quicklab page 438 Case Study: Hydraulic Fracturing page 440-441 Lab 17-1 Formative Assessment page 443 Exploration Lab page 454-455 Catalyst 17-2 Read pages 444- 447 Present 17-2 Lab 17-2 Points of View page 448-449 Formative Assessment page 447 Catalyst 18-1 Read pages 457- 465 Present 18-1 Case Study pages 458- 459 Formative Assessment page 465 Catalyst 18-2 Read Pages 466- 471 Maps in action page 472 1 Developing Energy Technologies CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 25 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study 1 Solid Waste 1 Reducing Solid Waste 1 Hazardous Waste 1 Summative Assessment Resources for this Unit ● steel file ● hand lens ● mineral guide ● imeral samples ● streak plate ● penny ● medicine dropper ● dilute hydrochloric acid ● rock samples ● cheesecloth ● hammer ● jar ● litmus paper ● marker ● safety goggle ● sulfur coal ● cloth towel ● masking tape CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Present 18-2 Formative Assessment page 471 Exploration Lab pages 478-479 Catalyst 19-1 Read pages 481- 487 Present 19-1 Formative Assessment 487 Exploration Lab : Out of Sight- Out of Mind Catalyst 19-2 Read pages 488- 492 Present 19-2 Case Study pages 490-491 Quicklab: Here Today- Gone Tomorrow Formative Assessment: page 492 Catalyst 19-3 Read Pages 493- 499 Case Study pages 496-497 Present 19-3 Points of View pages 500-501 Formative Assessment page 499 Unit #5 Test Page 26 of 27 Saucon Valley School District Planned Course of Study ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● pyrite distilled water electric bill notebook poster board shoe box clothes hanger clothes pin flashlight metric ruler plastic wrap balance paper towels plastic bags CP Environmental Science Summer 2014 Page 27 of 27